策略模式:定義了算法族,分別封裝起來,讓它們之間可以互相替換,此模式讓算法的變化獨立于使用算法的客戶。
傳統的策略模式一般是創建公共接口、定義公共方法――》然后創建實體類實現公共接口、根據各自的邏輯重寫公共方法――》創建一個行為隨著策略對象改變而改變的 context 對象――》根據不同的傳參,調用不同的接口實現類方法,達到只改變參數即可獲得不同結果的目的。

但是也可以明顯發現,這種策略模式的實現方式,代碼量較大,而且還要自定義要傳遞的參數,可能會引入一定數量的if/else,有一定的優化空間,接下來,我會結合實際開發經驗,分享一種策略模式的優化方式,進一步優化代碼結構、減少代碼量。
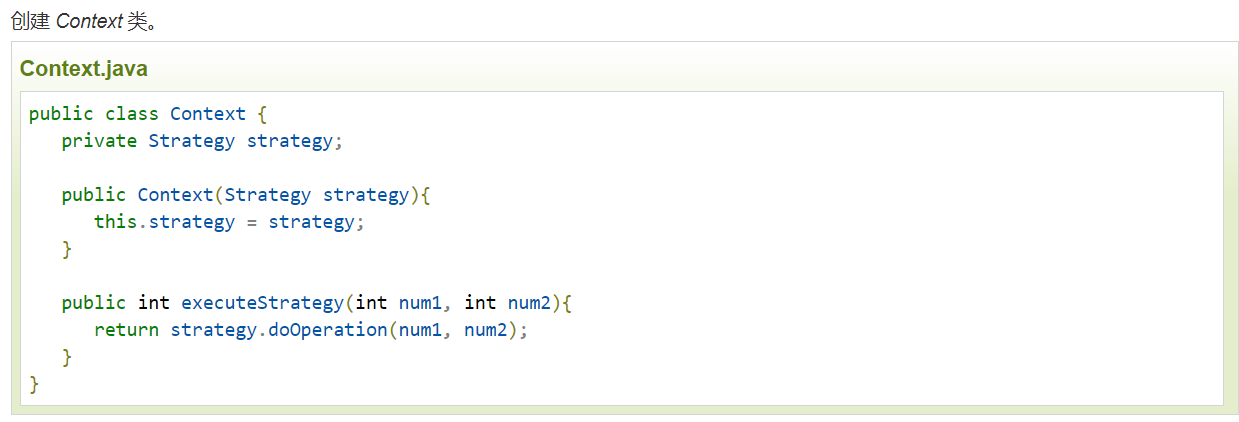
首先,必不可少的需要創建公共接口、定義公共方法,然后創建實體類實現公共接口、根據各自的邏輯重寫公共方法,參考代碼如下:
定義公共接口CommonService,以及公共方法push()
package com.itcq.service.StrategyPattern;
public interface CommonService {
String push(String key);
}
創建三個不同的接口實現類,重寫push()方法
package com.itcq.service.StrategyPattern;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TestOne implements CommonService {
@Override
public String push(String key) {
return "1.這是模式:" + key;
}
}
package com.itcq.service.StrategyPattern;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TestTwo implements CommonService{
@Override
public String push(String key) {
return "2.這是模式:"+key;
}
}
package com.itcq.service.StrategyPattern;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TestThree implements CommonService{
@Override
public String push(String key) {
return "3.這是模式:"+key;
}
}
接下來就是重點,我們利用到springboot初始化Bean的方式結合HashMap,來實現對策略模式的優化
@Service
public class TestServiceTwo implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private HashMap<String, CommonService> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
hashmap.put(StrategyTestEnum.STRATEGY_ONE.getTitle(), new TestOne());
hashmap.put(StrategyTestEnum.STRATEGY_TWO.getTitle(), this.applicationContext.getBean(TestTwo.class));
hashmap.put(StrategyTestEnum.STRATEGY_THREE.getTitle(), this.applicationContext.getBean(TestThree.class));
}
}
@Getter
public enum StrategyTestEnum {
STRATEGY_ONE("一", "模式一"),
STRATEGY_TWO("二", "模式二"),
STRATEGY_THREE("三", "模式三"),
;
private String title;
private String value;
StrategyTestEnum(String title, String value) {
this.title = title;
this.value = value;
}
}
TestServiceTwo實現InitializingBean接口,InitializingBean接口為bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是繼承該接口的類,在初始化bean的時候都會執行該方法。
定義一個hashmap集合,用來保存不同的公共接口實現類對象,這里把參數抽取成一個枚舉類,利用SpringBoot的高級容器ApplicationContext,獲取Bean對象,當然這里直接new一個實現類對象也是可以的,將不同的參數和實現對象封裝到map集合中,實現參數和邏輯一一對應。
測試方法如下,通過hashmap的key獲取對應的實現類對象,這樣就不必再自定義參數類型,徹底消除了if/else,也不用暴露給方法調用者過多的業務邏輯。
public String testMethod2(String key) {
CommonService commonService = hashmap.get(key);
Assert.notNull(commonService, "參數錯誤,找不到模式");
return commonService.push(key);
}
最后在controller層調用方法,進行測試:
@Autowired
private TestServiceTwo testServiceTwo;
@GetMapping("/test/two")
public String testMethodTwo(@RequestParam(name = "key") String key) {
return testServiceTwo.testMethod2(key);
}
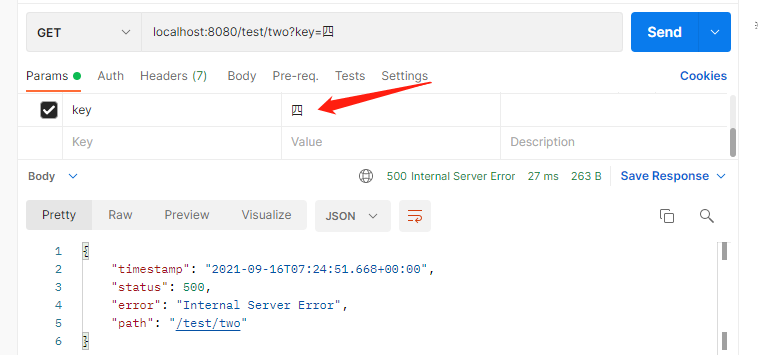
測試結果如下:
參數正確情況下:
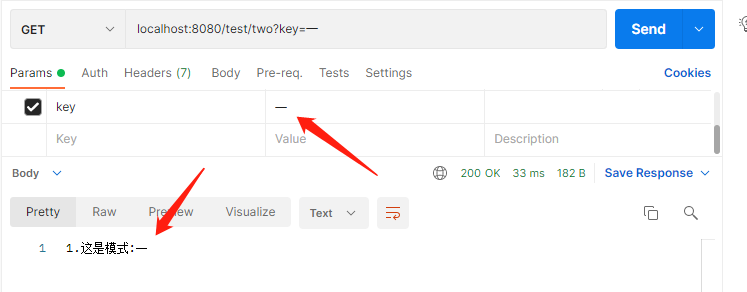
參數錯誤情況下:

利用這種自定義初始化bean+hashmap的方式完成了對策略模式的優化,優化了代碼的結構,并且徹底消除了if/else,個人認為可以很好地提升代碼質量。
代碼改變世界
到此這篇關于實踐講解SpringBoot自定義初始化Bean+HashMap優化策略模式的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關SpringBoot Bean HashMap優化策略內容請搜索服務器之家以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持服務器之家!
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/itcq/p/15293737.html