程序出錯的時候,我們往往需要根據(jù)異常信息來找到具體出錯的代碼。簡單地用print打印異常信息并不能很好地追溯出錯的代碼:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
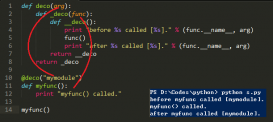
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- def foo(a, b): c = a + b raise ValueError('test') return c def bar(a): print('a + 100:', foo(a, 100)) def main(): try: bar(100) except Exception as e: print(repr(e)) if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
輸出:
ValueError('test',)
打印的異常信息不夠詳細(xì),對錯誤追蹤沒有多大幫助。這時候異常堆棧信息就派上用場了。下面簡單介紹幾種打印異常堆棧信息的方法。
1.最簡單的方法之一就是使用logging.exception
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import logging def foo(a, b): c = a + b raise ValueError('test') return c def bar(a): print('a + 100:', foo(a, 100)) def main(): try: bar(100) except Exception as e: logging.exception(e) if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
輸出:
ERROR:root:test
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "E:/git_work/scrapy_ppt/test.py", line 16, in main
bar(100)
File "E:/git_work/scrapy_ppt/test.py", line 11, in bar
print('a + 100:', foo(a, 100))
File "E:/git_work/scrapy_ppt/test.py", line 6, in foo
raise ValueError('test')
ValueError: test
從異常堆棧信息中我們可以不費(fèi)力氣就找出錯誤代碼是哪一行。
2.其它方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import tracebackimport sys def foo(a, b): c = a + b raise ValueError('test') return c def bar(a): print('a + 100:', foo(a, 100)) def main(): try: bar(100) except Exception as e: # 方法二 traceback.print_exc() # 方法三 msg = traceback.format_exc() print(msg) et, ev, tb = sys.exc_info() # 方法四 traceback.print_tb(tb) # 方法五 traceback.print_exception(et, ev, tb) # 方法六 msg = traceback.format_exception(et, ev, tb) for m in msg: print(m) if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
到此這篇關(guān)于Python捕獲異常堆棧信息的幾種方法(小結(jié))的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Python捕獲異常堆棧信息內(nèi)容請搜索服務(wù)器之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持服務(wù)器之家!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/xiemanR/article/details/82934936