用戶發(fā)送請求時攜帶的參數(shù)后端需要使用,而不同的發(fā)送參數(shù)的方式對應(yīng)了不同的提取參數(shù)的方式
利用HTTP協(xié)議向服務(wù)器傳參有幾種途徑?
1.查詢字符串?dāng)?shù)據(jù)(query string):
形如:?key1=value1&key2=value2
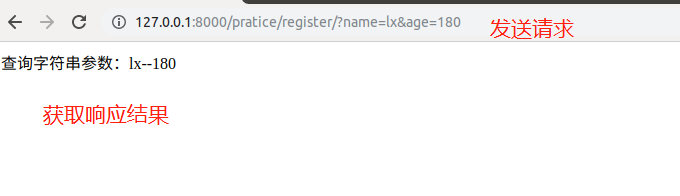
比如:http://127.0.0.1:8000/?name =lx&age=0中的?name =lx
1)獲取請求路徑中的查詢字符串參數(shù),形如:?k1=v1&k2=v2
2)可以通過request.GET屬性獲取,并返回QueryDict類型的對象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class TestQuery(View): def get(self, request): # 獲取查詢字符串參數(shù)name、age name = request.GET.get('name', 'lx') age = request.GET.get('age', '0') return HttpResponse('查詢字符串參數(shù):%s %s' % (name, age)) |
重要提示:
提取查詢字符串參數(shù)不區(qū)分請求方式,即使客戶端進行POST方式的請求,依然可以通過request.GET獲取請求中的查詢字符串參數(shù)。
QueryDict補充:
1)QueryDict是由Django自己封裝的一個數(shù)據(jù)類型,繼承自python的字典Dict,它被定義在django.http.QueryDict中專門用來存儲請求中提取的查詢字符串參數(shù)和請求體參數(shù).即,HttpRequest對象中的屬性GET、POST都是QueryDict類型的數(shù)據(jù)
2. 提取請求體數(shù)據(jù)
1)可以發(fā)送請求體數(shù)據(jù)的請求方式有:POST、PUT、PATCH、DELETE
2)請求體數(shù)據(jù)格式不固定,常見的有:表單類型數(shù)據(jù)和JSON字符串類型,我們應(yīng)區(qū)別對待
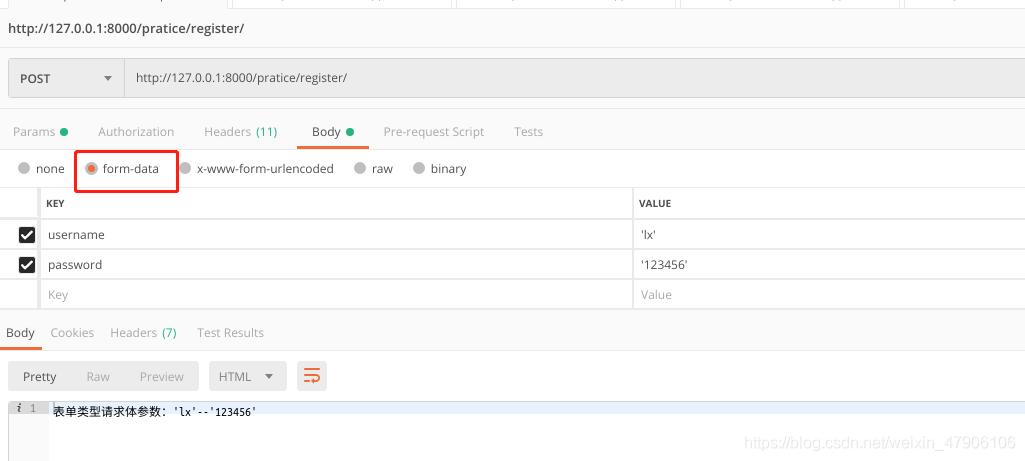
2.1 表單類型請求體數(shù)據(jù)(Form Data)
前端發(fā)送的表單類型的請求體數(shù)據(jù),可以通過request.POST屬性獲取,并返回QueryDict對象。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class TestQuery(View): def post(self, request): # 獲取表單類型請求體參數(shù)中的username、password username = request.POST.get('username') password = request.POST.get('password') return HttpResponse('表單類型請求體參數(shù):%s %s' % (username, password)) |
重要提示:
request.POST只能用來獲取POST表單發(fā)送的請求體數(shù)據(jù)
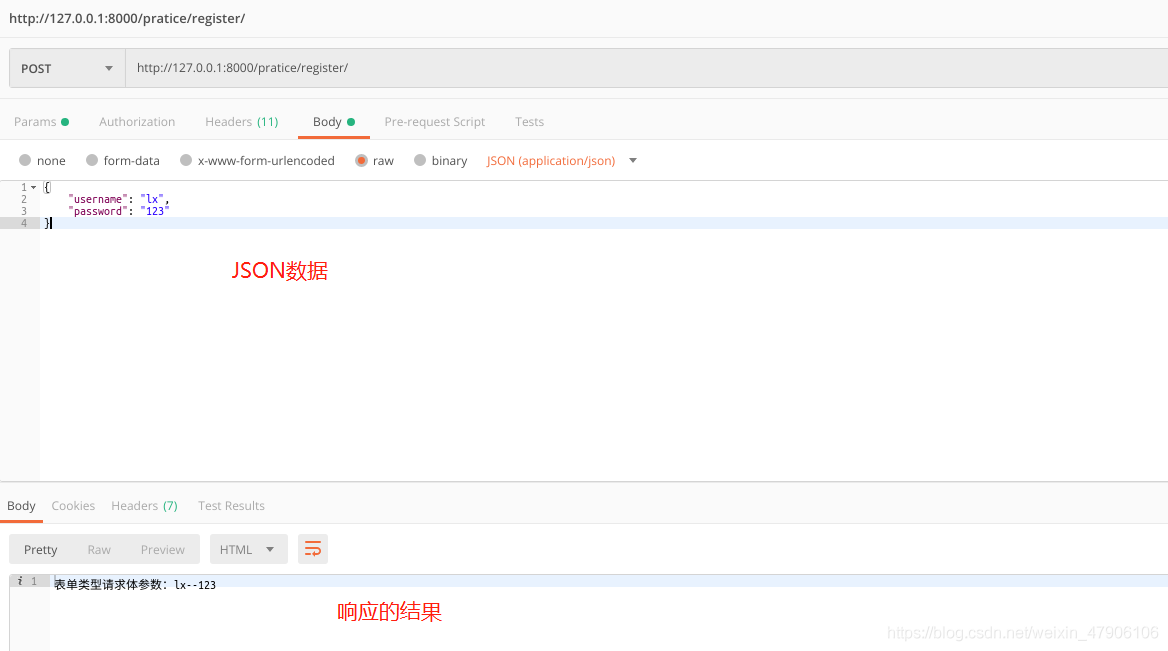
2.2 非表單類型請求體數(shù)據(jù)(Non-Form Data):JSON
1)非表單類型的請求體數(shù)據(jù),Django無法自動解析,可以通過request.body屬性獲取最原始的請求體數(shù)據(jù)
2)request.body獲取的是bytes類型的請求體原始數(shù)據(jù)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class TestQuery(View): def post(self, request): # 獲取請求體中原始的JSON數(shù)據(jù) json_str = request.body # 使用json模塊將原始的JSON數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)字典 json_dict = json.loads(json_str) # 請求體參數(shù)中的username、password username = json_dict.get('username') password = json_dict.get('password') return HttpResponse('表單類型請求體參數(shù):%s %s' % (username, password)) |
結(jié)果展示:
3. URL路徑參數(shù):提取URL路徑中的特定部分?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)
1)在定義路由時,可以從URL中獲取特定部分的路徑參數(shù)
2)Django的路由系統(tǒng)會將提取的路徑參數(shù)傳遞到視圖的內(nèi)部
3)path()和re_path()都可以提取路徑參數(shù)
需求1:http://127.0.0.1:8000/pratice/register/18/
提取路徑中的數(shù)字18
需求2:http://127.0.0.1:8000/pratice/register/18500000000/
提取路徑中的手機號18500000000
3.1 path()提取路徑參數(shù)
測試path()提取普通路徑參數(shù):http://127.0.0.1:8000/pratice/register/18/
path(‘pratice/register/int:age/', views.URLParam1View.as_view()),
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
class TestQuery(View): def get(self, request, age): #提取路徑參數(shù)是在路由中完成的,因為路徑是在路由系統(tǒng)中處理的 print('提取的路徑傳參:',age) return HttpResponse('path()提取普通路徑參數(shù):%s' % age) |
路由中提取路徑參數(shù)時,使用的關(guān)鍵字,必須跟視圖中參數(shù)名一致
思考:
實現(xiàn)需求1時提取age數(shù)字的int:age是什么?
路由轉(zhuǎn)換器
Django默認(rèn)封裝了一些正則表達式,用于在path()中要提取路徑參數(shù)時使用
默認(rèn)的路由轉(zhuǎn)換器:
位置在django.urls.converters.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
DEFAULT_CONVERTERS = { 'int': IntConverter(), # 匹配正整數(shù),包含0 'path': PathConverter(), # 匹配任何非空字符串,包含了路徑分隔符 'slug': SlugConverter(), # 匹配字母、數(shù)字以及橫杠、下劃線組成的字符串 'str': StringConverter(), # 匹配除了路徑分隔符(/)之外的非空字符串,這是默認(rèn)的形式 'uuid': UUIDConverter(), # 匹配格式化的uuid,如 075194d3-6885-417e-a8a8-6c931e272f00} |
源碼解析:

實現(xiàn)需求2
http://127.0.0.1:8000/pratice/register/18500000000/
提取路徑中的手機號18500000000
問題:
1)默認(rèn)的路由轉(zhuǎn)換器中,沒有專門用來匹配手機號的路由轉(zhuǎn)換器
2)所以在使用path()實現(xiàn)需求2時,就無法直接使用默認(rèn)的路由轉(zhuǎn)換器
解決方案:
如果默認(rèn)的路由轉(zhuǎn)換器無法滿足需求時,我們就需要自定義路由轉(zhuǎn)換器
在任意可以被導(dǎo)入的python文件中,都可以自定義路由轉(zhuǎn)換器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
from django.urls import path, register_converterfrom . import viewsclass MobileConverter: """自定義路由轉(zhuǎn)換器:匹配手機號""" # 匹配手機號碼的正則 regex = '1[3-9]\d{9}' def to_python(self, value): # 將匹配結(jié)果傳遞到視圖內(nèi)部時使用 return int(value) def to_url(self, value): # 將匹配結(jié)果用于反向解析傳值時使用 return str(value)# 注冊自定義路由轉(zhuǎn)換器# register_converter(自定義路由轉(zhuǎn)換器, '別名')register_converter(MobileConverter, 'mobile')urlpatterns = [ # path('pratice/register/<‘路由轉(zhuǎn)換器':<變量>, views.TestQuery.as_view()), # path('pratice/register/<int:age>', views.TestQuery.as_view()), path('pratice/register/<mobile:phone_num>', views.TestQuery.as_view()),] |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
class TestQuery(View): def get(self, request,phone_num): #提取路徑參數(shù)是在路由中完成的,因為路徑是在路由系統(tǒng)中處理的 print('提取的路徑傳參:',phone_num) return HttpResponse('path()提取普通路徑參數(shù):%s' % phone_num) |
效果展示

3.2 re_path()提取路徑參數(shù)
|
1
|
re_path(r'^pratice/register/(?P<phone_num>1[3-9]\d{9})/$', views.TestQuery.as_view()), |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
class TestQuery(View): def get(self, request,phone_num): #提取路徑參數(shù)是在路由中完成的,因為路徑是在路由系統(tǒng)中處理的 print('提取的路徑傳參:',phone_num) return HttpResponse('path()提取普通路徑參數(shù):%s' % phone_num) |
3.3 path()和re_path()如何選擇?
1)path()語法相對簡潔一些,如果沒有路徑參數(shù)要提取或者要提取的路徑參數(shù)可以使用默認(rèn)的路由轉(zhuǎn)換器實現(xiàn)時,就選擇path()。
2)re_path()語法相對復(fù)雜一些,但是,如果希望在匹配路由時,由自己編寫所有的正則式,就選擇re_path()。
需要注意的是,在使用re_path()時,網(wǎng)絡(luò)地址正則表達式一定要寫完整,要有嚴(yán)格的開頭和結(jié)尾
4. 請求頭
可以通過request.META屬性獲取請求頭headers中的數(shù)據(jù),request.META為字典類型。
常見的請求頭如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
CONTENT_LENGTH – The length of the request body (as a string).CONTENT_TYPE – The MIME type of the request body.HTTP_ACCEPT – Acceptable content types for the response.HTTP_ACCEPT_ENCODING – Acceptable encodings for the response.HTTP_ACCEPT_LANGUAGE – Acceptable languages for the response.HTTP_HOST – The HTTP Host header sent by the client.HTTP_REFERER – The referring page, if any.HTTP_USER_AGENT – The client's user-agent string.QUERY_STRING – The query string, as a single (unparsed) string.REMOTE_ADDR – The IP address of the client.REMOTE_HOST – The hostname of the client.REMOTE_USER – The user authenticated by the Web server, if any.REQUEST_METHOD – A string such as "GET" or "POST".SERVER_NAME – The hostname of the server.SERVER_PORT – The port of the server (as a string). |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
class HeadersParamView(View): """提取請求頭參數(shù)""" def get(self, request): # 獲取請求頭中文件的類型 ret = request.META.get('CONTENT_TYPE') return http.HttpResponse('go') |
5. 其他常用HttpRequest對象屬性
method:一個字符串,表示請求使用的HTTP方法,常用值包括:'GET'、'POST'。
FILES:一個類似于字典的對象,包含所有的上傳文件。
COOKIES:一個字符串,包含了瀏覽器自動發(fā)送的cookie緩存數(shù)據(jù)。
user:請求中認(rèn)證出來的用戶對象。
到此這篇關(guān)于Django使用HTTP協(xié)議向服務(wù)器傳參方式小結(jié)的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Django HTTP協(xié)議向服務(wù)器傳參內(nèi)容請搜索服務(wù)器之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持服務(wù)器之家!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47906106/article/details/119700560