1. fixture的聲明
我們使用@pytest.fixture()來聲明fixture函數。fixture()即可無參數進行聲明,也可以帶參數聲明。
示例1:
@pytest.fixture()無參數進行聲明
import pytest
@pytest.fixture #fixture()未帶任何參數,聲明一個fixture函數
def fixture_demo():
print("這個是一個fixture的demo演示")
def test_demo(fixture_demo): #調用fixture函數――fixture_demo
print("這是一個測試demo。")
@pytest.fixture()有參數的進行聲明
通過上文pytest中fixtureAPI簡單說明,我們對fixture()的參數有了一定了解。fixture()可以帶著這些參數去聲明一個fixture函數。
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(params=[1,2,3]) #fixture()帶著parmas對ids()進行fixture函數的聲明
def ids(request):
data=request.param
print(f'獲取測試數據{data}')
return data
def test_ids(ids): #調用fixture函數-ids()
print(ids)
2. fixture的調用
2.1 fixture的調用方式
fixture有三種調用方式,分別為:
1. 使用 fixturename
2. 使用@pytest.mark.usefixtures(“fixturename”)
3. autouse――自動應用
2.1.1 使用fixturename
通過pytest中fixtureAPI簡單說明中對@fixture()參數的介紹,我們知道fixturename默認是@pytest.fixture()所裝飾的函數的函數名,如果傳入name參數,則fixturename就是name傳入的內容。
當要調用fixture的時候,只要將fixturename作為參數傳入測試函數即可。
示例2:
1.使用被裝飾的函數的函數名
import pytest
@pytest.fixture() #未傳入name,因此fixturename為函數名login
def login():
print('login')
def test_case1(login): #將fixturename作為參數傳入
print('這是testcase1')
2.使用fixture別名
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(name='login1') #傳入name,因此fixturename為login1
def login():
print('login')
def test_case1(login1): #將fixturename作為參數傳入
print('這是testcase1')
注意:
當使用fixture的別名后,被裝束函數的函數名失效,無法再繼續使用其進行fixture的調用。

2.1.2 使用@pytest.mark.usefixtures("fixturename")
根據pytest官方文檔的介紹,如果想讓某個fixture適用于類、模塊和項目中所有測試函數的話,會使用usefixtures來調用fixture。當然,單個測試函數也可以使用此方法來調用fixture。
使用usefixtures調用fixture和直接使用fixturename來調用fixture是有區別的,可總結為:
使用usefixtures調用的fixture只能用于配置測試前系統的初始狀態,無法為測試用例提供測試數據;但使用fixturename調用的fixture卻可以實現這兩個功能。
示例:
1.聲明一個名為login的fixture,并通過fixture()傳入測試數據集。test_case1使用usefixtures的方法調用login,并且在函數內部想要打印login的返回值。
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(params=[1,2,3]) # 傳入測試數據集
def login(request):
print("登陸操作")
return request.param #返回測試數據
class TestClass1:
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('login') #使用usefixtures調用login
def test_case1(self):
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
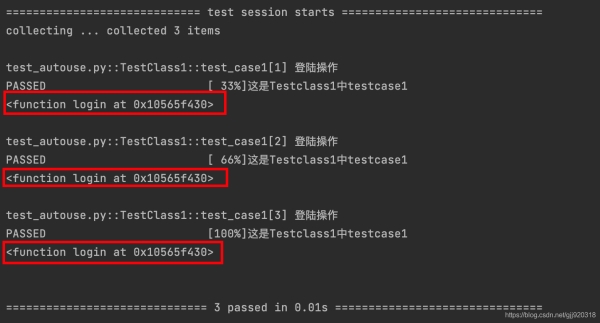
print(login) #打印login
運行后發現,結果和我們預期的不一樣,print(login)打印出的是函數對象信息,不是返回值。
2.修改剛剛的代碼,使用fixturename來調用login
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(params=[1,2,3]) # 傳入測試數據集
def login(request):
print("登陸操作")
return request.param #返回測試數據
class TestClass1:
#@pytest.mark.usefixtures('login') #使用usefixtures調用login
def test_case1(self,login): #使用fixturename的方式調用login
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
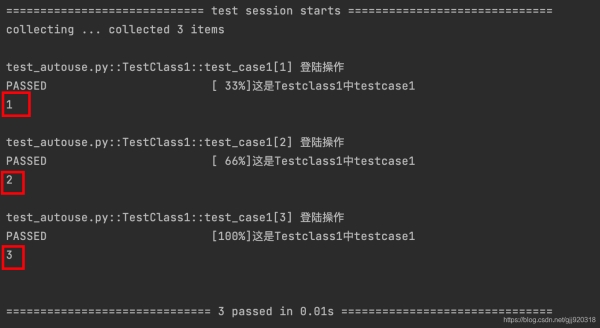
print(login) #打印login
運行后我們可以發現,結果和我們預期的一致,把login的返回值成功打印出來。
usefixtures調用fixture的方法只適用于測試函數,對于fixture函數不生效;使用fixturename調用fixture的方法對測試函數和fixture函數都適用。
示例:
1.以下demo想要實現執行測試用例前打印“登陸操作”,用例執行結束后打印“注銷操作”。聲明login和logout為fixture函數,并且讓logout使用usefixtures的方法調用login,再讓test_case1調用logout。
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("登陸操作")
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('login') @pytest.fixture() def logout():
yield
print("注銷操作")
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self,logout):
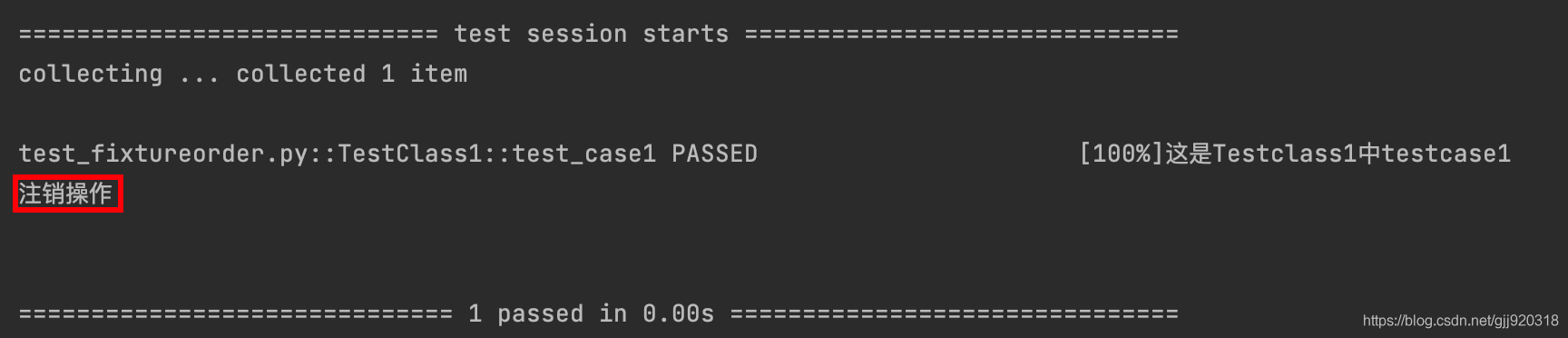
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
通過運行結果我們發現,結果只在執行測試函用例后打印了“注銷操作”,與我們預期的結果不一致。
2.修改上面的demo代碼,讓logout使用fixturename的方式調用login。
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("登陸操作")
#@pytest.mark.usefixtures('login')
@pytest.fixture()
def logout(login): #使用fixturename的方式調用login
yield
print("注銷操作")
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self,logout):
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
運行后我們發現,結果與我們預期的一致。

由此可以看出來,userfixtures的調用方法對于fixture函數無效。
下面我們將通過示例來演示userfixtures的使用方法:
為了演示效果,我們新建一個包,并在里面創建一個conftest.py。用于定義fixture函數。關于conftest.py的相關內容,后面會單獨寫一遍文章詳細介紹。
在conftest.py中聲明的一個login函數。
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print('登錄操作')
1.整個類中應用fixture
使用usefixtures,讓TestClass1這個類中所有測試函數都調用login。
import pytest
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('login') #讓TestClass1調用login
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self):
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
def test_case2(self):
print('這是Testclass1中testcase2')
class TestClass2:
def test_case3(self):
print('這是Testclass2中的testcase3')
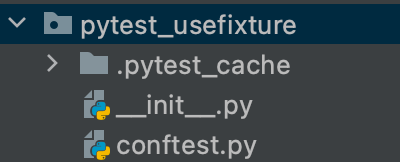
運行結果:
通過結果我們可以發現,只有TestClass1中的test_case1和test_case2調用了login。
2.整個模塊應用fixture
根據官方文檔說明,在整個模塊中應用fixture,可在模塊使用
pytestmark=pytest.mark.usefixtures("fixturename")。
修改測試代碼如下:
import pytest
pytestmark = pytest.mark.usefixtures("login") #使用pytestmark在模塊中使用usefixtures
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self):
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
def test_case2(self):
print('這是Testclass1中testcase2')
class TestClass2:
def test_case3(self):
print('這是Testclass2中的testcase3')
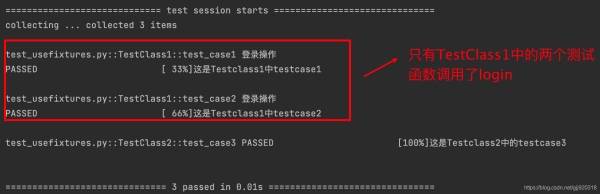
運行結果:
通過運行結果可發現,整個模塊中,所有測試類里面的測試函數都調用了login。

3.整個項目中使用
在pytest.ini中配置usefixtures。
演示項目結構如圖:

對應文件中的代碼如下:
test_demo中的test_demo.py:
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self):
print("這是pytest_demo包中test_demo模塊里Testclass1中testcase1")
class TestClass2:
def test_case2(self):
print('這是pytest_demo包中test_demo模塊里Testclass2中的testcase2')
test_usefixtures中的test_usefixtures.py:
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self):
print("這是pytest_usefixtures包中test_usefixtures模塊里Testclass1中testcase1")
class TestClass2:
def test_case2(self):
print('這是pytest_usefixtures包中test_usefixtures模塊里Testclass2中的testcase2')
TestDemo根目錄下的conftest.py:
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print('登錄操作')
TestDemo根目錄下的pytest.ini:
[pytest] usefixtures = login
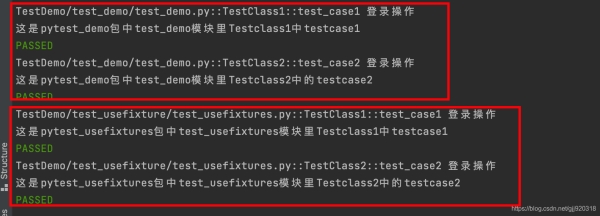
運行整個項目:
項目中的測試函數都調用了conftest.py中的login。
4.使用usefixtures調用多個fixture
我們可以使用@pytest.mark.usefixtures('fixturename1','fixturename2')來調用多個fixture。
conftest.py中新增一個fixture:
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print('登錄操作')
@pytest.fixture()
def printids():
print("打印ids。")
修改test_usefixtures.py:
@pytest.mark.usefixtures('login','printids')
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self):
print("這是pytest_usefixtures包中test_usefixtures模塊里Testclass1中testcase1")
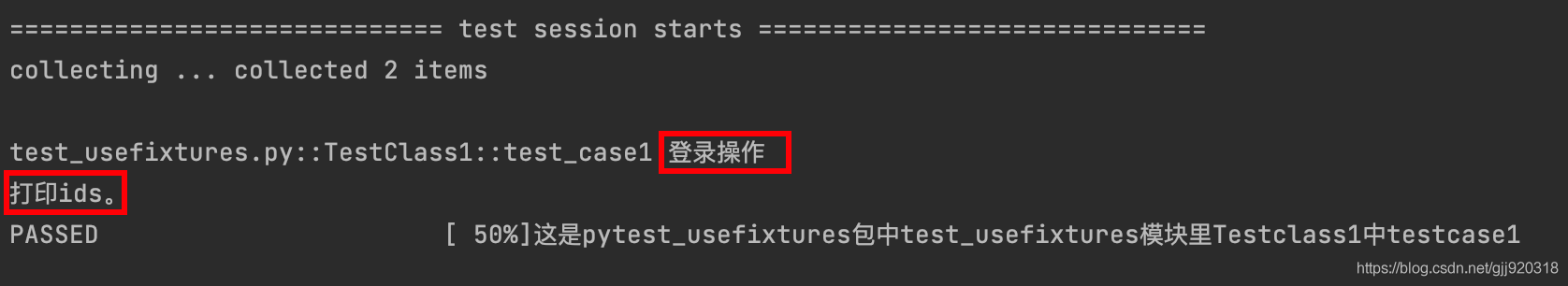
運行后結果:
test_case1測試函數調用login和printids兩個fixture。
2.1.3 autouse――自動應用
fixture()的autouse參數,是fixture自動應用的標識。
如果autouse=True,則在同作用域下的測試函數,會自動調用該fixture;如果autouse=False,則測試函數需要主動去調用該fixture。
autouse默認是False。
示例4:
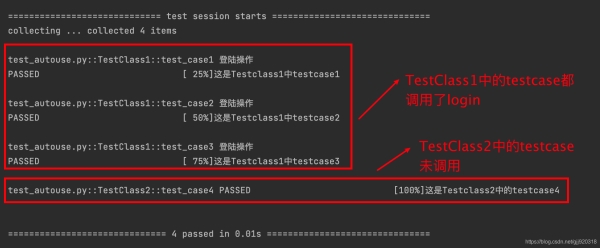
1.在TestClass1這個類中定義了一個login函數,聲明為fixture,并且autouse設置為True。
TestClass1中的test_case1主動調用了login,但是其他測試函數未主動調用。
我們還寫了一個TestClass2類,類中有一個test_case4的測試函數。
import pytest
class TestClass1:
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True) # 啟用自動應用
def login(self):
print("登陸操作")
def test_case1(self,login): # 調用了login這個fixture函數
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
def test_case2(self): # 沒有調用
print('這是Testclass1中testcase2')
def test_case3(self): # 沒有調用
print('這是Testclass1中testcase3')
class TestClass2:
def test_case4(self):
print('這是Testclass2中的testcase4')
運行結果:
通過運行結果我們可以知道,當fixture的autouse=True的時候,在同作用域內的測試函數會自動調用fixture,非同作用域內的測試函數無法調用。
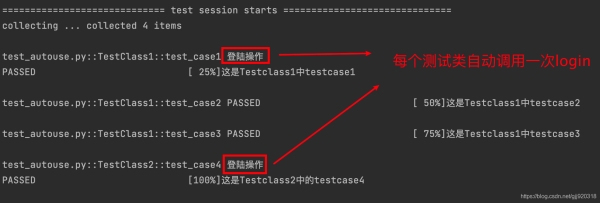
2.我們給fixture()帶上更多的參數,修改上面的demo,并設置fixture的scope=‘class'。
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope='class', autouse=True) # fixture的作用域設為class級別,啟用自動應用
def login():
print("登陸操作")
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self):
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
def test_case2(self):
print('這是Testclass1中testcase2')
def test_case3(self):
print('這是Testclass1中testcase3')
class TestClass2:
def test_case4(self):
print('這是Testclass2中的testcase4')
運行結果:
通過運行結果我們可以看出,當設置login的scope=‘class'的使用,每一個測試類都會自動調用一次login。
autouse的使用也是遵照fixture函數的設置來進行的。
2.2 fixture使用的靈活性
通過官方文檔的說明,我們知道了pytest的fixture系統是極其的靈活和強大的,官方文檔也為我們以下幾個靈活使用fixture的例子。
2.2.1 一個fixture函數可以調用其他的fixture
文章前面我們有演示過一個fixture函數調用其他fixture的例子。
代碼如下:
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("登陸操作")
@pytest.fixture()
def logout(login):
yield
print("注銷操作")
class TestClass1:
def test_case1(self,logout):
print("這是Testclass1中testcase1")
login()實現了測試執行的前置操作,logout()實現了測試執行的后置操作。logout()調用了login,測試函數則直接調用了logout。
fixture在執行的時候是依次執行的。假如fixture A 調用了fixture B,那么執行的時候會先執行fixture B,然后再執行fixture A。因為fixture B是fixture A的依賴條件。
所以我們運行上面代碼的時候,是會先調用login()然后再調用logout()的。而logout()中的yield會讓測試用例執行的時候先執行login中的測試前置操作,然后再執行測試用例中的內容,最后執行logout中yield后面測試后置操作。
這樣的一個操作,可以將復雜的測試需求,變成一個一個簡單而又有組織性的的功能函數,更加方便后期進行維護。
2.2.2 fixture函數可被反復重用
兩個不同的測試函數可以調用同一個fixture,并且獲得各自的運行結果。測試函數之間并不會因為調用了同一個fixture而相互之間產生任何影響。
示例5:
演示代碼:
import pytest @pytest.fixture() def first_number(): #fixture函數,返回1 return 1 @pytest.fixture() def order(first_number): #fixture函數,調用了first_number這個fixture,并且返回一個list return [first_number] def test_secondnum1(order): #調用order,并且在order返回的list中添加 2 這個元素 order.append(2) print(order) assert order==[1,2] #斷言 def test_secondnum2(order): #也調用了order,并在order返回的list中添加 3 這個元素 order.append(3) print(order) assert order==[1,3] #斷言
運行結果:
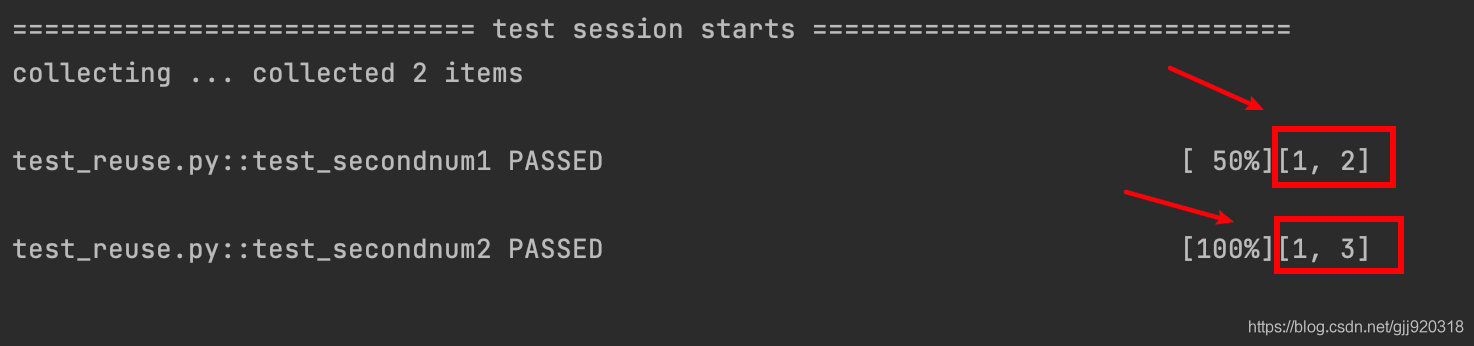
上面這段代碼我們聲明了:
兩個fixture――first_number和order。
first_number有一個返回值: 1 ;
order調用了first_number,并返回一個列表: [1] 。
我們還定義了:
兩個測試函數――test_secondnum1和test_secondnum2,這兩個測試函數都調用了order。
test_secondnum1對order的返回值做了一個append(2)的操作;test_secondnum1對order的返回值做了一個append(3)的操作。
根據運行結果我們可以看出,兩個測試函數對調用的fixture都做出了各自的操作,并且得到各自的一個運行結果。兩者的運行結果沒有因為都調用了order而相互產生影響。
fixture可被反復重用這一特點,對于確保測試之間彼此不受影響是非常有用的。我們可以聲明一個通用的fixture函數,并使用這個特性來確保每個測試都能得到未受污染的測試數據,并且能從一個干凈的初始狀態開始執行。
2.2.3 測試函數/fixture函數可以一次調用多個fixture
文章前面我們有介紹過如何使用usefixtures來調用多個fixture,由此我們可以知道,pytest是允許測試函數和fixture函數按照自己的需求一次調用多個fixture的。
示例6:
演示代碼:
import pytest @pytest.fixture() def first_number(): #第一個fixture,返回1 return 1 @pytest.fixture() def second_number(): #第二個fixture,返回2 return 2 @pytest.fixture() def third_number(): #第三個fixture,返回1 return 3 @pytest.fixture() def order(first_number,second_number): #調用first_number 和 second_number 返回 [1,2] return [first_number,second_number] def test_case(order,third_number): #調用order 和 third_number order.append(third_number) #對 order做append的操作,將third_number的返回值加入list中 print(order) assert order==[1,2,3] #斷言
運行結果:
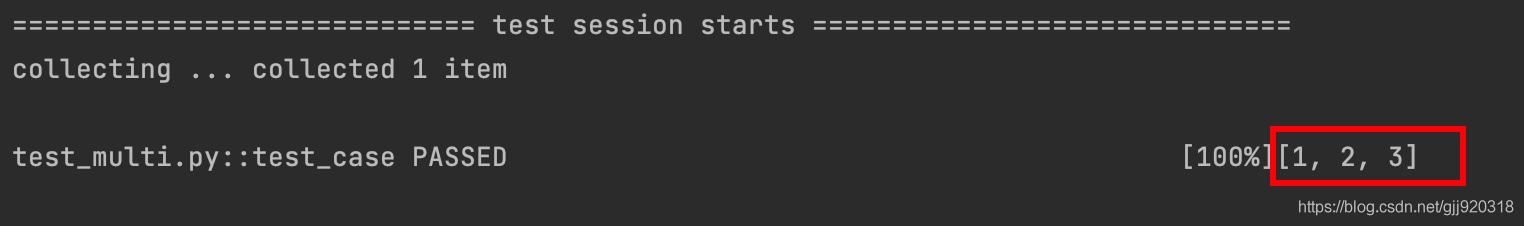
演示代碼中我們聲明了:
四個fixture――first_number、second_number、third_number和order;
一個測試函數――test_case。
order 調用了first_number和second_number;test_case調用了order和third_number。他們都根據自己的需求調用了多個fixture,并且正常被執行。
2.2.4 同一測試執行期間,fixture可被多次請求
其實在看官方文檔的時候,我有點不太理解這部分的內容。當時看文字的描述感覺與“fixture能夠被重復調用“這一點有沖突,但是通過官方文檔的代碼示例,我才明白這兩點其實是不沖突的。
下面我們先看一下官方示例。
示例7:
演示代碼:
import pytest @pytest.fixture def first_entry(): return "a" @pytest.fixture def order(): return [] @pytest.fixture def append_first(order, first_entry): return order.append(first_entry) def test_string_only(append_first,order, first_entry): print(order) assert order == [first_entry]
運行結果:
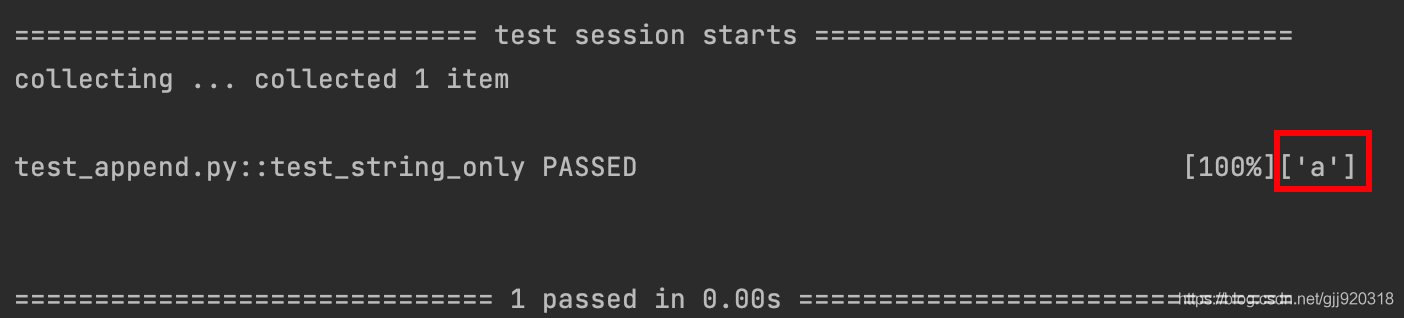
示例代碼中聲明了:
三個fixture函數――first_entry、order和append_first;
一個測試函數――test_string_only。
first_entry返回了一個str: "a";
order返回一個空list:[];
append_first調用了first_entry和order,并且返回 order.append(first_entry)。
test_string_only調用了first_entry、order和append_first,并做了一個打印order值的操作和斷言操作。
通過運行結果我們可以看到,test_string_only斷言成功,并且打印的order的值是['a']。
如果按照”fixture能夠被重復調用“這一特點看,打印的order不應該是空list的嗎?為什么會是[‘a']呢?
test_string_only在執行期間,先執行append_first,而append_first調用了order,并且對order進行了添加元素的操作,更改了order的值,此時order返回的值會存在緩存中。當test_string_only后面再去”調用“order的時候,其實和append_first引用的是同一個order對象,因此測試斷言才會成功。
通過pytest官方文檔我們知道,pytest一次只緩存一個fixture的實例,這意味著在使用參數化fixture時,pytest可以在給定范圍內多次調用一個fixture。
當測試過程中先調用的fixture對其他fixture有依賴關系的話,在調用這個fixture的時候它所依賴的fixture也會被調用。所以后面測試執行過程中,如果再次有請求到這些fixture的話,fixture就不會被再次執行,此時會直接從緩存中獲取到之前fixture執行后返回的數據來使用。
“fixture能夠被重復調用“――針對不同的測試過程,目的是為了保障每個測試執行時都是一個干凈的環境。
“同一測試執行期間,fixture可被多次請求”――同一測試過程中,目的是為了保障在測試過程中,前后使用的數據不會被重置。
文末說明:
以上內容是我在閱讀pytest官方文檔后,依照個人理解進行整理。內容可能會有理解錯誤之處,歡迎大家留言指正。謝謝
以上就是pytest自動化測試中的fixture的聲明和調用的詳細內容,更多關于fixture聲明和調用的資料請關注服務器之家其它相關文章!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/gjj920318/article/details/118704453