網(wǎng)上C#導(dǎo)出Excel的方法有很多。但用來用去感覺不夠自動化。于是花了點(diǎn)時(shí)間,利用特性做了個(gè)比較通用的導(dǎo)出方法。只需要根據(jù)實(shí)體類,自動導(dǎo)出想要的數(shù)據(jù)
1.在NuGet上安裝Aspose.Cells或者用微軟自帶類庫也可以
2.需要導(dǎo)出的數(shù)據(jù)的實(shí)例類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
using System.ComponentModel;using System.Reflection;using System.Runtime.Serialization;public class OrderReport{[DisplayName("訂單編號")]public string orderNo { get; set; }[IgnoreDataMember]public DateTime orderTime { get; set; }[DisplayName("訂單時(shí)間")]public String orderTime_fomart { get { return orderTime.ToShortDateString(); } }[DisplayName("商品編碼")]public string itemCode { get; set; }[DisplayName("商品名稱")]public string itemName { get; set; }} |
定義實(shí)體中加上 [DisplayName("訂單編號")]用來導(dǎo)出到Excel生成列名。不需在導(dǎo)出一一對應(yīng)寫列名。[IgnoreDataMember]屬性是用來導(dǎo)出是忽略掉不用導(dǎo)出 。
關(guān)于特性的介紹詳細(xì)請參考MSDN。
3.實(shí)現(xiàn)導(dǎo)出方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
|
/// <summary>/// 導(dǎo)出類/// </summary>public class ExportHandle{/// <summary>/// 掛起訂單報(bào)表導(dǎo)出/// </summary>public static void execExportOrderReport(){var orderReportList = new List<OrderReport>(){new OrderReport() { orderNo= "XD00001",orderTime=DateTime.Now, itemCode="G001" ,itemName="辣條"} ,new OrderReport() { orderNo= "XD00002", orderTime=DateTime.Now,itemCode="G002" ,itemName="茶蛋"} ,new OrderReport() { orderNo= "XD00003", orderTime=DateTime.Now,itemCode="G003" ,itemName="切糕"} ,new OrderReport() { orderNo= "XD00004", orderTime=DateTime.Now,itemCode="G004" ,itemName="大蝦"} ,new OrderReport() { orderNo= "XD00005", orderTime=DateTime.Now,itemCode="G005" ,itemName="帝王蟹"}};string path = "OrderReport.xlsx";Console.WriteLine("開始執(zhí)行導(dǎo)出");OutDataToExcel(orderReportList, "訂單報(bào)表", path);Console.WriteLine("導(dǎo)出完成:位置"+path);}/// <summary>/// 導(dǎo)出方法/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>/// <param name="list">導(dǎo)出的數(shù)據(jù)list</param>/// <param name="title">數(shù)據(jù)類容標(biāo)題</param>/// <param name="path">導(dǎo)出excel存放路徑</param>public static void OutDataToExcel<T>(List<T> list, string title, string path){Workbook workbook = new Workbook(); //工作簿 Worksheet sheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; //工作表 sheet.IsGridlinesVisible = false;//去掉初始單元線Cells cells = sheet.Cells;//單元格 //為標(biāo)題設(shè)置樣式 Style styleTitle = workbook.CreateStyle();//新增樣式 styleTitle.HorizontalAlignment = TextAlignmentType.Center;//文字居中 styleTitle.Font.Name = "微軟雅黑";//文字字體 styleTitle.Font.Size = 18;//文字大小 styleTitle.Font.IsBold = true;//粗體 //樣式1 標(biāo)題下方的日期Style style1 = workbook.CreateStyle();//新增樣式 style1.HorizontalAlignment = TextAlignmentType.Center;//文字居中 style1.Font.Name = "微軟雅黑";//文字字體 style1.Font.Size = 12;//文字大小 //樣式2 列名Style style2 = workbook.CreateStyle();//新增樣式 style2.HorizontalAlignment = TextAlignmentType.Center;//文字居中 style2.Font.Name = "微軟雅黑";//文字字體 style2.Font.Size = 12;//文字大小 style2.Font.IsBold = true;//粗體 style2.Borders[BorderType.LeftBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;style2.Borders[BorderType.RightBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;style2.Borders[BorderType.TopBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;style2.Borders[BorderType.BottomBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;//樣式3 數(shù)據(jù)的樣式Style style3 = workbook.CreateStyle();//新增樣式 style3.HorizontalAlignment = TextAlignmentType.Center;//文字居中 style3.Font.Name = "微軟雅黑";//文字字體 style3.Font.Size = 10;//文字大小 style3.Borders[BorderType.LeftBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;style3.Borders[BorderType.RightBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;style3.Borders[BorderType.TopBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;style3.Borders[BorderType.BottomBorder].LineStyle = CellBorderType.Thin;if (list.Count == 0) return;var t = list.First().GetType();//獲取列表的類的屬性//通過反射篩選忽略掉[IgnoreDataMemberAttribute]的字段var properties = t.GetProperties().Where(x => x.GetCustomAttribute<IgnoreDataMemberAttribute>() == null);int Colnum = properties.Count();//表格列數(shù) int Rownum = list.Count;//表格行數(shù) //生成行1 標(biāo)題行 cells.Merge(0, 0, 1, Colnum);//合并單元格 cells[0, 0].PutValue(title);//填寫內(nèi)容 cells[0, 0].SetStyle(styleTitle);cells.SetRowHeight(0, 38);//行高//生成行2 日期 cells.Merge(1, 0, 1, Colnum);//合并單元格 cells[1, 0].PutValue(DateTime.Now.ToShortDateString());//填寫內(nèi)容 cells[1, 0].SetStyle(style1);cells.SetRowHeight(1, 20);//行高//列名及數(shù)據(jù)行int i = 0;foreach (var item in properties){var itemType = t.GetProperty(item.Name);var colName = itemType.GetCustomAttribute<DisplayNameAttribute>().DisplayName;//反射獲取字段的DisplayName特性值cells[2, i].PutValue(colName);cells[2, i].SetStyle(style2);cells.SetColumnWidth(i, colName.Length * 3);//設(shè)置列寬int k = 0;foreach (var rowdata in list){//反射遍歷添加數(shù)據(jù)object value = rowdata.GetType().GetProperty(item.Name).GetValue(rowdata, null);string ss = value == null ? "" : value.ToString();cells[3 + k, i].PutValue(ss);cells[3 + k, i].SetStyle(style3);cells.SetRowHeight(3 + k, 18);//設(shè)置行高k++;}i++;}workbook.Save(path);//生成Excel}} |
導(dǎo)出方法 OutDataToExcel<T>(List<T> list, Enum en, string path)用了泛型參數(shù),將任意的實(shí)體list自動導(dǎo)出。
|
1
|
var properties = t.GetProperties().Where(x => AttributeAccessor.GetAttribute<IgnoreDataMemberAttribute>(x) == null); |
采用lamda表達(dá)式在傳過來的實(shí)體屬性中篩選出
不是IgnoreDataMemberAttribute的屬性字段
|
1
2
3
4
|
foreach (var item in properties){}遍歷實(shí)體類的屬性相當(dāng)于DataTable循環(huán)讀取數(shù)據(jù) object value = rowdata.GetType().GetProperty(item.Name).GetValue(rowdata, null); 通過屬性名稱獲取屬性值。通過以上兩個(gè)步驟,實(shí)現(xiàn)自動} |
4.導(dǎo)出結(jié)果:
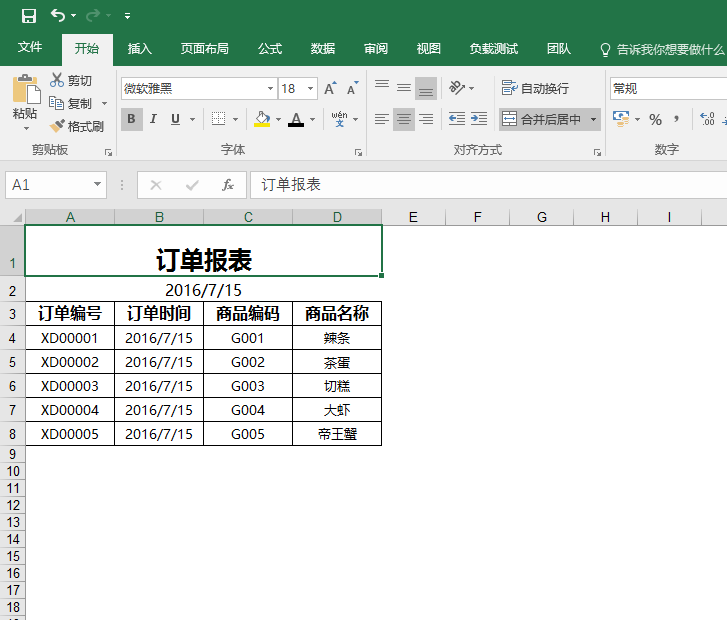
總結(jié),通過特性來實(shí)現(xiàn)通用的導(dǎo)出。只需要設(shè)置相關(guān)的類的字段和特性值即可自定義導(dǎo)出
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的C#開發(fā)教程之利用特性自定義數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)出到Excel,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時(shí)回復(fù)大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對服務(wù)器之家網(wǎng)站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/castyuan/p/5674363.html