本文實例講述了Python裝飾器模式定義與用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
裝飾器模式定義:動態地給一個對象添加一些額外的職責。
在Python中Decorator mode可以按照像其它編程語言如C++, Java等的樣子來實現,但是Python在應用裝飾概念方面的能力上遠不止于此,Python提供了一個語法和一個編程特性來加強這方面的功能。
首先需要了解一下Python中閉包的概念:如果在一個內部函數里,對在外部作用域(但不是在全局作用域)的變量進行引用,那么內部函數就被認為是閉包(closure)。

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
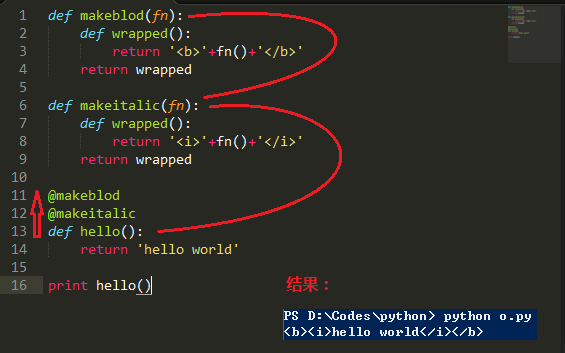
def makeblod(fn): def wrapped(): return '<b>'+fn()+'</b>' return wrappeddef makeitalic(fn): def wrapped(): return '<i>'+fn()+'</i>' return wrapped@makeblod@makeitalicdef hello(): return 'hello world'print hello() |
運行結果:
<b><i>hello world</i></b>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
def deco(arg): def _deco(func): def __deco(): print "before %s called [%s]." % (func.__name__, arg) func() print "after %s called [%s]." % (func.__name__, arg) return __deco return _deco@deco("mymodule")def myfunc(): print "myfunc() called."myfunc() |
運行結果:
before myfunc called [mymodule].
myfunc() called.
after myfunc called [mymodule].
關于閉包學習可參考:http://www.jfrwli.cn/article/103444.html
希望本文所述對大家Python程序設計有所幫助。
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zxlovenet/p/4042898.html