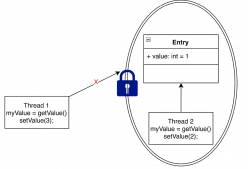
Bean的作用域

singleton作用域
當將bean的scope設置為singleton時,Spring IoC容器僅生成和管理一個Bean實例(單例)。使用id或name獲取Bean實例時,IoC容器將返回共享的Bean實例。
由于singleton是scope(范圍)的默認方式,因此有兩種方式將bean的scope設置為singleton。配置文件示例代碼如下:
<bean id="constructorInstance" class="instance.BeanClass"/> 或 <bean id="constructorInstance" class="instance.BeanClass" scope="singleton"/>
測試singleton作用域,代碼如下:
//初始化Spring容器ApplicationContext,加載配置文件
ApplicationContext appCon = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//測試構造方法實例化Bean
BeanClass b1 = (BeanClass)appCon.getBean("constructorInstance");
System.out.println(b1);
BeanClass b2 = (BeanClass)appCon.getBean("constructorInstance");
System.out.println(b2);
prototype作用域
當bean的scope設置為prototype(原型)時,Spring IoC容器將為每次請求創建一個新的實例。如果將3.3.1中bean的配置修改如下:
<bean id="constructorInstance" class="instance.BeanClass" scope="prototype"/>
Bean的生命周期
Bean的生命周期整個過程如下:
1.根據Bean的配置情況,實例化一個Bean。
2.根據Spring上下文對實例化的Bean進行依賴注入,即對Bean的屬性進行初始化。
3.如果Bean實現了BeanNameAware接口,將調用它實現的setBeanName(String beanId)方法,此處參數傳遞的是Spring配置文件中Bean的ID。
4.如果Bean實現了BeanFactoryAware接口,將調用它實現的setBeanFactory()方法,此處參數傳遞的是當前Spring工廠實例的引用。
5.如果Bean實現了ApplicationContextAware接口,將調用它實現的setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext)方法,此處參數傳遞的是Spring上下文實例的引用。
6.如果Bean關聯了BeanPostProcessor接口,將調用預初始化方法postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object obj, String s)對Bean進行操作。
7.如果Bean實現了InitializingBean接口,將調用afterPropertiesSet()方法。
8.如果Bean在Spring配置文件中配置了init-method屬性,將自動調用其配置的初始化方法。
9.如果Bean關聯了BeanPostProcessor接口,將調用postProcessAfterInitialization(Object obj, String s)方法,由于是在Bean初始化結束時調用After方法,也可用于內存或緩存技術。
以上工作(1至9)完成以后就可以使用該Bean,由于該Bean的作用域是singleton,所以調用的是同一個Bean實例。
10.當Bean不再需要時,將經過銷毀階段,如果Bean實現了DisposableBean接口,將調用其實現的destroy方法將Spring中的Bean銷毀。
11.如果在配置文件中通過destroy-method屬性指定了Bean的銷毀方法,將調用其配置的銷毀方法進行銷毀。
1.創建Bean的實現類
package life;
public class BeanLife {
public void initMyself() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() + "執行自定義的初始化方法");
}
public void destroyMyself() {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() +"執行自定義的銷毀方法");
}
}
2.配置Bean
在Spring配置文件中,使用實現類BeanLife配置一個id為beanLife的Bean。具體代碼如下:
<!-- 配置bean,使用init-method屬性指定初始化方法,使用 destroy-method屬性指定銷毀方法--> <bean id="beanLife" class="life.BeanLife" init-method="initMyself" destroy-method="destroyMyself"/>
3.測試生命周期
在ch3應用的test包中,創建測試類TestLife,具體代碼如下:
//初始化Spring容器,加載配置文件
//為了方便演示銷毀方法的執行,這里使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
//實現類聲明容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
System.out.println("獲得對象前");
BeanLife blife = (BeanLife)ctx.getBean("beanLife");
System.out.println("獲得對象后" + blife);
ctx.close();//關閉容器,銷毀Bean對象
Bean的裝配方式
Bean的裝配可以理解為將Bean依賴注入到Spring容器中,Bean的裝配方式即Bean依賴注入的方式。Spring容器支持基于XML配置的裝配、基于注解的裝配以及自動裝配等多種裝配方式。本節將主要講解基于XML配置的裝配和基于注解的裝配。
基于XML配置的裝配
package assemble;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class ComplexUser {
private String uname;
private List<String> hobbyList;
private Map<String,String> residenceMap;//Map存儲鍵值對
private Set<String> aliasSet;
private String[] array;
//使用構造方法注入,需要提供帶參數的構造方法
public ComplexUser(String uname, List<String> hobbyList, Map<String, String> residenceMap, Set<String> aliasSet,
String[] array) {
super();
this.uname = uname;
this.hobbyList = hobbyList;
this.residenceMap = residenceMap;
this.aliasSet = aliasSet;
this.array = array;
}
//使用setter方法注入,提供默認無參數的構造方法,并為注入的屬性提供setter方法
public ComplexUser() {
super();
}
public void setUname(String uname) {
this.uname = uname;
}
public void setHobbyList(List<String> hobbyList) {
this.hobbyList = hobbyList;
}
public void setResidenceMap(Map<String, String> residenceMap) {
this.residenceMap = residenceMap;
}
public void setAliasSet(Set<String> aliasSet) {
this.aliasSet = aliasSet;
}
public void setArray(String[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "uname="+uname+";hobbyList="+hobbyList+";residenceMap="+residenceMap+";alisaSet="+aliasSet+";array="+array;
}
}
<!-- 使用構造方法注入方式裝配ComplexUser實例user1 --> <bean id="user1" class="assemble.ComplexUser" > <constructor-arg index="0" value="chenheng1" /> <constructor-arg index="1"> <list> <value>唱歌</value> <value>跳舞</value> <value>籃球</value> </list> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="2"> <map> <entry key="dalian" value="大連" /> <entry key="beijing" value="北京" /> <entry key="shanghai" value="上海" /> </map> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="3"> <set> <value>陳恒100</value> <value>陳恒101</value> <value>陳恒102</value> </set> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="4"> <array> <value>aaaaa</value> <value>bbbbb</value> </array> </constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 使用setter方法注入方式裝配ComplexUser實例user2 --> <bean id="user2" class="assemble.ComplexUser" > <property name="uname" value="chenheng2"></property> <property name="hobbyList"> <list> <value>看書</value> <value>學習Spring</value> </list> </property> <property name="residenceMap"> <map> <entry key="shenzhen" value="深圳"></entry> <entry key="guangzhou" value="廣州"></entry> <entry key="tianjin" value="天津"></entry> </map> </property> <property name="aliasSet"> <set> <value>陳恒103</value> <value>陳恒104</value> <value>陳恒105</value> </set> </property> <property name="array"> <array> <value>ccccc</value> <value>ddddd</value> </array> </property> </bean>
package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import assemble.ComplexUser;
public class TestAssemble {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext appCon=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ComplexUser u1=(ComplexUser) appCon.getBean("user1");
//構造方法裝配測試
System.out.println(u1);
//setter方法裝配測試
ComplexUser u2=(ComplexUser) appCon.getBean("user2");
System.out.println(u2);
appCon.close();
}
}
基于注解的裝配
1.@Component
該注解是一個泛化的概念,僅僅表示一個組件對象(Bean),可以作用在任何層次上。
(1)創建Bean的實現類
package annotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component()
/**相當于@Component("annotationUser")或@Component(value = "annotationUser"),annotationUser為Bean的id,默認為首字母小寫的類名**/
public class AnnotationUser {
@Value("chenheng")//只注入了簡單的值,復雜值的注入目前使用該方式還解決不了
private String uname;
public String getUname() {
return uname;
}
public void setUname(String uname) {
this.uname = uname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "uname="+uname;
}
}
(2)配置注解
現在有了Bean的實現類,但還不能進行測試,因為Spring容器并不知道去哪里掃描Bean對象。需要在配置文件中配置注解,注解配置方式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 使用context命名空間,通過Spring掃描指定包下所有Bean的實現類,進行注解解析 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="annotation" />
</beans>
(3)測試Bean實例
package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import annotation.AnnotationUser;
public class TestAnnoation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext appcon=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("annotationContext.xml");
AnnotationUser au=(AnnotationUser) appcon.getBean("annotationUser");
System.out.println(au.getUname());
}
}
2.@Repository
該注解用于將數據訪問層(DAO)的類標識為Bean,即注解數據訪問層Bean,其功能與@Component()相同。
3.@Service
該注解用于標注一個業務邏輯組件類(Service層),其功能與@Component()相同。
4.@Controller
該注解用于標注一個控制器組件類(Spring MVC的Controller),其功能與@Component()相同。
5.@Autowired
該注解可以對類成員變量、方法及構造方法進行標注,完成自動裝配的工作。 通過 @Autowired的使用來消除setter 和getter方法。默認按照Bean的類型進行裝配。
6.@Resource
該注解與@Autowired功能一樣。區別在于,該注解默認是按照名稱來裝配注入的,只有當找不到與名稱匹配的Bean才會按照類型來裝配注入;而@Autowired默認按照Bean的類型進行裝配,如果想按照名稱來裝配注入,則需要結合@Qualifier注解一起使用。
@Resource注解有兩個屬性:name和type。name屬性指定Bean實例名稱,即按照名稱來裝配注入;type屬性指定Bean類型,即按照Bean的類型進行裝配。
7.@Qualifier
該注解與@Autowired注解配合使用。當@Autowired注解需要按照名稱來裝配注入,則需要結合該注解一起使用,Bean的實例名稱由@Qualifier注解的參數指定。
上面幾個注解中,雖然@Repository、@Service和 @Controller等注解的功能與@Component()相同,但為了使標注類的用途更加清晰(層次化),在實際開發中推薦使用@Repository標注數據訪問層(DAO層)、使用@Service標注業務邏輯層(Service層)以及使用@Controller標注控制器層(控制層)。

package annotation.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("testDao")
/**相當于@Repository,但如果在service層使用@Resource(name="testDao")的話,testDdao不能省略**/
public class TestDaoImpl implements TestDao {
@Override
public void save() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("testDao save");
}
}
package annotation.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import annotation.dao.TestDao;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
@Service("testService")
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Autowired
/**相當于@Autowired.@Autowired默認按照Bean類型裝配**/
private TestDao testDao;
@Override
public void save() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
testDao.save();
System.out.println("testService save");
}
}
package annotation.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import annotation.service.TestService;
@Controller("testController")
public class TestControllerImpl {
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
public void save() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
testService.save();
System.out.println("testController save");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 使用context命名空間,通過Spring掃描指定包下所有Bean的實現類,進行注解解析 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="annotation" />
</beans>
package test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import annotation.controller.TestControllerImpl;
public class TestMoreAnnotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext appcon=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("annotationContext.xml");
TestControllerImpl testc=(TestControllerImpl) appcon.getBean("testController");
testc.save();
}
}
總結
本篇文章就到這里了,希望能夠給你帶來幫助,也希望您能夠多多關注服務器之家的更多內容!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34266854/article/details/121002293