一、前言
thymeleaf 的出現(xiàn)是為了取代 jsp,雖然 jsp 存在了很長時間,并在 java web 開發(fā)中無處不在,但是它也存在一些缺陷:
1、jsp 最明顯的問題在于它看起來像html或xml,但它其實上并不是。大多數(shù)的jsp模板都是采用html的形式,但是又摻雜上了各種jsp標簽庫的標簽,使其變得很混亂。
2、jsp 規(guī)范是與 servlet 規(guī)范緊密耦合的。這意味著它只能用在基于 servlet 的web應用之中。jsp模板不能作為通用的模板(如格式化email),也不能用于非servlet的 web 應用。
相較于 jsp 來說,thymeleaf 很好的解決了這些缺點:
1、thymeleaf模板是原生的,不依賴于標簽庫。它能在接受原始 html 的地方進行編輯和渲染。
2、因為它沒有與servlet規(guī)范耦合,因此 thymeleaf 模板能夠進入jsp所無法涉足的領域。這意味著thymeleaf模板與jsp不同,它能夠按照原始的方式進行編輯甚至渲染,而不必經(jīng)過任何類型的處理器。當然,我們需要thymeleaf來處理模板并渲染得到最終期望的輸出。即便如此,如果沒有任何特殊的處理,home.html也能夠加載到web瀏覽器中,并且看上去與完整渲染的效果很類似。
spring boot不建議使用 jsp 開發(fā)web。
二、集成 thymeleaf 模板引擎
springboot 對 thymeleaf 模板引擎的支持也很簡單:
1、pom.xml
|
1
2
3
4
|
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactid></dependency> |
這時候,springboot 對 thymeleaf 模板的支持就完成了,我們就能在 web 開發(fā)中使用 thymeleaf 模板了,簡單吧?
之前的文章有提到 springboot 的關鍵是 “約定俗成”。既然我們選擇了這么簡單的配置,那么在開發(fā)中就要遵守 springboot 對 thymeleaf 約定俗成的方案,最重要的一點就是 模板文件放在 templates 目錄下,即模板解析器前綴是 /templates/ ,后綴是 .html 。
2、application.yml
如果不想要所謂約定俗成的方案,想進行一些自定義的配置呢?且看下方:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
spring: thymeleaf: prefix: classpath:/templates/ suffix: .html servlet: content-type: text/html enabled: true encoding: utf-8 mode: html5 cache: false |
3、webconfig.java
如果上面的配置還不能達到你的要求,你想要更細化對 thymeleaf 的控制,包括配置視圖解析器、模板解析器以及模板引擎這些,那么請看下面的方案!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
/** * 1、thymeleafviewresolver 接收邏輯視圖名稱將它解析為視圖 * 2、springtemplateengine會在spring中啟用thymeleaf引擎,用來解析模板,并基于這些模板渲染結(jié)果 * 3、templateresolver會最終定位和查找模板。 */@configurationpublic class webconfig { /** * 配置 thymeleaf 視圖解析器 —— 將邏輯視圖名稱解析為 thymeleaf 模板視圖 * * @param springtemplateengine 模板引擎 * @return */ @bean public viewresolver viewresolver(springtemplateengine springtemplateengine){ thymeleafviewresolver resolver = new thymeleafviewresolver(); resolver.settemplateengine(springtemplateengine); return resolver; } /** * 模板引擎 —— 處理模板并渲染結(jié)果 * * @param templateresolver 模板解析器 * @return */ @bean public springtemplateengine springtemplateengine(itemplateresolver templateresolver) { springtemplateengine springtemplateengine = new springtemplateengine(); springtemplateengine.settemplateresolver(templateresolver); return springtemplateengine; } /** * 模板解析器 —— 加載 thymeleaf 模板 * * @return */ @bean public itemplateresolver templateresolver() { springresourcetemplateresolver templateresolver = new springresourcetemplateresolver(); templateresolver.setprefix("classpath:/templates/"); templateresolver.setsuffix(".html"); templateresolver.settemplatemode(templatemode.html); templateresolver.setcacheable(false); templateresolver.settemplatemode("html5"); return templateresolver; }} |
三、使用 thymeleaf 模板
做好了上面的配置后,讓我們來看看如何在 springboot 中使用 thymeleaf 模板吧:
1、模板文件 — /templates/user/list.html
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<!doctype html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"><head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>insert title here</title></head><body><h2>用戶列表</h2><div> <ul> <li th:each="user:${users}"> <span th:text="${user.uuid}"></span>- <span th:text="${user.name}"></span>- <span th:text="${user.age}"></span>- <span th:text="${user.address}"></span> </li> </ul></div></body></html> |
2、控制層 — modelandviews
這里 model 指的是:控制層處理完請求,返回需要渲染的結(jié)果;views 指的是:模板的邏輯視圖名(前后端分離)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
@controller@requestmapping("/user")public class usercontroller { @requestmapping("/list") public string listuser(model model) { list<userdto> userlist = new arraylist<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { userlist.add(new userdto(uuid.randomuuid().tostring().replace("-", ""), "張三" + i, 1, "中國北京")); } model.addattribute("users", userlist); return "user/list"; }} |
3、效果
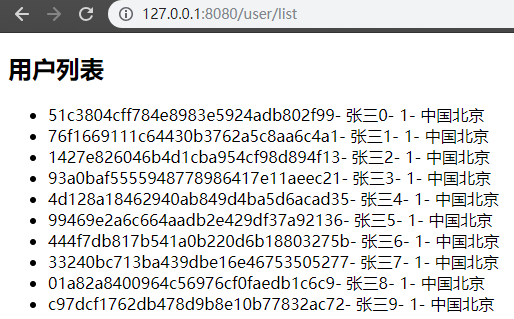
演示源代碼:https://github.com/jmcuixy/thymeleaf
總結(jié)
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的springboot中的thymeleaf模板,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時回復大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對服務器之家網(wǎng)站的支持!
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/jmcui/p/9765785.html