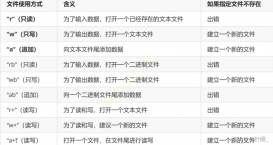
1.基本函數實現
a.代碼1(向下調整)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
void AdjustDown(DateType*a, int n, int parent){ int child = parent * 2 + 1; while (child<n) { if ((child+1) < n && a[child] > a[child + 1]) { ++child; } if (a[parent] > a[child]) { Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } }} |
注意:if里面的條件語句(child +1)<n是防止越界的,因為不能保證有右孩子。
b.代碼2(向上調整)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
void AdjustUp(DateType*a , int child){ int parent = (child - 1) / 2; while (child > 0) { if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); child = parent; parent = (child - 1) / 2; } else { break; } }} |
注意:while里面的條件語句是不能夠寫成(parent<0),因為當child==0時,parent=(child - 1) / 2,parent==0,再次進入循環不滿足a[child] < a[parent],恰好跳出循環。如果寫成(a[child] <= a[parent])就死循環了
c.代碼3(交換)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
void Swap(DateType*p1, DateType*p2){ DateType tmp = *p1; *p1 = *p2; *p2 = tmp;} |
2.建堆
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
void CreatHeap(Heap*p,DateType*num,int n){ assert(p); p->a = (DateType*)malloc(n * sizeof(DateType)); if (p->a == NULL) { printf("malloc failed\n"); exit(-1); } memcpy(p->a, num, n * sizeof(DateType)); p->size = n; p->capacity = n; //建小堆 for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDown(p->a, p->size, i); }} |
3.插入數據
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
void HeapPush(Heap*p, DateType x){ assert(p); if (p->size == p->capacity) { DateType*tmp = (DateType*)realloc(p->a, (p->capacity) * 2 * sizeof(DateType)); if (tmp == NULL) { printf("realloc failed\n "); exit(-1); } } (p->capacity) *= 2; p->a[p->size] = x; ++(p->size); //向上調整 AdjustUp(p->a, p->size-1);} |
4. 刪除數據
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
void HeapPop(Heap*p, DateType x){ assert(p); Swap(&p->a[0], &p->a[p->size-1]); --(p->size); AdjustDown(p->a, p->size, 0); //左右子樹還是小堆,直接調整行了} |
把堆頂的數據與最后一個數據交換,再次調整size-1個數據。
5.獲取堆頂的數據
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
DateType HeapTop(Heap*p){ assert(p); return p->a[0];} |
6.堆的數據個數
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
int HeapSize(Heap*p){ assert(p); return p->size;} |
7.判空
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
bool HeapIsEmpty(Heap*p){ assert(p); return p->size == 0;} |
8.打印
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
void Print(Heap*p){ assert(p); for (int i = 0; i < p->size; i++) { printf("%d ", (p->a)[i]); } printf("\n"); int count = 0;//計數 int levelsize = 1; for (int i = 0; i < p->size; i++) { printf("%d ", p->a[i]); ++count; if (count == levelsize) { printf("\n"); levelsize *= 2; count = 0;//重新計數 } } printf("\n");} |
9.銷毀
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
void HeapDestory(Heap*p){ assert(p); free(p->a); p->a = NULL; p->capacity = p->size = 0;} |
10.測試
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
int main(){ int num[] = { 12,15,17,23,10,25 }; int n = sizeof(num) / sizeof(num[0]); Heap a; //創建小堆 CreatHeap(&a,num, n); Print(&a); printf("\n"); //插入數據 HeapPush(&a, 1); Print(&a); //刪除對頂的數據 HeapPop(&a); Print(&a); printf("\n"); //獲取堆頂數據 int ret=HeapTop(&a); printf("The top date is %d\n",ret); //堆的數據個數 int number=HeapSize(&a); printf("The number of heap is %d\n", number); //銷毀 HeapDestory(&a); return 0;} |
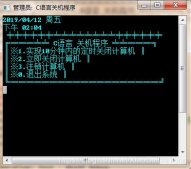
11.測試結果

12.用堆排序(降序)
a.代碼1
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
int main(){ DateType num[] = { 12,15,17,23,10,25 }; int n = sizeof(num) / sizeof(num[0]); HeapSort(num, n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d ", num[i]); } printf("\n\n"); return 0;} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
void HeapSort(int*num, int n){ //建小堆 for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDown(num, n, i); } int end = n - 1; while (end>0) { Swap(&num[0], &num[end]); AdjustDown(num, end, 0); --end; }} |
運行結果

堆的基本操作今天就分享在到這里了,謝謝你的瀏覽,如果對你有幫助的話請大家以后多多支持服務器之家!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_59799963/article/details/121444793