簡要:
EigenFace是基于PCA降維的人臉識別算法,PCA是使整體數(shù)據(jù)降維后的方差最大,沒有考慮降維后類間的變化。 它是將圖像每一個像素當作一維特征,然后用SVM或其它機器學習算法進行訓練。但這樣維數(shù)太多,根本無法計算。我這里用的是ORL人臉數(shù)據(jù)庫,英國劍橋?qū)嶒炇遗臄z的,有40位志愿者的人臉,在不同表情不同光照下每位志愿者拍攝10張,共有400張圖片,大小為112*92,所以如果把每個像素當做特征拿來訓練的話,一張人臉就有10304維特征,這么高維的數(shù)據(jù)根本無法處理。所以需要先對數(shù)據(jù)進行降維,去掉一些冗余的特征。
第一步:將ORL人臉圖片的地址統(tǒng)一放在一個文件里,等會通過對該文件操作,將圖片全部加載進來。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
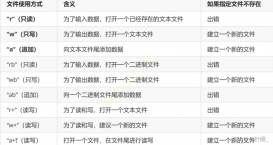
//ofstream一般對文件進行讀寫操作,ifstream一般對文件進行讀操作ofstream file; file.open("path.txt");//新建并打開文件 char str[50] = {}; for (int i = 1; i <= 40; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++) { sprintf_s(str, "orl_faces/s%d/%d.pgm;%d", i, j, i);//將數(shù)字轉(zhuǎn)換成字符 file << str << endl;//寫入 } } |
得到路勁文件如下圖所示:

第二步:讀入模型需要輸入的數(shù)據(jù),即用來訓練的圖像vector<Mat>images和標簽vector<int>labels
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
string filename = string("path.txt"); ifstream file(filename); if (!file) { printf("could not load file"); } vector<Mat>images; vector<int>labels; char separator = ';'; string line,path, classlabel; while (getline(file,line)) { stringstream lines(line); getline(lines, path, separator); getline(lines, classlabel); images.push_back(imread(path, 0)); labels.push_back(atoi(classlabel.c_str()));//atoi(ASCLL to int)將字符串轉(zhuǎn)換為整數(shù)型 } |
第三步:加載、訓練、預測模型
|
1
2
3
4
|
Ptr<BasicFaceRecognizer> model = EigenFaceRecognizer::create(); model->train(images, labels); int predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample); printf("actual label:%d,predict label :%d\n", testLabel, predictedLabel); |
補充:
1、顯示平均臉
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
//計算特征值特征向量及平均值 Mat vals = model->getEigenValues();//89*1 printf("%d,%d\n", vals.rows, vals.cols); Mat vecs = model->getEigenVectors();//10324*89 printf("%d,%d\n", vecs.rows, vecs.cols); Mat mean = model->getMean();//1*10304 printf("%d,%d\n", mean.rows, mean.cols); //顯示平均臉 Mat meanFace = mean.reshape(1, height);//第一個參數(shù)為通道數(shù),第二個參數(shù)為多少行 normalize(meanFace, meanFace, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); imshow("Mean Face", meanFace); |

2、顯示前部分特征臉
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//顯示特征臉 for (int i = 0; i<min(10, vals.rows); i++) { Mat feature_vec = vecs.col(i).clone(); Mat feature_face= feature_vec.reshape(1, height); normalize(feature_face, feature_face, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); Mat colorface; applyColorMap(feature_face, colorface, COLORMAP_BONE); sprintf_s(win_title, "eigenface%d", i); imshow(win_title, colorface); } |

3、對第一張人臉在特征向量空間進行人臉重建(分別基于前10,20,30,40,50,60個特征向量進行人臉重建)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//重建人臉 for (int i = min(10, vals.rows); i <min(61, vals.rows); i+=10) { Mat vecs_space = Mat(vecs, Range::all(), Range(0, i)); Mat projection = LDA::subspaceProject(vecs_space, mean, images[0].reshape(1, 1));//投影到子空間 Mat reconstruction = LDA::subspaceReconstruct(vecs_space, mean, projection);//重建 Mat result = reconstruction.reshape(1, height); normalize(result, result, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); //char wintitle[40] = {}; sprintf_s(win_title, "recon face %d", i); imshow(win_title, result); } |

完整代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
|
#include<opencv2\opencv.hpp>#include<opencv2\face.hpp>using namespace cv;using namespace face;using namespace std;char win_title[40] = {}; int main(int arc, char** argv) { namedWindow("input",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); //讀入模型需要輸入的數(shù)據(jù),用來訓練的圖像vector<Mat>images和標簽vector<int>labels string filename = string("path.txt"); ifstream file(filename); if (!file) { printf("could not load file"); } vector<Mat>images; vector<int>labels; char separator = ';'; string line,path, classlabel; while (getline(file,line)) { stringstream lines(line); getline(lines, path, separator); getline(lines, classlabel); //printf("%d\n", atoi(classlabel.c_str())); images.push_back(imread(path, 0)); labels.push_back(atoi(classlabel.c_str()));//atoi(ASCLL to int)將字符串轉(zhuǎn)換為整數(shù)型 } int height = images[0].rows; int width = images[0].cols; printf("height:%d,width:%d\n", height, width); //將最后一個樣本作為測試樣本 Mat testSample = images[images.size() - 1]; int testLabel = labels[labels.size() - 1]; //刪除列表末尾的元素 images.pop_back(); labels.pop_back(); //加載,訓練,預測 Ptr<BasicFaceRecognizer> model = EigenFaceRecognizer::create(); model->train(images, labels); int predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample); printf("actual label:%d,predict label :%d\n", testLabel, predictedLabel); //計算特征值特征向量及平均值 Mat vals = model->getEigenValues();//89*1 printf("%d,%d\n", vals.rows, vals.cols); Mat vecs = model->getEigenVectors();//10324*89 printf("%d,%d\n", vecs.rows, vecs.cols); Mat mean = model->getMean();//1*10304 printf("%d,%d\n", mean.rows, mean.cols); //顯示平均臉 Mat meanFace = mean.reshape(1, height);//第一個參數(shù)為通道數(shù),第二個參數(shù)為多少行 normalize(meanFace, meanFace, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); imshow("Mean Face", meanFace); //顯示特征臉 for (int i = 0; i<min(10, vals.rows); i++) { Mat feature_vec = vecs.col(i).clone(); Mat feature_face= feature_vec.reshape(1, height); normalize(feature_face, feature_face, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); Mat colorface; applyColorMap(feature_face, colorface, COLORMAP_BONE); sprintf_s(win_title, "eigenface%d", i); imshow(win_title, colorface); } //重建人臉 for (int i = min(10, vals.rows); i <min(61, vals.rows); i+=10) { Mat vecs_space = Mat(vecs, Range::all(), Range(0, i)); Mat projection = LDA::subspaceProject(vecs_space, mean, images[0].reshape(1, 1)); Mat reconstruction = LDA::subspaceReconstruct(vecs_space, mean, projection); Mat result = reconstruction.reshape(1, height); normalize(result, result, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1); //char wintitle[40] = {}; sprintf_s(win_title, "recon face %d", i); imshow(win_title, result); } waitKey(0); return 0;} |
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_24946843/article/details/82876629