本文實(shí)例講述了Java基于socket服務(wù)實(shí)現(xiàn)UDP協(xié)議的方法。分享給大家供大家參考。具體如下:
示例1:
接收類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
package com.socket.demo; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; public class UDPReceiveDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ System.out.println("接收端啟動(dòng)…………"); /* 2、建立UDP的socket的服務(wù),必須明確一個(gè)端口號(hào) 3、創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)包,用于儲(chǔ)存接收到的數(shù)據(jù),方便用數(shù)據(jù)包對(duì)象的方法解析這些數(shù)據(jù) 4、使用DatagramSocket的receive方法將接收到的數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)到數(shù)據(jù)包中 5、通過數(shù)據(jù)包的方法解析數(shù)據(jù)包中的數(shù)據(jù) 5、關(guān)閉socket服務(wù) */ //udpsocket服務(wù),使用DatagramSocket對(duì)象 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(10002); //使用DatagramPacket將數(shù)據(jù)封裝到該對(duì)象中 byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); //通過udp的socket服務(wù)將數(shù)據(jù)包發(fā)送出去,通過send方法 ds.receive(dp); //通過數(shù)據(jù)包的方法解析數(shù)據(jù)包中的數(shù)據(jù),比如,地址、端口、數(shù)據(jù)內(nèi)容等 String ip=dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); //String name=dp.getAddress().getHostName(); int port=dp.getPort(); String text=new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength()); //System.out.println("-----"+ip+"-----"+name+"-----"+port+"-----"+text); System.out.println("-----"+ip+"----------"+port+"-----"+text); //關(guān)閉資源 ds.close(); } } |
發(fā)送類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
package com.socket.demo; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.SocketException; import java.net.UnknownHostException; public class UDPSendDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ System.out.println("發(fā)送端啟動(dòng)…………"); /* * 1、創(chuàng)建udp傳輸?shù)陌l(fā)送端 2、建立UDP的socket的服務(wù) 3、將要發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù)封裝到數(shù)據(jù)包中 4、通過udp的socket服務(wù)將數(shù)據(jù)包發(fā)送出去 5、關(guān)閉socket服務(wù) */ //udpsocket服務(wù),使用DatagramSocket對(duì)象 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(8888);//監(jiān)聽端口 //將要發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù)封裝到數(shù)據(jù)包中 String str="udp傳輸演示,go"; //使用DatagramPacket將數(shù)據(jù)封裝到該對(duì)象中 byte[] buf=str.getBytes(); DatagramPacket dp= new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.1.100"),10002); //通過udp的socket服務(wù)將數(shù)據(jù)包發(fā)送出去,通過send方法 ds.send(dp); //關(guān)閉資源 ds.close(); } } |
示例2:
接收類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package com.socket.demo; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; public class UDPReceiveDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ System.out.println("接收端啟動(dòng)…………"); /* 2、建立UDP的socket的服務(wù),必須明確一個(gè)端口號(hào) 3、創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)包,用于儲(chǔ)存接收到的數(shù)據(jù),方便用數(shù)據(jù)包對(duì)象的方法解析這些數(shù)據(jù) 4、使用DatagramSocket的receive方法將接收到的數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)到數(shù)據(jù)包中 5、通過數(shù)據(jù)包的方法解析數(shù)據(jù)包中的數(shù)據(jù) 5、關(guān)閉socket服務(wù) */ //udpsocket服務(wù),使用DatagramSocket對(duì)象 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(10003); while(true){ //使用DatagramPacket將數(shù)據(jù)封裝到該對(duì)象中 byte[] buf=new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); //通過udp的socket服務(wù)將數(shù)據(jù)包發(fā)送出去,通過send方法 ds.receive(dp);//阻塞式的。 //通過數(shù)據(jù)包的方法解析數(shù)據(jù)包中的數(shù)據(jù),比如,地址、端口、數(shù)據(jù)內(nèi)容等 String ip=dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); //String name=dp.getAddress().getHostName(); int port=dp.getPort(); String text=new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength()); //System.out.println("-----"+ip+"-----"+name+"-----"+port+"-----"+text); System.out.println("-----"+ip+"----------"+port+"-----"+text); } //關(guān)閉資源 //ds.close(); } } |
發(fā)送類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
package com.socket.demo; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; public class UDPSendDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ System.out.println("發(fā)送端啟動(dòng)…………"); /* * 1、創(chuàng)建udp傳輸?shù)陌l(fā)送端 2、建立UDP的socket的服務(wù) 3、將要發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù)封裝到數(shù)據(jù)包中 4、通過udp的socket服務(wù)將數(shù)據(jù)包發(fā)送出去 5、關(guān)閉socket服務(wù) */ //udpsocket服務(wù),使用DatagramSocket對(duì)象 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(9999);//監(jiān)聽端口 //將要發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù)封裝到數(shù)據(jù)包中 //String str="udp傳輸演示,go"; BufferedReader bufr=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));//鍵盤輸入 String line=null; //使用DatagramPacket將數(shù)據(jù)封裝到該對(duì)象中 while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){ byte[] buf=line.getBytes();// DatagramPacket dp= new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.1.100"),10003); //通過udp的socket服務(wù)將數(shù)據(jù)包發(fā)送出去,通過send方法 ds.send(dp); if("886".equals(line)){ break; } } //關(guān)閉資源 ds.close(); } } |
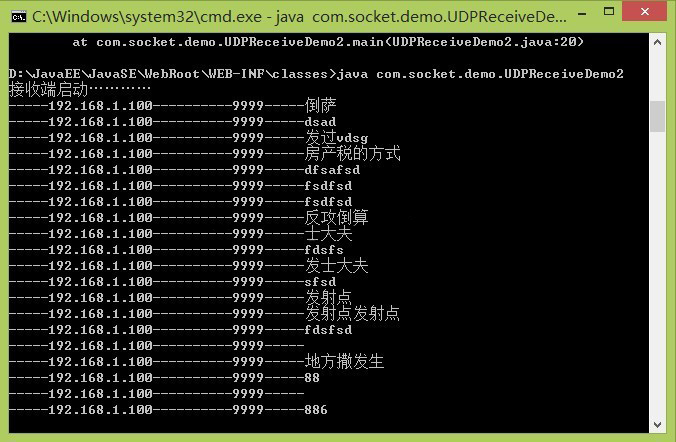
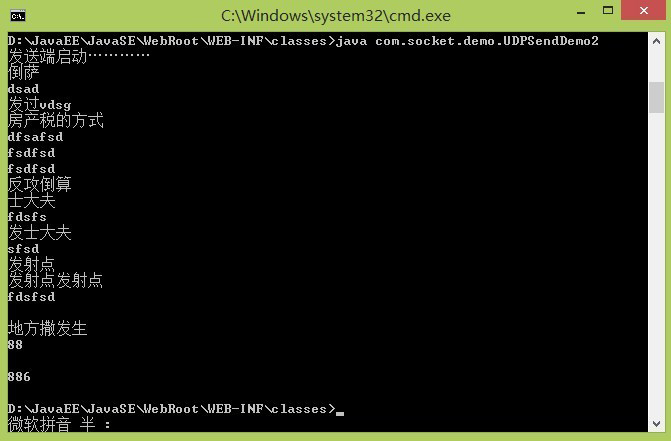
運(yùn)行效果圖如下:
接收:
發(fā)送:
希望本文所述對(duì)大家的java程序設(shè)計(jì)有所幫助。