前言
前一篇我們講解了View的Measure過程,那今天我們來講解下Layout;
View的layout方法作用是確定View的位置,ViewGroup的layout方法不僅要確定自身的位置,還有確定子View的位置;
Android進(jìn)階之深入理解View的測量(Measure)流程機(jī)制
一、Layout流程源碼詳解
1、performLayout
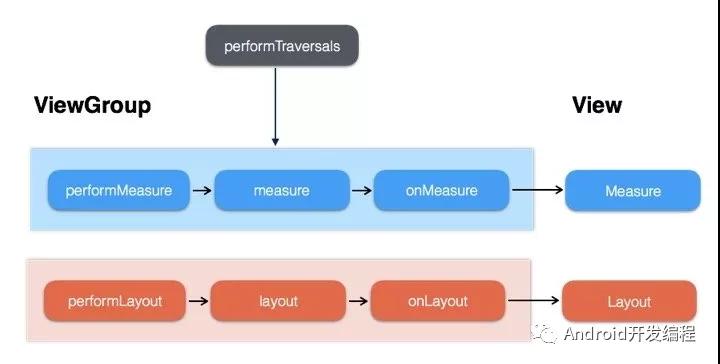
View三大工作流程是從ViewRootImpl#performTraversals開始的,其中performMeasure、performLayout、performDraw方法分別對應(yīng)了View的測量、布局、繪制;
從performLayout開始分析View布局流程;
- privatevoidperformLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParamslp,intdesiredWindowWidth,
- intdesiredWindowHeight){
- mLayoutRequested=false;
- mScrollMayChange=true;
- mInLayout=true;
- finalViewhost=mView;
- Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW,"layout");
- try{
- host.layout(0,0,host.getMeasuredWidth(),host.getMeasuredHeight());
- //省略...
- }finally{
- Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
- }
- mInLayout=false;
- }
方法中的mView其實就是DecorView,那么host也就代表了DecorView,DecorView其實是個FrameLayout,ViewGroup并沒有重寫layout方法,所以我們來看下View#layout方法
2、layout
- /**
- *源碼分析起始點:layout()
- *作用:確定View本身的位置,即設(shè)置View本身的四個頂點位置
- */
- publicvoidlayout(intl,intt,intr,intb){
- //當(dāng)前視圖的四個頂點
- intoldL=mLeft;
- intoldT=mTop;
- intoldB=mBottom;
- intoldR=mRight;
- //1.確定View的位置:setFrame()/setOpticalFrame()
- //即初始化四個頂點的值、判斷當(dāng)前View大小和位置是否發(fā)生了變化&返回
- //setFrame()->分析1
- //setOpticalFrame()->分析2
- booleanchanged=isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)?setOpticalFrame(l,t,r,b):setFrame(l,t,r,b);
- //2.若視圖的大小&位置發(fā)生變化
- //會重新確定該View所有的子View在父容器的位置:onLayout()
- if(changed||(mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED)==PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED){
- onLayout(changed,l,t,r,b);
- //對于單一View的laytou過程:由于單一View是沒有子View的,故onLayout()是一個空實現(xiàn)->分析3
- //對于ViewGroup的laytou過程:由于確定位置與具體布局有關(guān),所以onLayout()在ViewGroup為1個抽象方法,需自定義重寫實現(xiàn)(下面的章節(jié)會詳細(xì)說明)
- }
- /**
- *分析1:setFrame()
- *作用:根據(jù)傳入的4個位置值,設(shè)置View本身的四個頂點位置
- *即:最終確定View本身的位置
- */
- protectedbooleansetFrame(intleft,inttop,intright,intbottom){
- //通過以下賦值語句記錄下了視圖的位置信息,即確定View的四個頂點
- //從而確定了視圖的位置
- mLeft=left;
- mTop=top;
- mRight=right;
- mBottom=bottom;
- mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft,mTop,mRight,mBottom);
- }
- /**
- *分析2:setOpticalFrame()
- *作用:根據(jù)傳入的4個位置值,設(shè)置View本身的四個頂點位置
- *即:最終確定View本身的位置
- */
- privatebooleansetOpticalFrame(intleft,inttop,intright,intbottom){
- InsetsparentInsets=mParentinstanceofView?
- ((View)mParent).getOpticalInsets():Insets.NONE;
- InsetschildInsets=getOpticalInsets();
- //內(nèi)部實際上是調(diào)用setFrame()
- returnsetFrame(
- left+parentInsets.left-childInsets.left,
- top+parentInsets.top-childInsets.top,
- right+parentInsets.left+childInsets.right,
- bottom+parentInsets.top+childInsets.bottom);
- }
- //回到調(diào)用原處
- /**
- *分析3:onLayout()
- *注:對于單一View的laytou過程
- *1.由于單一View是沒有子View的,故onLayout()是一個空實現(xiàn)
- *2.由于在layout()中已經(jīng)對自身View進(jìn)行了位置計算:setFrame()/setOpticalFrame()
- *3.所以單一View的layout過程在layout()后就已完成了
- */
- protectedvoidonLayout(booleanchanged,intleft,inttop,intright,intbottom){
- //參數(shù)說明
- //changed當(dāng)前View的大小和位置改變了
- //left左部位置
- //top頂部位置
- //right右部位置
- //bottom底部位置
- }
3、setFrame
layout方法是用來確定自身位置的,其內(nèi)部調(diào)用了setOpticalFrame、setFrame和onLayout方法,setOpticalFrame內(nèi)部又會調(diào)用setFrame。所以我們先來看setFrame方法,如下
- protectedbooleansetFrame(intleft,inttop,intright,intbottom){
- booleanchanged=false;
- if(mLeft!=left||mRight!=right||mTop!=top||mBottom!=bottom){
- //判斷View的位置是否發(fā)生改變
- changed=true;
- //Rememberourdrawnbit
- intdrawn=mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_DRAWN;
- intoldWidth=mRight-mLeft;//獲取原來的寬度
- intoldHeight=mBottom-mTop;//獲取原來的高度
- intnewWidth=right-left;//獲取新的寬度
- intnewHeight=bottom-top;//獲取新的高度
- //判斷View的尺寸是否發(fā)生改變
- booleansizeChanged=(newWidth!=oldWidth)||(newHeight!=oldHeight);
- //Invalidateouroldposition
- invalidate(sizeChanged);
- //對mLeft、mTop、mRight、mBottom初始化,View自身的位置也就確定了。
- mLeft=left;
- mTop=top;
- mRight=right;
- mBottom=bottom;
- mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft,mTop,mRight,mBottom);
- mPrivateFlags|=PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS;
- //如果View尺寸發(fā)生改變,將執(zhí)行View#sizeChange方法,在sizeChange方法內(nèi)部會調(diào)用View#onSizeChanged方法。
- if(sizeChanged){
- sizeChange(newWidth,newHeight,oldWidth,oldHeight);
- }
- //省略...
- }
- returnchanged;
- }
在setFrame方法中對mLeft、mTop、mRight 、mBottom進(jìn)行初始化,mLeft、mTop分別對應(yīng)View左上角的橫坐標(biāo)和縱坐標(biāo),mRight 、mBottom分別對應(yīng)了View右下角的橫坐標(biāo)和縱坐標(biāo),View的四個頂點的坐標(biāo)確定了,View自身的位置也就確定了;
4、FrameLayout#onLayout
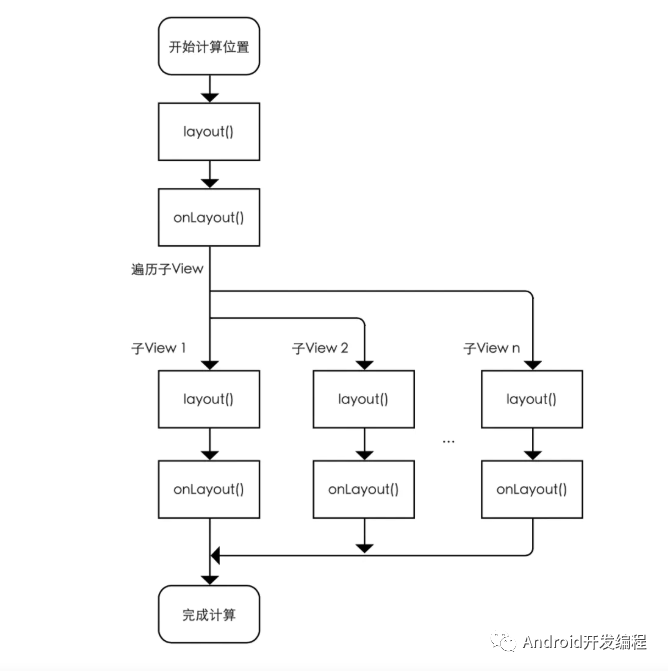
再回到layout方法,在通過setFrame方法確定了自身位置后,接下來會調(diào)用onLayout方法,這個方法其實用來確定子View的位置的;
不過View和ViewGroup都沒有真正實現(xiàn)onLayout,因為onLayout和onMeasure類似,其過程都與具體的布局有關(guān);
以FrameLayout為例來分析onLayout過程,F(xiàn)rameLayout#onLayout
- @Override
- protectedvoidonLayout(booleanchanged,intleft,inttop,intright,intbottom){
- layoutChildren(left,top,right,bottom,false/*noforceleftgravity*/);
- }
- 其內(nèi)部調(diào)用了layoutChildren方法
- voidlayoutChildren(intleft,inttop,intright,intbottom,
- booleanforceLeftGravity){
- finalintcount=getChildCount();//獲取子View的數(shù)量
- //parentLeft、parentTop分別代表子View所占區(qū)域左上角的橫坐標(biāo)和縱坐標(biāo)
- //parentRight、parentBottom分別代表子View所占區(qū)域右下角的橫坐標(biāo)和縱坐標(biāo)
- finalintparentLeft=getPaddingLeftWithForeground();
- finalintparentRight=right-left-getPaddingRightWithForeground();
- finalintparentTop=getPaddingTopWithForeground();
- finalintparentBottom=bottom-top-getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
- mForegroundBoundsChanged=true;
- //遍歷子View
- for(inti=0;i<count;i++){
- finalViewchild=getChildAt(i);
- if(child.getVisibility()!=GONE){
- finalLayoutParamslp=(LayoutParams)child.getLayoutParams();
- //獲取子View的測量寬、高
- finalintwidth=child.getMeasuredWidth();
- finalintheight=child.getMeasuredHeight();
- intchildLeft;
- intchildTop;
- //獲取子View設(shè)置的Gravity,如果子View沒有設(shè)置Gravity,則用默認(rèn)的Gravity:DEFAULT_CHILD_GRAVITY。
- intgravity=lp.gravity;
- if(gravity==-1){
- gravity=DEFAULT_CHILD_GRAVITY;
- }
- finalintlayoutDirection=getLayoutDirection();
- finalintabsoluteGravity=Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity,layoutDirection);
- finalintverticalGravity=gravity&Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
- //水平方向上,通過設(shè)置的Gravity,來確定childLeft,即每個子View左上角的橫坐標(biāo)
- switch(absoluteGravity&Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK){
- caseGravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
- childLeft=parentLeft+(parentRight-parentLeft-width)/2+
- lp.leftMargin-lp.rightMargin;
- break;
- caseGravity.RIGHT:
- if(!forceLeftGravity){
- childLeft=parentRight-width-lp.rightMargin;
- break;
- }
- caseGravity.LEFT:
- default:
- childLeft=parentLeft+lp.leftMargin;
- }
- //豎直方向上,通過設(shè)置的Gravity,來確定childTop,即每個子View左上角的縱坐標(biāo)
- switch(verticalGravity){
- caseGravity.TOP:
- childTop=parentTop+lp.topMargin;
- break;
- caseGravity.CENTER_VERTICAL:
- childTop=parentTop+(parentBottom-parentTop-height)/2+
- lp.topMargin-lp.bottomMargin;
- break;
- caseGravity.BOTTOM:
- childTop=parentBottom-height-lp.bottomMargin;
- break;
- default:
- childTop=parentTop+lp.topMargin;
- }
- //調(diào)用子View的layout方法
- child.layout(childLeft,childTop,childLeft+width,childTop+height);
- }
- }
- }
在該方法內(nèi)部遍歷所有子View過程中,通過子View設(shè)置的Gravity,獲去其childLeft、childTop即子View的左上角的橫坐標(biāo)和縱坐標(biāo),最后執(zhí)行子View的layout方法,來確定子View的位置
5、LinearLayout#onLayout
LinearLayout復(fù)寫的onLayout()分析
- /**
- *源碼分析:LinearLayout復(fù)寫的onLayout()
- *注:復(fù)寫的邏輯和LinearLayoutmeasure過程的onMeasure()類似
- */
- @Override
- protectedvoidonLayout(booleanchanged,intl,intt,intr,intb){
- //根據(jù)自身方向?qū)傩裕x擇不同的處理方式
- if(mOrientation==VERTICAL){
- layoutVertical(l,t,r,b);
- }else{
- layoutHorizontal(l,t,r,b);
- }
- }
- //由于垂直/水平方向類似,所以此處僅分析垂直方向(Vertical)的處理過程->分析1
- /**
- *分析1:layoutVertical(l,t,r,b)
- */
- voidlayoutVertical(intleft,inttop,intright,intbottom){
- //子View的數(shù)量
- finalintcount=getVirtualChildCount();
- //1.遍歷子View
- for(inti=0;i<count;i++){
- finalViewchild=getVirtualChildAt(i);
- if(child==null){
- childTop+=measureNullChild(i);
- }elseif(child.getVisibility()!=GONE){
- //2.計算子View的測量寬/高值
- finalintchildWidth=child.getMeasuredWidth();
- finalintchildHeight=child.getMeasuredHeight();
- //3.確定自身子View的位置
- //即:遞歸調(diào)用子View的setChildFrame(),實際上是調(diào)用了子View的layout()->分析2
- setChildFrame(child,childLeft,childTop+getLocationOffset(child),
- childWidth,childHeight);
- //childTop逐漸增大,即后面的子元素會被放置在靠下的位置
- //這符合垂直方向的LinearLayout的特性
- childTop+=childHeight+lp.bottomMargin+getNextLocationOffset(child);
- i+=getChildrenSkipCount(child,i);
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- *分析2:setChildFrame()
- */
- privatevoidsetChildFrame(Viewchild,intleft,inttop,intwidth,intheight){
- child.layout(left,top,left++width,top+height);
- //setChildFrame()僅僅只是調(diào)用了子View的layout()而已
- //在子View的layout()又通過調(diào)用setFrame()確定View的四個頂點
- //即確定了子View的位置
- //如此不斷循環(huán)確定所有子View的位置,最終確定ViewGroup的位置
- }
總結(jié)
View的layout流程核心在于覆寫ViewGroup的onLayout方法,它的流程是拿到子View的寬高,然后實現(xiàn)自己的布局子View的邏輯,它一般結(jié)合onMeasure方法使用。
原文鏈接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/tJwWblrSglqBpY54FbHewQ