這里有numpy數組的相關介紹http://www.jfrwli.cn/article/126285.html
numpy與python列表內置的方法類似,也可通過sort方法進行排序。
用法如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
In [1]: import numpy as npIn [2]: x = np.random.randn(9)In [3]: xOut[3]:array([-0.4041504 , -0.42198556, 0.92807217, -2.66609196, 1.50915897, 0.38080873, 1.05325796, -1.16488798, 0.04062064])In [4]: x.sort()In [5]: xOut[5]:array([-2.66609196, -1.16488798, -0.42198556, -0.4041504 , 0.04062064, 0.38080873, 0.92807217, 1.05325796, 1.50915897]) |
可以發現上述的sort方法是直接對x進行了排序而并沒有創建一個副本。
但是np.sort()這個頂級的方法,會返回一個副本:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
In [6]: x = np.random.randn(6)In [7]: xOut[7]:array([ 0.14240205, 0.48903869, 0.22528632, 1.31659382, 0.00352338, 0.95574862])In [8]: np.sort(x)Out[8]:array([ 0.00352338, 0.14240205, 0.22528632, 0.48903869, 0.95574862, 1.31659382])In [9]: xOut[9]:array([ 0.14240205, 0.48903869, 0.22528632, 1.31659382, 0.00352338, 0.95574862]) |
傳入軸編號,可以實現在某一個軸向上進行排序。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
In [34]: x = np.random.randn(5,4)In [35]: xOut[35]:array([[-0.26646799, -0.40714749, -0.76788268, -0.25340467], [ 0.70099086, -0.88716684, 0.13461279, 2.14412835], [ 0.39718924, -0.14671297, -0.67821163, 1.85798273], [-0.29389289, 0.0346094 , 0.25213133, 0.87105479], [-0.10797243, 1.60188878, 0.67829493, 0.43291808]])In [36]: s = xIn [37]: s.sort(0)#按列進行排序In [38]: sOut[38]:array([[-0.29389289, -0.88716684, -0.76788268, -0.25340467], [-0.26646799, -0.40714749, -0.67821163, 0.43291808], [-0.10797243, -0.14671297, 0.13461279, 0.87105479], [ 0.39718924, 0.0346094 , 0.25213133, 1.85798273], [ 0.70099086, 1.60188878, 0.67829493, 2.14412835]])In [39]: xOut[39]:array([[-0.29389289, -0.88716684, -0.76788268, -0.25340467], [-0.26646799, -0.40714749, -0.67821163, 0.43291808], [-0.10797243, -0.14671297, 0.13461279, 0.87105479], [ 0.39718924, 0.0346094 , 0.25213133, 1.85798273], [ 0.70099086, 1.60188878, 0.67829493, 2.14412835]])In [40]: x = np.random.randn(5,4)In [41]: xOut[41]:array([[ 0.82309157, -0.56413805, -0.1766557 , -0.31924962], [-1.25606694, 2.63622922, 2.47481377, 0.27840961], [ 0.63659583, 1.52779004, -0.90582752, 0.82325241], [-1.52664294, -0.5285837 , -1.96380368, -0.44323125], [ 1.94859294, 2.55676806, 1.53614848, -0.43366557]])In [42]: x.sort(1)#按行進行排序In [43]: xOut[43]:array([[-0.56413805, -0.31924962, -0.1766557 , 0.82309157], [-1.25606694, 0.27840961, 2.47481377, 2.63622922], [-0.90582752, 0.63659583, 0.82325241, 1.52779004], [-1.96380368, -1.52664294, -0.5285837 , -0.44323125], [-0.43366557, 1.53614848, 1.94859294, 2.55676806]]) |
在這兒,我試圖將x賦值給s,結果發現對s排序后,x也變了,這說明,在內存中,實際上,s,x是指向同一組值得。
我也曾試圖輸入s.sort(2),結果出現了ValueError:axis(=2)outofbounds,這也就和前面的統計函數的axis參數是一致的。
那么也就是說,他的用法和axis一致。
利用排序,我們還能得到分位數(
分位數(英語:Quantile),亦稱分位點,是指將一個隨機變量的概率分布范圍分為幾個等份的數值點,常用的有中位數(即二分位數)、四分位數、百分位數等。具體可自行搜索),從而得到特定位置的值。
|
1
2
3
4
|
In [44]: x = np.random.randn(500)In [45]: x.sort()In [46]: x[int(0.05 * len(x))] #5%分位數Out[46]: -1.7657191623368329 |
還有很多沒有深入了解,比如怎么降序排列,待續。
集合運算
unique(x)返回集合中的唯一值,并排序,其實也就是去除重復值。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
In [1]: import numpy as npIn [2]: str = np.array(['s','f','r','s','d','f','w','r'])In [3]: np.unique(str)Out[3]:array(['d', 'f', 'r', 's', 'w'], dtype='<U1')In [4]: i = np.array([2,2,2,2,1,1,3,4,5,4,3,5])In [5]: np.unique(i)Out[5]: array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) |
intersect1d(x,y)返回集合A和B的交集,并排序
|
1
2
3
4
|
In [6]: k = np.arange(8)In [7]: np.intersect1d(i, k)Out[7]: array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) |
union1d(x,y)返回集合A和B的并集,并排序
|
1
2
|
In [8]: np.union1d(i,k)Out[8]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) |
in1d(x,y)返回一個A包含于B的布爾型數組
|
1
2
|
In [10]: np.in1d(k,i)Out[10]: array([False, True, True, True, True, True, False, False], dtype=bool) |
setdiff1d(x,y)集合的差,包含于A但不包含于B,相當于A-(A∩B)
|
1
2
|
In [12]: np.setdiff1d(k,i)Out[12]: array([0, 6, 7]) |
|
1
|
setxor1d(x,y)存在于A中但不同時存在于B中,也就是對稱差,說白了就是A和B交集之外的部分。 |
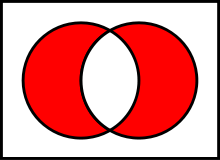
就是紅色的部分。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
In [13]: s = np.arange(4,12)In [14]: sOut[14]: array([ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11])In [15]: np.setxor1d(s,k)Out[15]: array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10, 11]) |
總結
以上就是本文關于numpy排序與集合運算用法示例的全部內容,希望對大家有所幫助。感興趣的朋友可以繼續參閱本站其他相關專題,如有不足之處,歡迎留言指出。感謝朋友們對本站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/sunshinewang/p/6905791.html