使用POI讀寫Word doc文件
Apache poi的hwpf模塊是專門用來對word doc文件進行讀寫操作的。在hwpf里面我們使用HWPFDocument來表示一個word doc文檔。在HWPFDocument里面有這么幾個概念:
Range:它表示一個范圍,這個范圍可以是整個文檔,也可以是里面的某一小節(Section),也可以是某一個段落(Paragraph),還可以是擁有共同屬性的一段文本(CharacterRun)。
Section:word文檔的一個小節,一個word文檔可以由多個小節構成。
Paragraph:word文檔的一個段落,一個小節可以由多個段落構成。
CharacterRun:具有相同屬性的一段文本,一個段落可以由多個CharacterRun組成。
Table:一個表格。
TableRow:表格對應的行。
TableCell:表格對應的單元格。
Section、Paragraph、CharacterRun和Table都繼承自Range。
1 讀word doc文件
在日常應用中,我們從word文件里面讀取信息的情況非常少見,更多的還是把內容寫入到word文件中。使用POI從word doc文件讀取數據時主要有兩種方式:通過WordExtractor讀和通過HWPFDocument讀。在WordExtractor內部進行信息讀取時還是通過HWPFDocument來獲取的。
1.1 通過WordExtractor讀文件
在使用WordExtractor讀文件時我們只能讀到文件的文本內容和基于文檔的一些屬性,至于文檔內容的屬性等是無法讀到的。如果要讀到文檔內容的屬性則需要使用HWPFDocument來讀取了。下面是使用WordExtractor讀取文件的一個示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
public class HwpfTest { @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Test public void testReadByExtractor() throws Exception { InputStream is = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.doc"); WordExtractor extractor = new WordExtractor(is); //輸出word文檔所有的文本 System.out.println(extractor.getText()); System.out.println(extractor.getTextFromPieces()); //輸出頁眉的內容 System.out.println("頁眉:" + extractor.getHeaderText()); //輸出頁腳的內容 System.out.println("頁腳:" + extractor.getFooterText()); //輸出當前word文檔的元數據信息,包括作者、文檔的修改時間等。 System.out.println(extractor.getMetadataTextExtractor().getText()); //獲取各個段落的文本 String paraTexts[] = extractor.getParagraphText(); for (int i=0; i<paraTexts.length; i++) { System.out.println("Paragraph " + (i+1) + " : " + paraTexts[i]); } //輸出當前word的一些信息 printInfo(extractor.getSummaryInformation()); //輸出當前word的一些信息 this.printInfo(extractor.getDocSummaryInformation()); this.closeStream(is); } /** * 輸出SummaryInfomation * @param info */ private void printInfo(SummaryInformation info) { //作者 System.out.println(info.getAuthor()); //字符統計 System.out.println(info.getCharCount()); //頁數 System.out.println(info.getPageCount()); //標題 System.out.println(info.getTitle()); //主題 System.out.println(info.getSubject()); } /** * 輸出DocumentSummaryInfomation * @param info */ private void printInfo(DocumentSummaryInformation info) { //分類 System.out.println(info.getCategory()); //公司 System.out.println(info.getCompany()); } /** * 關閉輸入流 * @param is */ private void closeStream(InputStream is) { if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
1.2 通過HWPFDocument讀文件
HWPFDocument是當前Word文檔的代表,它的功能比WordExtractor要強。通過它我們可以讀取文檔中的表格、列表等,還可以對文檔的內容進行新增、修改和刪除操作。只是在進行完這些新增、修改和刪除后相關信息是保存在HWPFDocument中的,也就是說我們改變的是HWPFDocument,而不是磁盤上的文件。如果要使這些修改生效的話,我們可以調用HWPFDocument的write方法把修改后的HWPFDocument輸出到指定的輸出流中。這可以是原文件的輸出流,也可以是新文件的輸出流(相當于另存為)或其它輸出流。下面是一個通過HWPFDocument讀文件的示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
|
public class HwpfTest { @Test public void testReadByDoc() throws Exception { InputStream is = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.doc"); HWPFDocument doc = new HWPFDocument(is); //輸出書簽信息 this.printInfo(doc.getBookmarks()); //輸出文本 System.out.println(doc.getDocumentText()); Range range = doc.getRange();// this.insertInfo(range); this.printInfo(range); //讀表格 this.readTable(range); //讀列表 this.readList(range); //刪除range Range r = new Range(2, 5, doc); r.delete();//在內存中進行刪除,如果需要保存到文件中需要再把它寫回文件 //把當前HWPFDocument寫到輸出流中 doc.write(new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.doc")); this.closeStream(is); } /** * 關閉輸入流 * @param is */ private void closeStream(InputStream is) { if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 輸出書簽信息 * @param bookmarks */ private void printInfo(Bookmarks bookmarks) { int count = bookmarks.getBookmarksCount(); System.out.println("書簽數量:" + count); Bookmark bookmark; for (int i=0; i<count; i++) { bookmark = bookmarks.getBookmark(i); System.out.println("書簽" + (i+1) + "的名稱是:" + bookmark.getName()); System.out.println("開始位置:" + bookmark.getStart()); System.out.println("結束位置:" + bookmark.getEnd()); } } /** * 讀表格 * 每一個回車符代表一個段落,所以對于表格而言,每一個單元格至少包含一個段落,每行結束都是一個段落。 * @param range */ private void readTable(Range range) { //遍歷range范圍內的table。 TableIterator tableIter = new TableIterator(range); Table table; TableRow row; TableCell cell; while (tableIter.hasNext()) { table = tableIter.next(); int rowNum = table.numRows(); for (int j=0; j<rowNum; j++) { row = table.getRow(j); int cellNum = row.numCells(); for (int k=0; k<cellNum; k++) { cell = row.getCell(k); //輸出單元格的文本 System.out.println(cell.text().trim()); } } } } /** * 讀列表 * @param range */ private void readList(Range range) { int num = range.numParagraphs(); Paragraph para; for (int i=0; i<num; i++) { para = range.getParagraph(i); if (para.isInList()) { System.out.println("list: " + para.text()); } } } /** * 輸出Range * @param range */ private void printInfo(Range range) { //獲取段落數 int paraNum = range.numParagraphs(); System.out.println(paraNum); for (int i=0; i<paraNum; i++) {// this.insertInfo(range.getParagraph(i)); System.out.println("段落" + (i+1) + ":" + range.getParagraph(i).text()); if (i == (paraNum-1)) { this.insertInfo(range.getParagraph(i)); } } int secNum = range.numSections(); System.out.println(secNum); Section section; for (int i=0; i<secNum; i++) { section = range.getSection(i); System.out.println(section.getMarginLeft()); System.out.println(section.getMarginRight()); System.out.println(section.getMarginTop()); System.out.println(section.getMarginBottom()); System.out.println(section.getPageHeight()); System.out.println(section.text()); } } /** * 插入內容到Range,這里只會寫到內存中 * @param range */ private void insertInfo(Range range) { range.insertAfter("Hello"); } } |
2 寫word doc文件
在使用POI寫word doc文件的時候我們必須要先有一個doc文件才行,因為我們在寫doc文件的時候是通過HWPFDocument來寫的,而HWPFDocument是要依附于一個doc文件的。所以通常的做法是我們先在硬盤上準備好一個內容空白的doc文件,然后建立一個基于該空白文件的HWPFDocument。之后我們就可以往HWPFDocument里面新增內容了,然后再把它寫入到另外一個doc文件中,這樣就相當于我們使用POI生成了word doc文件。
在實際應用中,我們在生成word文件的時候都是生成某一類文件,該類文件的格式是固定的,只是某些字段不一樣罷了。所以在實際應用中,我們大可不必將整個word文件的內容都通過HWPFDocument生成。而是先在磁盤上新建一個word文檔,其內容就是我們需要生成的word文件的內容,然后把里面一些屬于變量的內容使用類似于“${paramName}”這樣的方式代替。這樣我們在基于某些信息生成word文件的時候,只需要獲取基于該word文件的HWPFDocument,然后調用Range的replaceText()方法把對應的變量替換為對應的值即可,之后再把當前的HWPFDocument寫入到新的輸出流中。這種方式在實際應用中用的比較多,因為它不但可以減少我們的工作量,還可以讓文本的格式更加的清晰。下面我們就來基于這種方式做一個示例。
假設我們現在擁有一些變動的信息,然后需要通過這些信息生成如下格式的word doc文件:
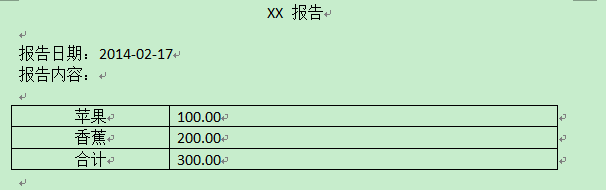
那么根據上面的描述,首先第一步,我們建立一個對應格式的doc文件作為模板,其內容是這樣的:
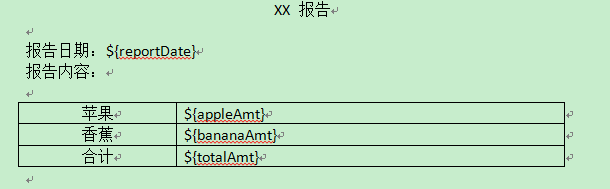
有了這樣一個模板之后,我們就可以建立對應的HWPFDocument,然后替換對應的變量為相應的值,再把HWPFDocument輸出到對應的輸出流即可。下面是對應的代碼。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
public class HwpfTest { @Test public void testWrite() throws Exception { String templatePath = "D:\\word\\template.doc"; InputStream is = new FileInputStream(templatePath); HWPFDocument doc = new HWPFDocument(is); Range range = doc.getRange(); //把range范圍內的${reportDate}替換為當前的日期 range.replaceText("${reportDate}", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").format(new Date())); range.replaceText("${appleAmt}", "100.00"); range.replaceText("${bananaAmt}", "200.00"); range.replaceText("${totalAmt}", "300.00"); OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("D:\\word\\write.doc"); //把doc輸出到輸出流中 doc.write(os); this.closeStream(os); this.closeStream(is); } /** * 關閉輸入流 * @param is */ private void closeStream(InputStream is) { if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 關閉輸出流 * @param os */ private void closeStream(OutputStream os) { if (os != null) { try { os.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
(注:本文是基于poi3.9所寫)
感謝閱讀,希望能幫助到大家,謝謝大家對本站的支持!
原文鏈接:https://my.oschina.net/elim1/blog/812322