想往某個(gè)表中插入幾百萬條數(shù)據(jù)做下測試,原先的想法,直接寫個(gè)循環(huán)10W次隨便插入點(diǎn)數(shù)據(jù)試試吧,好吧,我真的很天真....
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS proc_initData;--如果存在此存儲(chǔ)過程則刪掉DELIMITER $CREATE PROCEDURE proc_initData()BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1; WHILE i<=100000 DO INSERT INTO text VALUES(i,CONCAT('姓名',i),'XXXXXXXXX'); SET i = i+1; END WHILE;END $CALL proc_initData(); |
執(zhí)行CALL proc_initData()后,本來想想,再慢10W條數(shù)據(jù)頂多30分鐘能搞定吧,結(jié)果我打了2把LOL后,回頭一看,還在執(zhí)行,此時(shí)心里是徹底懵逼的....待我打完第三把結(jié)束后,終于執(zhí)行完了,這種方法若是讓我等上幾百萬條數(shù)據(jù),是不是早上去上班,下午下班回來還沒結(jié)束呢?10W條數(shù)據(jù),有圖有真相
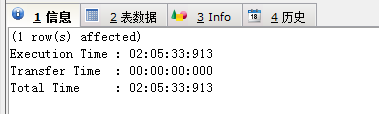
JDBC往數(shù)據(jù)庫中普通插入方式
后面查了一下,使用JDBC批量操作往數(shù)據(jù)庫插入100W+的數(shù)據(jù)貌似也挺快的,
先來說說JDBC往數(shù)據(jù)庫中普通插入方式,簡單的代碼大致如下,循環(huán)了1000條,中間加點(diǎn)隨機(jī)的數(shù)值,畢竟自己要拿數(shù)據(jù)測試,數(shù)據(jù)全都一樣也不好區(qū)分
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01"; private String user = "root"; private String password = "123456"; @Test public void Test(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstm =null; ResultSet rt = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "INSERT INTO userinfo(uid,uname,uphone,uaddress) VALUES(?,CONCAT('姓名',?),?,?)"; pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql); Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Random rand = new Random(); int a,b,c,d; for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) { pstm.setInt(1, i); pstm.setInt(2, i); a = rand.nextInt(10); b = rand.nextInt(10); c = rand.nextInt(10); d = rand.nextInt(10); pstm.setString(3, "188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d); pstm.setString(4, "xxxxxxxxxx_"+"188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d);27 pstm.executeUpdate(); } Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("OK,用時(shí):" + (endTime - startTime)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally{ if(pstm!=null){ try { pstm.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } |
輸出結(jié)果:OK,用時(shí):738199,單位毫秒,也就是說這種方式與直接數(shù)據(jù)庫中循環(huán)是差不多的。
在討論批量處理之前,先說說遇到的坑,首先,JDBC連接的url中要加rewriteBatchedStatements參數(shù)設(shè)為true是批量操作的前提,其次就是檢查mysql驅(qū)動(dòng)包時(shí)候是5.1.13以上版本(低于該版本不支持),因網(wǎng)上隨便下載了5.1.7版本的,然后執(zhí)行批量操作(100W條插入),結(jié)果因?yàn)轵?qū)動(dòng)器版本太低緣故并不支持,導(dǎo)致停止掉java程序后,mysql還在不斷的往數(shù)據(jù)庫中插入數(shù)據(jù),最后不得不停止掉數(shù)據(jù)庫服務(wù)才停下來...
那么低版本的驅(qū)動(dòng)包是否對100W+數(shù)據(jù)插入就無力了呢?實(shí)際還有另外一種方式,效率相比來說還是可以接受的。
使用事務(wù)提交方式
先將命令的提交方式設(shè)為false,即手動(dòng)提交conn.setAutoCommit(false);最后在所有命令執(zhí)行完之后再提交事務(wù)conn.commit();
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01"; private String user = "root"; private String password = "123456"; @Test public void Test(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstm =null; ResultSet rt = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "INSERT INTO userinfo(uid,uname,uphone,uaddress) VALUES(?,CONCAT('姓名',?),?,?)"; pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql); conn.setAutoCommit(false); Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Random rand = new Random(); int a,b,c,d; for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) { pstm.setInt(1, i); pstm.setInt(2, i); a = rand.nextInt(10); b = rand.nextInt(10); c = rand.nextInt(10); d = rand.nextInt(10); pstm.setString(3, "188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d); pstm.setString(4, "xxxxxxxxxx_"+"188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d); pstm.executeUpdate(); } conn.commit(); Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("OK,用時(shí):" + (endTime - startTime)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally{ if(pstm!=null){ try { pstm.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } |
以上代碼插入10W條數(shù)據(jù),輸出結(jié)果:OK,用時(shí):18086,也就十八秒左右的時(shí)間,理論上100W也就是3分鐘這樣,勉強(qiáng)還可以接受。
批量處理
接下來就是批量處理了,注意,一定要5.1.13以上版本的驅(qū)動(dòng)包。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01?rewriteBatchedStatements=true"; private String user = "root"; private String password = "123456"; @Test public void Test(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstm =null; ResultSet rt = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "INSERT INTO userinfo(uid,uname,uphone,uaddress) VALUES(?,CONCAT('姓名',?),?,?)"; pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql); Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Random rand = new Random(); int a,b,c,d; for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) { pstm.setInt(1, i); pstm.setInt(2, i); a = rand.nextInt(10); b = rand.nextInt(10); c = rand.nextInt(10); d = rand.nextInt(10); pstm.setString(3, "188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d); pstm.setString(4, "xxxxxxxxxx_"+"188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d); pstm.addBatch(); } pstm.executeBatch(); Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("OK,用時(shí):" + (endTime - startTime)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally{ if(pstm!=null){ try { pstm.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } |
10W輸出結(jié)果:OK,用時(shí):3386,才3秒鐘.
批量操作+事務(wù)
然后我就想,要是批量操作+事務(wù)提交呢?會(huì)不會(huì)有神器的效果?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01?rewriteBatchedStatements=true"; private String user = "root"; private String password = "123456"; @Test public void Test(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstm =null; ResultSet rt = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "INSERT INTO userinfo(uid,uname,uphone,uaddress) VALUES(?,CONCAT('姓名',?),?,?)"; pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql); conn.setAutoCommit(false); Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Random rand = new Random(); int a,b,c,d; for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) { pstm.setInt(1, i); pstm.setInt(2, i); a = rand.nextInt(10); b = rand.nextInt(10); c = rand.nextInt(10); d = rand.nextInt(10); pstm.setString(3, "188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d); pstm.setString(4, "xxxxxxxxxx_"+"188"+a+"88"+b+c+"66"+d); pstm.addBatch(); } pstm.executeBatch(); conn.commit(); Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("OK,用時(shí):" + (endTime - startTime)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally{ if(pstm!=null){ try { pstm.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } } |
以下是100W數(shù)據(jù)輸出對比:(5.1.17版本MySql驅(qū)動(dòng)包下測試,交替兩種方式下的數(shù)據(jù)測試結(jié)果對比)
|
批量操作(10W) |
批量操作+事務(wù)提交(10W) |
批量操作(100W) |
批量錯(cuò)作+事務(wù)提交(100W) |
|
OK,用時(shí):3901 |
OK,用時(shí):3343 |
OK,用時(shí):44242 |
OK,用時(shí):39798 |
|
OK,用時(shí):4142 |
OK,用時(shí):2949 |
OK,用時(shí):44248 |
OK,用時(shí):39959 |
|
OK,用時(shí):3664 |
OK,用時(shí):2689 |
OK,用時(shí):44389 |
OK,用時(shí):39367 |
可見有一定的效率提升,但是并不是太明顯,當(dāng)然因?yàn)閿?shù)據(jù)差不算太大,也有可能存在偶然因數(shù),畢竟每項(xiàng)只測3次。
預(yù)編譯+批量操作
網(wǎng)上還有人說使用預(yù)編譯+批量操作的方式能夠提高效率更明顯,但是本人親測,效率不高反降,可能跟測試的數(shù)據(jù)有關(guān)吧。
預(yù)編譯的寫法,只需在JDBC的連接url中將寫入useServerPrepStmts=true即可,
如:
private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test01?useServerPrepStmts=true&rewriteBatchedStatements=true"
好了,先到這里...
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務(wù)器之家。
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/fnz0/p/5713102.html