介紹
JSR-380 是 J2EE 的一個規范,用于校驗實體屬性,它是 JSR-303 的升級版,在 Spring Boot 中可以基于它優雅實現參數校驗。
<!--more-->
示例
在沒有使用 JSR-380 之前,我們一般都會將參數校驗硬編碼在 controller 類中,示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public Result add(@RequestBody User user){ if(StringUtils.isBlank(user.getName())){ return Result.error("用戶名不能為空"); } // ...} |
而使用 JSR-380 只需要通過添加對應的注解即可實現校驗,示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Datapublic class User{ @NotBlank private String name; private Integer age;} |
|
1
2
3
|
public Result register(@Validated @RequestBody User user){ // ...} |
這樣看起來代碼是不是清爽了很多,只需要在需要校驗的字段上加上對應的校驗注解,然后對需要校驗的地方加上 @Validated 注解,然后框架就會幫我們完成校驗。
通過全局異常自定義錯誤響應
框架校驗失敗之后會拋出異常,需要捕獲這個異常然后來自定義校驗不通過的錯誤響應,這里直接貼代碼,兼容 @RequestBody 、 @ModelAttribute 、 @RequestParam 三種入參的校驗:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
@ControllerAdvicepublic class GlobalExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(value = {MethodArgumentNotValidException.class, BindException.class}) public ResponseEntity<Result> methodArgumentNotValidHandler(HttpServletRequest request, Exception e) { BindingResult bindingResult; if (e instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) { //@RequestBody參數校驗 bindingResult = ((MethodArgumentNotValidException) e).getBindingResult(); } else { //@ModelAttribute參數校驗 bindingResult = ((BindException) e).getBindingResult(); } FieldError fieldError = bindingResult.getFieldError(); return ResponseEntity.ok(Result.fail(Result.CODE_PARAMS_INVALID, "[" + fieldError.getField() + "]" + fieldError.getDefaultMessage())); } //@RequestParam參數校驗 @ExceptionHandler(value = {ConstraintViolationException.class, MissingServletRequestParameterException.class}) public ResponseEntity<Result> constraintViolationHandler(Exception e) { String field; String msg; if (e instanceof ConstraintViolationException) { ConstraintViolation<?> constraintViolation = ((ConstraintViolationException) e).getConstraintViolations().stream().findFirst().get(); List<Path.Node> pathList = StreamSupport.stream(constraintViolation.getPropertyPath().spliterator(), false) .collect(Collectors.toList()); field = pathList.get(pathList.size() - 1).getName(); msg = constraintViolation.getMessage(); } else { // 這個不是JSR標準返回的異常,要自定義提示文本 field = ((MissingServletRequestParameterException) e).getParameterName(); msg = "不能為空"; } return ResponseEntity.ok(Result.fail(Result.CODE_PARAMS_INVALID, "[" + field + "]" + msg)); }} |
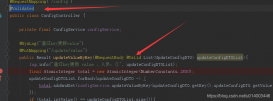
然后再訪問一下接口,可以看到錯誤提示已經按自定義的規范顯示了:
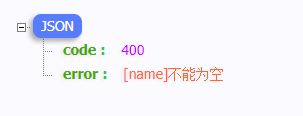
可以看到都不需要寫任何提示文本就可以完成校驗和提示,上圖的 不能為空 是框架內置的 I18N 國際化支持,每個注解都內置相應的提示模板。
常用校驗注解
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @NotNull | 驗證值不為 null |
| @AssertTrue | 驗證值為 true |
| @Size | 驗證值的長度介于 min 和 max 之間,可應用于 String、Collection、Map 和數組類型 |
| @Min | 驗證值不小于該值 |
| @Max | 驗證值不大于該值 |
| 驗證字符串是有效的電子郵件地址 | |
| @NotEmpty | 驗證值不為 null 或空,可應用于 String、Collection、Map 和數組類型 |
| @NotBlank | 驗證字符串不為 null 并且不是空白字符 |
| @Positive | 驗證數字為正數 |
| @PositiveOrZero | 驗證數字為正數(包括 0) |
| @Negative | 驗證數字為負數 |
| @NegativeOrZero | 驗證數字為負數(包括 0) |
| @Past | 驗證日期值是過去 |
| @PastOrPresent | 驗證日期值是過去(包括現在) |
| @Future | 驗證日期值是未來 |
| @FutureOrPresent | 驗證日期值是未來(包括現在) |
本文完整代碼放在 github 。
到此這篇關于Spring Boot使用JSR-380進行校驗的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Spring Boot使用JSR-380校驗內容請搜索服務器之家以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持服務器之家!
原文鏈接:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000039305630