摘要:
最近在做任務管理,任務可以無限派生子任務且沒有數量限制,前端采用easyui的treegrid樹形展示控件。
一、遇到的問題
獲取全部任務拼接樹形速度過慢(數據量大約在900條左右)且查詢速度也并不快;
二、解決方法
1、tree轉化的json數據格式
a.json數據格式:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
[ { "children":[ { "children":[ ], "username":"username2", "password":"password2", "id":"2", "pid":"1", "name":"節點2" }, { "children":[ ], "username":"username2", "password":"password2", "id":"a2", "pid":"1", "name":"節點2" } ], "username":"username1", "password":"password1", "id":"1", "pid":"0", "name":"節點1" }, { "children":[ ], "username":"username1", "password":"password1", "id":"a1", "pid":"0", "name":"節點1" }] |
b.定義實體必要字段
為了tree結構的通用性,我們可以定義一個抽象的公用實體treeobject以保證后續涉及到的list<t>轉化樹形json
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
using system;using system.collections.generic;using system.linq;using system.text;using system.threading.tasks;namespace mytree.abs{ public abstract class treeobejct { public string id { set; get; } public string pid { set; get; } public string name { set; get; } public ilist<treeobejct> children = new list<treeobejct>(); public virtual void addchildren(treeobejct node) { this.children.add(node); } }} |
c.實際所需實體treemodel讓它繼承treeobject,這樣對于id,pid,name,children我們就可以適用于其它實體了,這也相當于我們代碼的特殊約定:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
using mytree.abs;using system;using system.collections.generic;using system.linq;using system.text;using system.threading.tasks;namespace mytree.models{ public class treemodel : treeobejct { public string username { set; get; } public string password { set; get; } }} |
2、遞歸遍歷
獲取全部任務并轉化為樹形
獲取全部任務轉化為樹形是比較簡單的,我們首先獲取到pid=0的頂級數據(即不存在父級的任務),我們通過頂級任務依次遞歸遍歷它們的子節點。
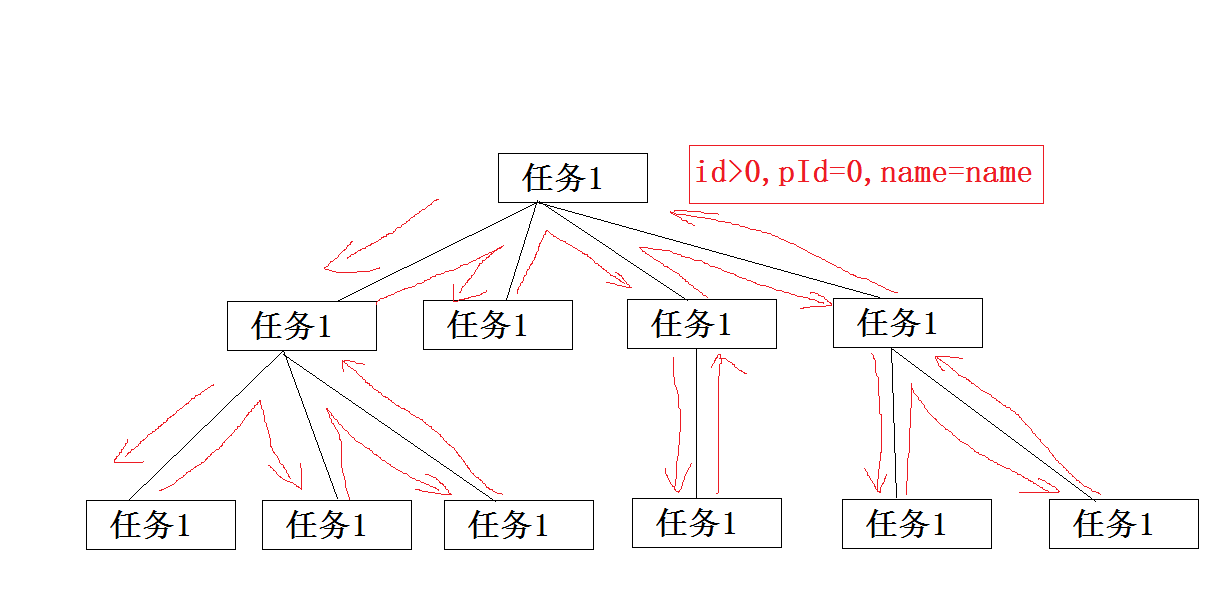
b.我們暫時id以1開始則pid=0的都為頂級任務
我們首先寫一段生成數據的方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public static ilist<treeobejct> getdata(int number = 11){ ilist<treeobejct> datas = new list<treeobejct>(); for (int i = 1; i < number; i++) { datas.add(new treemodel { id = i.tostring(), pid = (i - 1).tostring(), name = "節點" + i, username = "username" + i, password = "password" + i }); datas.add(new treemodel { id = "a" + i.tostring(), pid = (i - 1).tostring(), name = "節點" + i, username = "username" + i, password = "password" + i }); } return datas;} |
其次我們定義一些變量:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
private static ilist<treeobejct> models;private static ilist<treeobejct> models2;private static thread t1;private static thread t2;static void main(string[] args){ int count = 21; console.writeline("生成任務數:"+count+"個"); console.read();} |
我們再寫一個遞歸獲取子節點的遞歸方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public static ilist<treeobejct> getchildrens(treeobejct node){ ilist<treeobejct> childrens = models.where(c => c.pid == node.id.tostring()).tolist(); foreach (var item in childrens) { item.children = getchildrens(item); } return childrens;} |
編寫調用遞歸方法recursion:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public static void recursion(){ #region 遞歸遍歷 system.diagnostics.stopwatch sw = new system.diagnostics.stopwatch(); sw.start(); var mds_0 = models.where(c => c.pid == "0");//獲取頂級任務 foreach (var item in mds_0) { item.children = getchildrens(item); } sw.stop(); console.writeline("----------遞歸遍歷用時:" + sw.elapsedmilliseconds + "----------線程名稱:"+t1.name+",線程id:"+t1.managedthreadid); #endregion} |
編寫main函數啟動測試:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
private static ilist<treeobejct> models;private static ilist<treeobejct> models2;private static thread t1;private static thread t2;static void main(string[] args){ int count = 1001; console.writeline("生成任務數:"+count+"個"); models = getdata(count); t1 = new thread(recursion); t1.name = "遞歸遍歷"; t1.start(); console.read();} |
輸出結果:
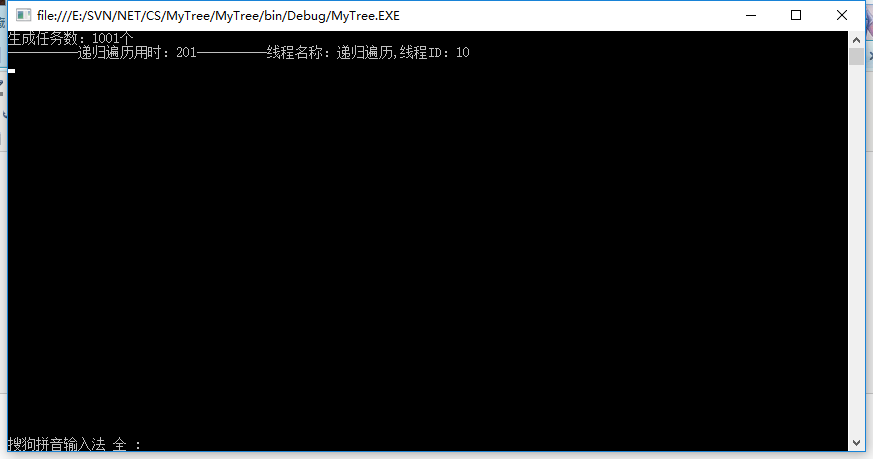
遞歸遍歷至此結束。
3、非遞歸遍歷
非遞歸遍歷在操作中不需要遞歸方法的參與即可實現tree的拼接
對于以上的代碼,我們不需要修改,只需要定義一個非遞歸遍歷方法notrecursion:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public static void notrecursion(){ #region 非遞歸遍歷 system.diagnostics.stopwatch sw2 = new system.diagnostics.stopwatch(); sw2.start(); dictionary<string, treeobejct> dtomap = new dictionary<string, treeobejct>(); foreach (var item in models) { dtomap.add(item.id, item); } ilist<treeobejct> result = new list<treeobejct>(); foreach (var item in dtomap.values) { if (item.pid == "0") { result.add(item); } else { if (dtomap.containskey(item.pid)) { dtomap[item.pid].addchilrden(item); } } } sw2.stop(); console.writeline("----------非遞歸遍歷用時:" + sw2.elapsedmilliseconds + "----------線程名稱:" + t2.name + ",線程id:" + t2.managedthreadid); #endregion} |
編寫main函數:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
private static ilist<treeobejct> models;private static ilist<treeobejct> models2;private static thread t1;private static thread t2;static void main(string[] args){ int count = 6; console.writeline("生成任務數:"+count+"個"); models = getdata(count); models2 = getdata(count); t1 = new thread(recursion); t2 = new thread(notrecursion); t1.name = "遞歸遍歷"; t2.name = "非遞歸遍歷"; t1.start(); t2.start(); console.read();} |
啟動查看執行結果:

發現一個問題,遞歸3s,非遞歸0s,隨后我又進行了更多的測試:
執行時間測試
| 任務個數 | 遞歸(ms) | 非遞歸(ms) |
| 6 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 |
| 101 | 1 | 0 |
| 101 | 4 | 0 |
| 101 | 5 | 0 |
| 1001 | 196 | 5 |
| 1001 | 413 | 1 |
| 1001 | 233 | 7 |
| 5001 | 4667 | 5 |
| 5001 | 4645 | 28 |
| 5001 | 5055 | 7 |
| 10001 | stackoverflowexception | 66 |
| 10001 | stackoverflowexception | 81 |
| 10001 | stackoverflowexception | 69 |
| 50001 | - | 46 |
| 50001 | - | 47 |
| 50001 | - | 42 |
| 100001 | - | 160 |
| 100001 | - | 133 |
| 100001 | - | 129 |
stackoverflowexception:因包含的嵌套方法調用過多而導致執行堆棧溢出時引發的異常。 此類不能被繼承。
stackoverflowexception 執行堆棧溢出發生錯誤時引發,通常發生非常深度或無限遞歸。
-:沒有等到結果。
當然這個測試并不專業,但是也展示出了它的效率的確滿足了當前的需求。
4、查找構建樹形結果
原理同上述非遞歸相同,不同之處是我們通過查找的數據去構建樹形

我們通過查找獲取到圈中的任務,再通過當前節點獲取到父級節點,因為當時沒考慮到任務層級的關系,因此為添加層級編號,為此可能會有重復的存在,因此我們使用hashset<t>來剔除我們的重復數據,最終獲取到有用數據再通過非遞歸遍歷方法,我們便可以再次構建出樹形(tree),來轉化為json數據。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/umeall/p/7660351.html?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral