pyecharts介紹
pyecharts 是一個用于生成 echarts 圖表的類庫。echarts 是百度開源的一個數據可視化 js 庫。用 echarts 生成的圖可視化效果非常棒
為避免繪制缺漏,建議全部安裝
為了避免下載緩慢,作者全部使用鏡像源下載過了
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ echarts-countries-pypkgpip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ echarts-china-provinces-pypkgpip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ echarts-china-cities-pypkgpip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ echarts-china-counties-pypkgpip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ echarts-china-misc-pypkgpip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ echarts-united-kingdom-pypkg |
基礎案例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
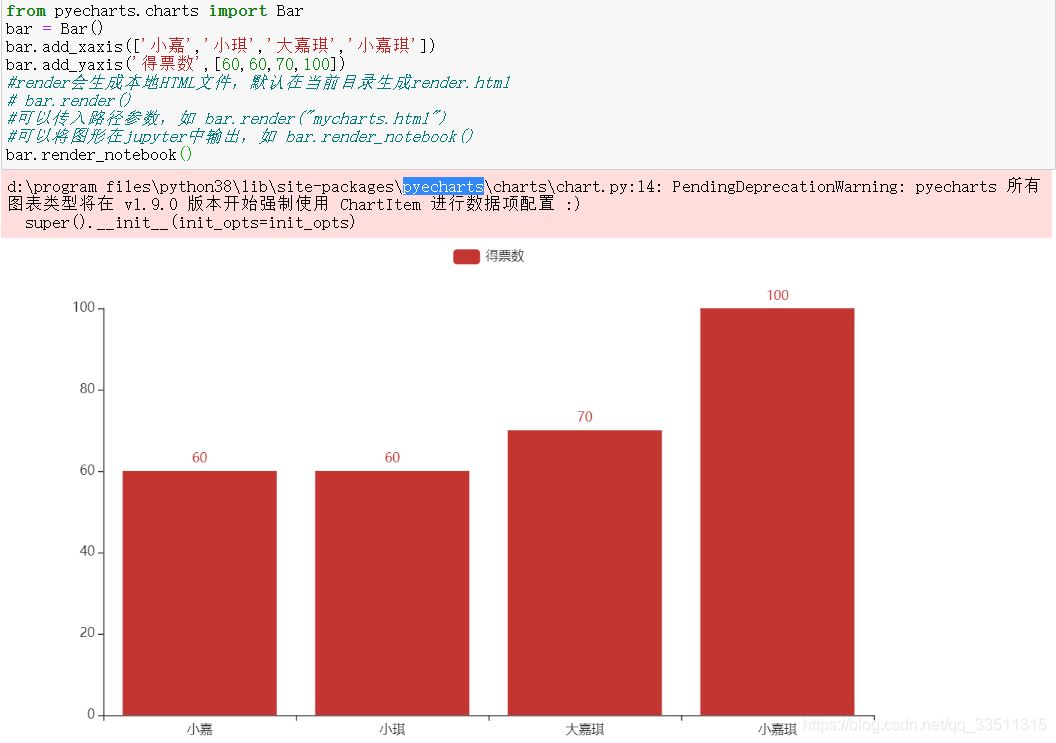
from pyecharts.charts import barbar = bar()bar.add_xaxis(['小嘉','小琪','大嘉琪','小嘉琪'])bar.add_yaxis('得票數',[60,60,70,100])#render會生成本地html文件,默認在當前目錄生成render.html# bar.render()#可以傳入路徑參數,如 bar.render("mycharts.html")#可以將圖形在jupyter中輸出,如 bar.render_notebook()bar.render_notebook() |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
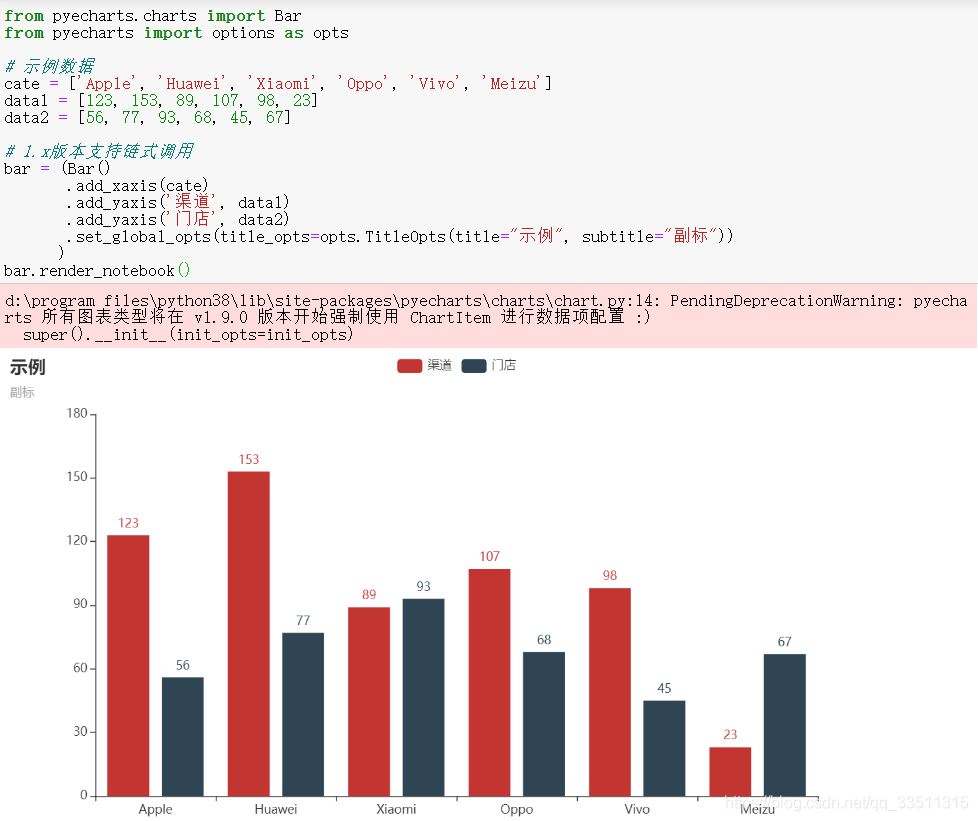
from pyecharts.charts import barfrom pyecharts import options as opts# 示例數據cate = ['apple', 'huawei', 'xiaomi', 'oppo', 'vivo', 'meizu']data1 = [123, 153, 89, 107, 98, 23]data2 = [56, 77, 93, 68, 45, 67]# 1.x版本支持鏈式調用bar = (bar() .add_xaxis(cate) .add_yaxis('渠道', data1) .add_yaxis('門店', data2) .set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.titleopts(title="示例", subtitle="副標")) )bar.render_notebook() |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
from pyecharts.charts import piefrom pyecharts import options as opts# 示例數據cate = ['apple', 'huawei', 'xiaomi', 'oppo', 'vivo', 'meizu']data = [153, 124, 107, 99, 89, 46]pie = (pie() .add('', [list(z) for z in zip(cate, data)], radius=["30%", "75%"], rosetype="radius") .set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.titleopts(title="pie-基本示例", subtitle="我是副標題")) .set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.labelopts(formatter="{b}: ldzjh9fvzrv3%")) )pie.render_notebook() |
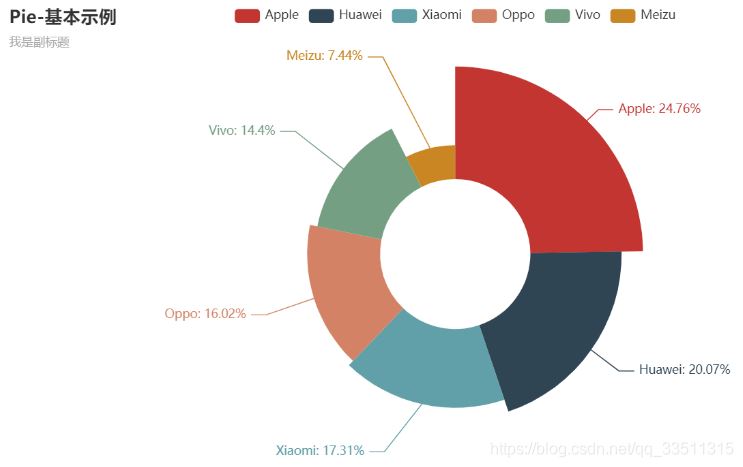
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
from pyecharts.charts import linefrom pyecharts import options as opts# 示例數據cate = ['apple', 'huawei', 'xiaomi', 'oppo', 'vivo', 'meizu']data1 = [123, 153, 89, 107, 98, 23]data2 = [56, 77, 93, 68, 45, 67]"""折線圖示例:1. is_smooth 折線 or 平滑2. markline_opts 標記線 or 標記點"""line = (line() .add_xaxis(cate) .add_yaxis('電商渠道', data1, markline_opts=opts.marklineopts(data=[opts.marklineitem(type_="average")])) .add_yaxis('門店', data2, is_smooth=true, markpoint_opts=opts.markpointopts(data=[opts.markpointitem(name="自定義標記點", coord=[cate[2], data2[2]], value=data2[2])])) .set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.titleopts(title="line-基本示例", subtitle="我是副標題")) )line.render_notebook() |
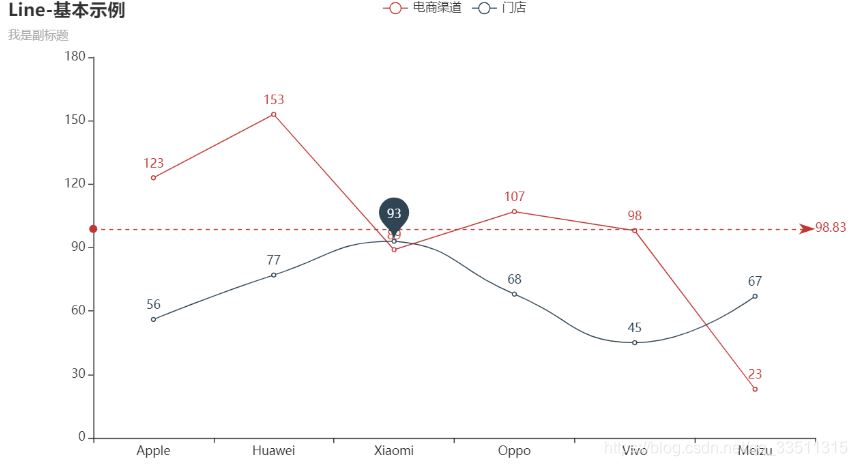
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
from pyecharts import options as optsfrom pyecharts.charts import geofrom pyecharts.globals import charttypeimport randomprovince = ['福州市', '莆田市', '泉州市', '廈門市', '漳州市', '龍巖市', '三明市', '南平']data = [(i, random.randint(200, 550)) for i in province]geo = (geo() .add_schema(maptype="福建") .add("門店數", data, type_=charttype.heatmap) .set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.labelopts(is_show=false)) .set_global_opts( visualmap_opts=opts.visualmapopts(), legend_opts=opts.legendopts(is_show=false), title_opts=opts.titleopts(title="福建熱力地圖")) )geo.render_notebook() |
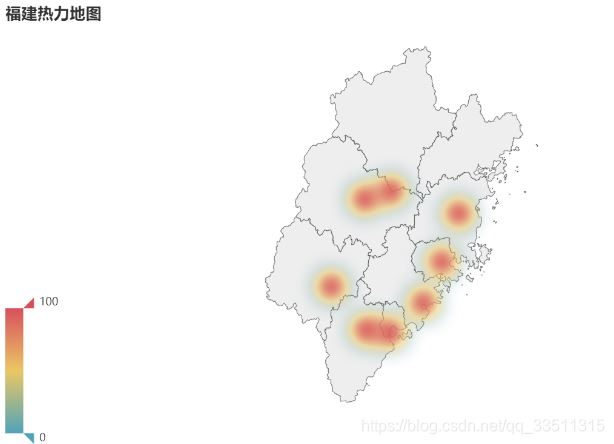

啊哈這個還訪問不了哈
importerror: missing optional dependency ‘xlrd'. install xlrd >= 1.0.0 for excel support use pip or conda to install xlrd.

20200822pyecharts+pandas 初步學習
作者今天學習做數據分析,有錯誤請指出
下面貼出源代碼
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
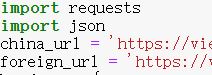
# 獲取數據import requestsimport jsonchina_url = 'https://view.inews.qq.com/g2/getonsinfo?name=disease_h5'#foreign_url = 'https://view.inews.qq.com/g2/getonsinfo?name=disease_foreign'headers = { 'user-agent': 'mozilla/5.0 (windows nt 10.0; win64; x64) applewebkit/537.36 (khtml, like gecko) chrome/84.0.4147.125 safari/537.36 edg/84.0.522.59', 'referer': 'https://news.qq.com/zt2020/page/feiyan.htm'}#獲取json數據response = requests.get(url=china_url,headers=headers).json()print(response)#先將json數據轉 python的字典data = json.loads(response['data'])#保存數據 這里使用encoding='utf-8' 是因為作者想在jupyter上面看with open('./國內疫情.json','w',encoding='utf-8') as f: #再將python的字典轉json數據 # json默認中文以ascii碼顯示 在這里我們以中文顯示 所以false #indent=2:開頭空格2 f.write(json.dumps(data,ensure_ascii=false,indent=2)) |
轉換為json格式輸出的文件

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
# 將json數據轉存到excel中import pandas as pd#讀取文件with open('./國內疫情.json',encoding='utf-8') as f: data = f.read() #將數據轉為python數據格式data = json.loads(data)type(data)#字典類型lastupdatetime = data['lastupdatetime']#獲取中國所有數據chinaareadict = data['areatree'][0]#獲取省級數據provincelist = chinaareadict['children']# 獲取的數據有幾個省市和地區print('數據共有:',len(provincelist),'省市和地區')#將中國數據按城市封裝,例如【{湖北,武漢},{湖北,襄陽}】,為了方便放在dataframe中china_citylist = []for x in range(len(provincelist)): # 每一個省份的數據 province =provincelist[x]['name'] #有多少個市 province_list = provincelist[x]['children'] for y in range(len(province_list)): # 每一個市的數據 city = province_list[y]['name'] # 累積所有的數據 total = province_list[y]['total'] # 今日的數據 today = province_list[y]['today'] china_dict = {'省份':province, '城市':city, 'total':total, 'today':today } china_citylist.append(china_dict)chinatotaldata = pd.dataframe(china_citylist)nowconfirmlist=[]confirmlist=[]suspectlist=[]deadlist=[]heallist=[]deadratelist=[]healratelist=[]# 將整體數據chinatotaldata的數據添加dataframefor value in chinatotaldata['total'] .values.tolist():#轉成列表 confirmlist.append(value['confirm']) suspectlist.append(value['suspect']) deadlist.append(value['dead']) heallist.append(value['heal']) deadratelist.append(value['deadrate']) healratelist.append(value['healrate']) nowconfirmlist.append(value['nowconfirm']) chinatotaldata['現有確診']=nowconfirmlist chinatotaldata['累計確診']=confirmlistchinatotaldata['疑似']=suspectlistchinatotaldata['死亡']=deadlistchinatotaldata['治愈']=heallistchinatotaldata['死亡率']=deadratelistchinatotaldata['治愈率']=healratelist#拆分today列today_confirmlist=[]today_confirmcutlist=[]for value in chinatotaldata['today'].values.tolist(): today_confirmlist.append(value['confirm']) today_confirmcutlist.append(value['confirmcuts'])chinatotaldata['今日確診']=today_confirmlistchinatotaldata['今日死亡']=today_confirmcutlist#刪除total列 在原有的數據基礎chinatotaldata.drop(['total','today'],axis=1,inplace=true)# 將其保存到excel中from openpyxl import load_workbookbook = load_workbook('國內疫情.xlsx')# 避免了數據覆蓋writer = pd.excelwriter('國內疫情.xlsx',engine='openpyxl')writer.book = bookwriter.sheets = dict((ws.title,ws) for ws in book.worksheets)chinatotaldata.to_excel(writer,index=false)writer.save()writer.close()chinatotaldata |
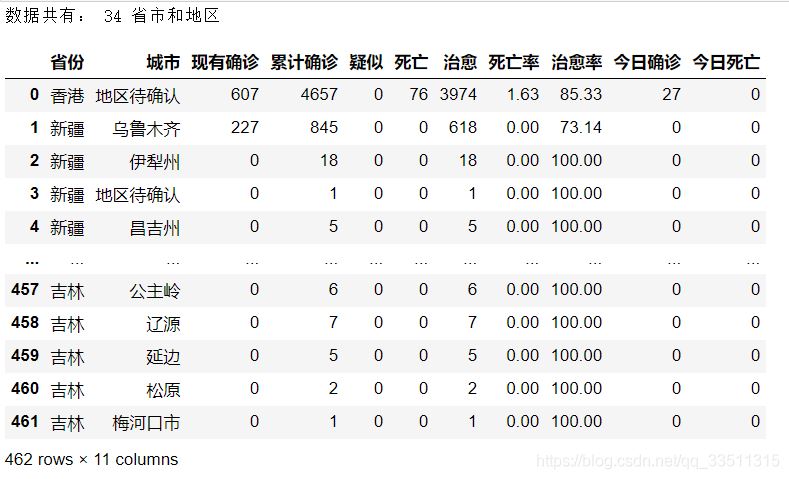
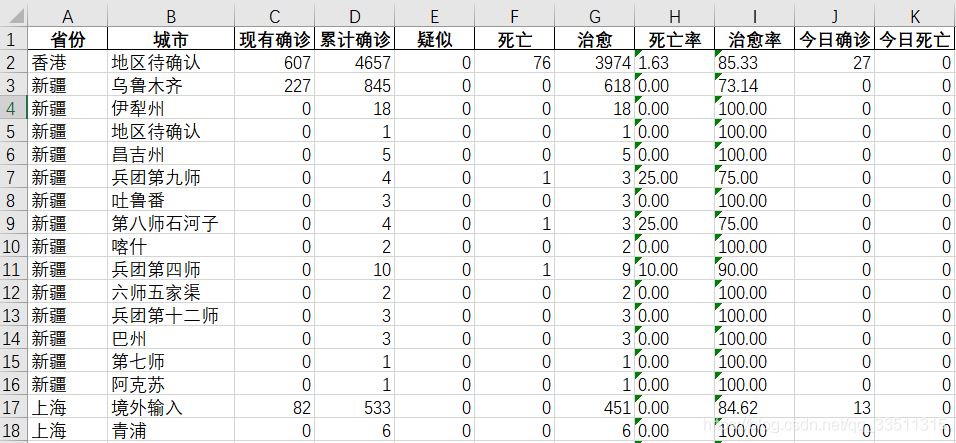
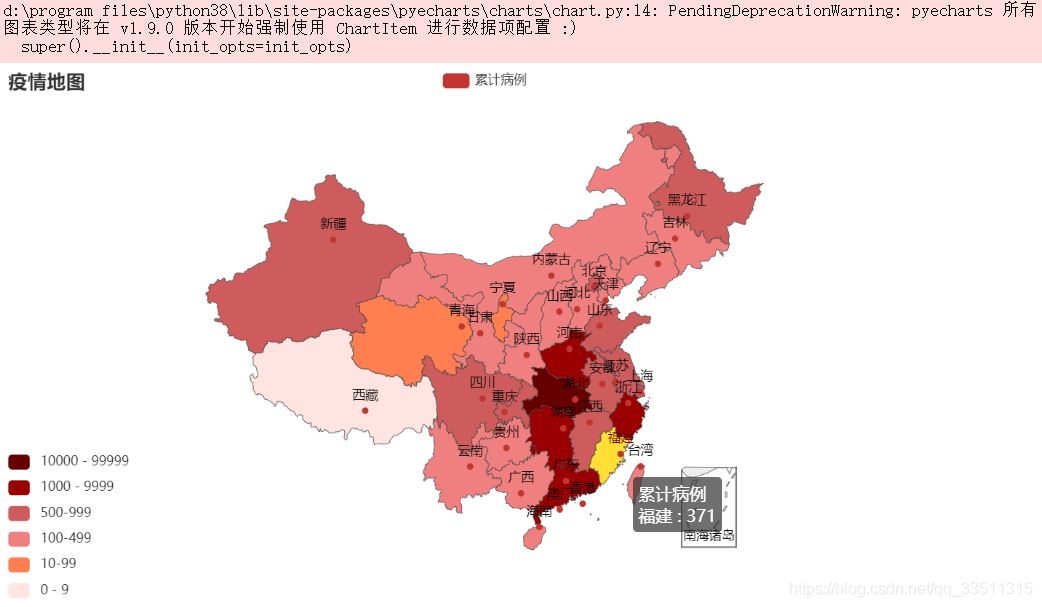
作者這邊還有國外的,不過沒打算分享出來,大家就看看,總的來說我們國內情況還是非常良好的
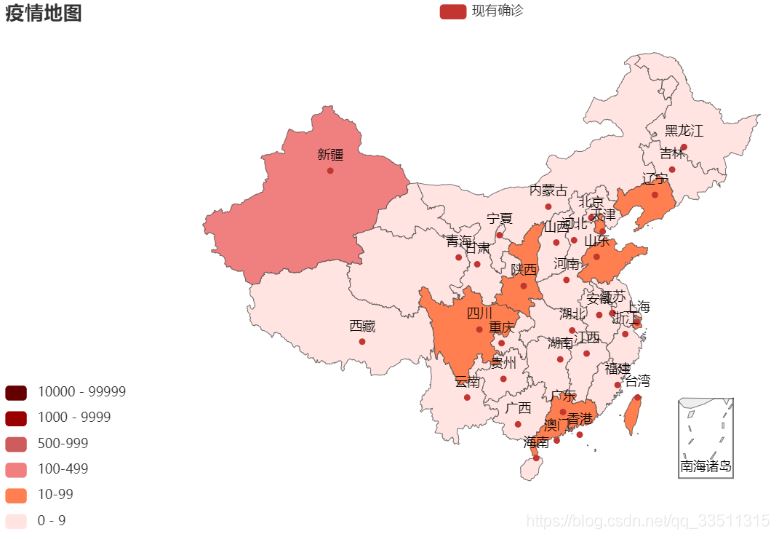
到此這篇關于python繪圖pyecharts+pandas的使用詳解的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關pyecharts pandas使用內容請搜索服務器之家以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持服務器之家!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33511315/article/details/108173301