逆向最大匹配方法
有正即有負,正向最大匹配算法大家可以參閱http://www.jfrwli.cn/article/123273.html
逆向最大匹配分詞是中文分詞基本算法之一,因為是機械切分,所以它也有分詞速度快的優點,且逆向最大匹配分詞比起正向最大匹配分詞更符合人們的語言習慣。逆向最大匹配分詞需要在已有詞典的基礎上,從被處理文檔的末端開始匹配掃描,每次取最末端的i個字符(分詞所確定的閾值i)作為匹配字段,若匹配失敗,則去掉匹配字段最前面的一個字,繼續匹配。而且選擇的閾值越大,分詞越慢,但準確性越好。
逆向最大匹配算法python實現:
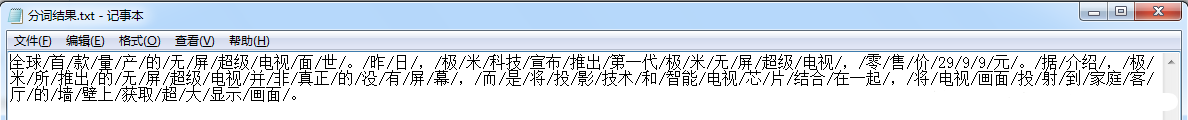
分詞文本示例:

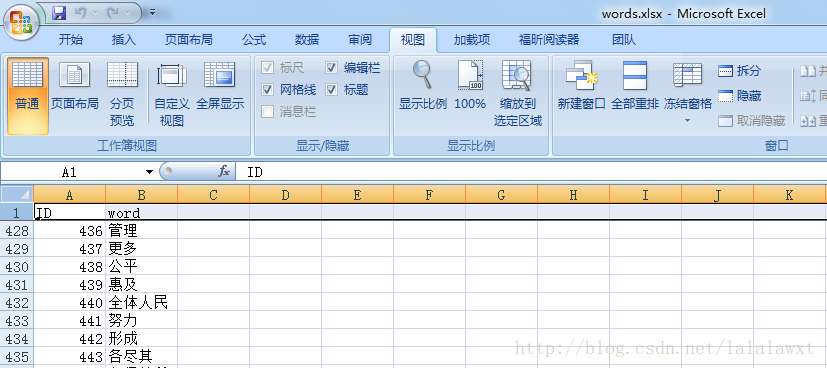
分詞詞典words.xlsx示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
#!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- ''''' 用逆向最大匹配法分詞,不去除停用詞 '''import codecs import xlrd #讀取待分詞文本,readlines()返回句子list def readfile(raw_file_path): with codecs.open(raw_file_path,"r",encoding="ANSI") as f: raw_file=f.readlines() return raw_file #讀取分詞詞典,返回分詞詞典list def read_dic(dic_path): excel = xlrd.open_workbook(dic_path) sheet = excel.sheets()[0] # 讀取第二列的數據 data_list = list(sheet.col_values(1))[1:] return data_list #逆向最大匹配法分詞 def cut_words(raw_sentences,word_dic): word_cut=[] #最大詞長,分詞詞典中的最大詞長,為初始分詞的最大詞長 max_length=max(len(word) for word in word_dic) for sentence in raw_sentences: #strip()函數返回一個沒有首尾空白字符(‘\n'、‘\r'、‘\t'、‘')的sentence,避免分詞錯誤 sentence=sentence.strip() #單句中的字數 words_length = len(sentence) #存儲切分出的詞語 cut_word_list=[] #判斷句子是否切分完畢 while words_length > 0: max_cut_length = min(words_length, max_length) for i in range(max_cut_length, 0, -1): #根據切片性質,截取words_length-i到words_length-1索引的字,不包括words_length,所以不會溢出 new_word = sentence[words_length - i: words_length] if new_word in word_dic: cut_word_list.append(new_word) words_length = words_length - i break elif i == 1: cut_word_list.append(new_word) words_length = words_length - 1 #因為是逆向最大匹配,所以最終需要把結果逆向輸出,轉換為原始順序 cut_word_list.reverse() words="/".join(cut_word_list) #最終把句子首端的分詞符號刪除,是避免以后將分詞結果轉化為列表時會出現空字符串元素 word_cut.append(words.lstrip("/")) return word_cut #輸出分詞文本 def outfile(out_path,sentences): #輸出模式是“a”即在原始文本上繼續追加文本 with codecs.open(out_path,"a","utf8") as f: for sentence in sentences: f.write(sentence) print("well done!") def main(): #讀取待分詞文本 rawfile_path = r"逆向分詞文本.txt" raw_file=readfile(rawfile_path) #讀取分詞詞典 wordfile_path = r"words.xlsx" words_dic = read_dic(wordfile_path) #逆向最大匹配法分詞 content_cut = cut_words(raw_file,words_dic) #輸出文本 outfile_path = r"分詞結果.txt" outfile(outfile_path,content_cut) if __name__=="__main__": main() |
總結
分析分詞結果可以知道,機械分詞的效果優劣,一方面與分詞匹配算法有關,另外一方面極其依賴分詞詞典。所以若想得到好的分詞效果,處理相關領域的文本時,需要在分詞詞典中加入特定領域的詞匯。
以上就是本文關于python實現機械分詞之逆向最大匹配算法代碼示例的全部內容,希望對大家有所幫助。感興趣的朋友可以繼續參閱本站其他相關專題,如有不足之處,歡迎留言指出。感謝朋友們對本站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/lalalawxt/article/details/75477931