subview的事件響應
在view的層級里面,默認情況下subview是可以顯示到其父view的frame區域以外的,通過設置cliptobounds屬性為yes,可以限制subview的顯示區域。但是touch在各個uiview中傳遞的時候,區域時限制在view的frame內,此處包含兩個信息:1、在當前view的frame以外所做的操作是不會傳遞到該view中的,這一點很容易理解。2、如果touch事件是發生在當前view的frame以外,該view所有的subview將也不會再收到該消息。這一點通常容易被我們忽略,很多奇怪的問題就是這個引起的。
下面請看一個小例子,定制view的代碼如下:
svtestclipsubviewevent.h
//
// svtestclipsubviewevent.h
// svuiviewsample
//
// created by maple on 3/19/12.
// copyright (c) 2012 smileevday. all rights reserved.
//
// 默認的情況下,subview可以超出父view的frame,即可以顯示到父view的外邊
// 但是消息的接受返回卻是由于父view的大小限制,即出了父view的subview將不能收到消息
// 在程序中一定要注意當前程序view的最底層是充滿整個window的可用區域的,
// 否則將會導致某些區域明明有按鈕但是卻點不中的問題
#import <uikit/uikit.h>
@interface svtestclipsubviewevent : uiview
@end
//
// svtestclipsubviewevent.m
// svuiviewsample
//
// created by maple on 3/19/12.
// copyright (c) 2012 smileevday. all rights reserved.
//
#import "svtestclipsubviewevent.h"
@interface svtestclipsubviewevent()
- (void)btnaction:(uibutton*)btn;
@end
@implementation svtestclipsubviewevent
- (id)initwithframe:(cgrect)frame
{
self = [super initwithframe:frame];
if (self) {
// initialization code
self.backgroundcolor = [uicolor redcolor];
uibutton *testoutbtn = [uibutton buttonwithtype:uibuttontyperoundedrect]; testoutbtn.frame = cgrectmake(-80, -50, 70, 30);
[testoutbtn addtarget:self action:@selecto (btnaction: forcontrolevents:uicontroleventtouchupinside];
[testoutbtn settitle:@"i'm out" forstate:uicontrolstatenormal];
[self addsubview:testoutbtn];
uibutton *testinbtn = [uibutton buttonwithtype:uibuttontyperoundedrect]; testinbtn.frame = cgrectmake(20, 30, 70, 30);
[testinbtn settitle:@"i'm in" forstate:uicontrolstatenormal];
[testinbtn addtarget:self action:@selector(btnaction: forcontrolevents:uicontroleventtouchupinside];
[self addsubview:testinbtn];
}
return self;
}
/*
// only override drawrect: if you perform custom drawing.
// an empty implementation adversely affects performance during animation.
- (void)drawrect:(cgrect)rect
{
// drawing code
}
*/
- (void)btnaction:(uibutton*)sender
{
nslog(@"hi, you tap button %@", [sender titleforstate:uicontrolstatenormal]);
}
@end
在程序的viewcontroller中添加如下測試代碼:
svtestclipsubviewevent *testclipsubview = [[svtestclipsubviewevent alloc]initwithframe:cgrectmake(100, 100, 150, 150)];
[self.view addsubview:testclipsubview];
[testclipsubview release];
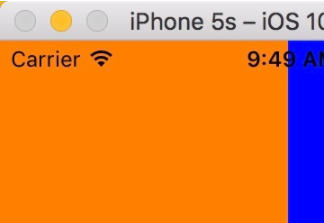
運行可以看到如下界面:

獲取subview
通常我們在view層級里面對subview的操作可以通過兩種方式:1、保留一個subview的引用,然后在類中通過該引用對該subview進行操作,但是要注意在適當的位置添加內存維護的代碼,退出前手動釋放。2、設置subview的tag,讓后在要使用的時候,通過viewwithtag獲取到相應的subview,這種方法比較簡潔,也不用自己去維護內存。
viewwithtag: 通常采用深度遍歷優先的算法,返回第一個tag和給定tag相等的subview。這就導致了一個當一個view的多個subview的tag相同的時候,我們通過該方法得到的view可能并不是自己想要的。
下面通過一個小例子驗證一下,代碼如下:
//
// svtestviewtag.h
// svuiviewsample
//
// created by maple on 3/18/12.
// copyright (c) 2012 smileevday. all rights reserved.
//
// view根據tag獲取subview的時候執行的是深度優先遍歷的算法
// 返回第一個tag和請求tag相等的子view
// 從subviews中查找,最下層的優先找到
#import <uikit/uikit.h>
@interface svtestviewwithtag : uiview
@end

例子中每個subview都是一個uilabel,而且設置了相應的內容。按鈕的響應函數的實現思路:首先隱藏所有類型為uilabel的subview(排除uibutton,因為button需要一直顯示),然后根據指定的tag獲取到相應的subview,該subview及其superview的hidden屬性為no。這樣就可以保證點擊按鈕的時候只顯示的是第一個tag和指定tag相等的subview。
為了驗證viewwithtag獲取subview的原理:
首先我在subview1中添加了兩個tag都為11的subview11和subview12。 運行程序可以,當我們點擊"show tag 11"按鈕的時候屏幕上將顯示“subview11”,而非“subview12”。同時不管你點擊幾次該按鈕,始終只顯示“subview11”。這樣可以看出來同一層級中獲取subview時候查找順序為index從小到大的原則,即位于相對下層的將首先被找到。
其次我還在subview1中添加了tag均為13的subview13,同時向view中添加了tag也為13的subview2,運行程序點擊“show tag 13”按鈕,屏幕上將會顯示“subview13”,而非“subview2”。這可以驗證viewwithtag在搜索的時候遵循深度優先遍歷的原則,即會首先查找最下層的view并遞歸查詢其subview。
綜上兩點我們可以看出來viewwithtag獲取subview的基本原則,即遵循深度優先,下層優先兩個原則。