在java中我們常常使用加鎖機制來確保線程安全,但是如果過度使用加鎖,則可能導致鎖順序死鎖。同樣,我們使用線程池和信號量來限制對資源的使用,但是這些被限制的行為可能會導致資源死鎖。java應用程序無法從死鎖中恢復過來,因此設計時一定要排序那些可能導致死鎖出現的條件。
1.一個最簡單的死鎖案例
當一個線程永遠地持有一個鎖,并且其他線程都嘗試獲得這個鎖時,那么它們將永遠被阻塞。在線程a持有鎖l并想獲得鎖m的同時,線程b持有鎖m并嘗試獲得鎖l,那么這兩個線程將永遠地等待下去。這種就是最簡答的死鎖形式(或者叫做"抱死")。
2.鎖順序死鎖
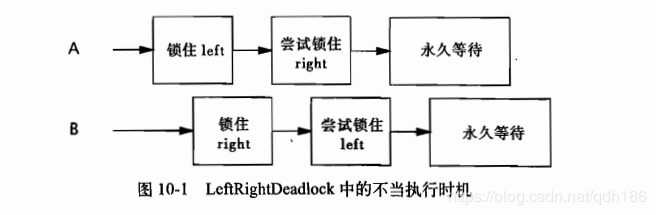
如圖:leftright和rightleft這兩個方法分別獲得left鎖和right鎖。如果一個線程調用了leftright,而另一個線程調用了rightleft,并且這兩個線程的操作是交互執行,那么它們就會發生死鎖。
死鎖的原因就是兩個線程試圖以不同的順序來獲得相同的鎖。所以,如果所有的線程以固定的順序來獲得鎖,那么在程序中就不會出現鎖順序死鎖的問題。
2.1.動態的鎖順序死鎖
我以一個經典的轉賬案例來進行說明,我們知道轉賬就是將資金從一個賬戶轉入另一個賬戶。在開始轉賬之前,首先需要獲得這兩個賬戶對象得鎖,以確保通過原子方式來更新兩個賬戶中的余額,同時又不破壞一些不變形條件,例如 賬戶的余額不能為負數。
所以寫出的代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
//動態的鎖的順序死鎖public class dynamicorderdeadlock { public static void transfermoney(account fromaccount,account toaccount,int amount,int from_index,int to_index) throws exception { system.out.println("賬戶 "+ from_index+"~和賬戶~"+to_index+" ~請求鎖"); synchronized (fromaccount) { system.out.println(" 賬戶 >>>"+from_index+" <<<獲得鎖"); synchronized (toaccount) { system.out.println(" 賬戶 "+from_index+" & "+to_index+"都獲得鎖"); if (fromaccount.compareto(amount) < 0) { throw new exception(); }else { fromaccount.debit(amount); toaccount.credit(amount); } } } } static class account { private int balance = 100000;//這里假設每個人賬戶里面初始化的錢 private final int accno; private static final atomicinteger sequence = new atomicinteger(); public account() { accno = sequence.incrementandget(); } void debit(int m) throws interruptedexception { thread.sleep(5);//模擬操作時間 balance = balance + m; } void credit(int m) throws interruptedexception { thread.sleep(5);//模擬操作時間 balance = balance - m; } int getbalance() { return balance; } int getaccno() { return accno; } public int compareto(int money) { if (balance > money) { return 1; }else if (balance < money) { return -1; }else { return 0; } } }} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public class demonstratedeadlock { private static final int num_threads = 5; private static final int num_accounts = 5; private static final int num_iterations = 100000; public static void main(string[] args) { final random rnd = new random(); final account[] accounts = new account[num_accounts]; for(int i = 0;i < accounts.length;i++) { accounts[i] = new account(); } class transferthread extends thread{ @override public void run() { for(int i = 0;i < num_iterations;i++) { int fromacct = rnd.nextint(num_accounts); int toacct =rnd.nextint(num_accounts); int amount = rnd.nextint(100); try { dynamicorderdeadlock.transfermoney(accounts[fromacct],accounts[toacct], amount,fromacct,toacct); //inducelockorder.transfermoney(accounts[fromacct],accounts[toacct], amount); //inducelockorder2.transfermoney(accounts[fromacct],accounts[toacct], amount); }catch (exception e) { system.out.println("發生異常-------"+e); } } } } for(int i = 0;i < num_threads;i++) { new transferthread().start(); } }} |
打印結果如下:
注意:這里的結果是我把已經執行完的給刪除后,只剩下導致死鎖的請求.

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
//通過鎖順序來避免死鎖public class inducelockorder { private static final object tielock = new object(); public static void transfermoney(final account fromacct, final account toacct, final int amount) throws exception { class helper { public void transfer() throws exception { if (fromacct.compareto(amount) < 0) { throw new exception(); } else { fromacct.debit(amount); toacct.credit(amount); } } } int fromhash = system.identityhashcode(fromacct); int tohash = system.identityhashcode(toacct); if (fromhash < tohash) { synchronized (fromacct) { synchronized (toacct) { new helper().transfer(); } } } else if (fromhash > tohash) { synchronized (toacct) { synchronized (fromacct) { new helper().transfer(); } } } else { synchronized (tielock) { synchronized (fromacct) { synchronized (toacct) { new helper().transfer(); } } } } } static class account { private int balance = 100000; public account() { } void debit(int m) throws interruptedexception { thread.sleep(5); balance = balance + m; } void credit(int m) throws interruptedexception { thread.sleep(5); balance = balance - m; } int getbalance() { return balance; } public int compareto(int money) { if (balance > money) { return 1; }else if (balance < money) { return -1; }else { return 0; } } }} |
經過我測試,此方案可行,不會造成死鎖。
方案二
在account中包含一個唯一的,不可變的,值。比如說賬號等。通過對這個值對對象進行排序。
具體代碼如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
public class inducelockorder2 { public static void transfermoney(final account fromacct, final account toacct, final int amount) throws exception { class helper { public void transfer() throws exception { if (fromacct.compareto(amount) < 0) { throw new exception(); } else { fromacct.debit(amount); toacct.credit(amount); } } } int fromhash = fromacct.getaccno(); int tohash = toacct.getaccno(); if (fromhash < tohash) { synchronized (fromacct) { synchronized (toacct) { new helper().transfer(); } } } else if (fromhash > tohash) { synchronized (toacct) { synchronized (fromacct) { new helper().transfer(); } } } } static class account { private int balance = 100000; private final int accno; private static final atomicinteger sequence = new atomicinteger(); public account() { accno = sequence.incrementandget(); } void debit(int m) throws interruptedexception { thread.sleep(6); balance = balance + m; } void credit(int m) throws interruptedexception { thread.sleep(6); balance = balance - m; } int getbalance() { return balance; } int getaccno() { return accno; } public int compareto(int money) { if (balance > money) { return 1; }else if (balance < money) { return -1; }else { return 0; } } }} |
經過測試此方案也可行。
2.2在協作對象之間發生的死鎖
如果在持有鎖時調用某外部的方法,那么將出現活躍性問題。在這個外部方法中可能會獲取其他的鎖(這個可能產生死鎖),或阻塞時間過長,導致其他線程無法及時獲得當前持有的鎖。
場景如下:taxi代表出租車對象,包含當前位置和目的地。dispatcher代表車隊。當一個線程收到gps更新事件時掉用setlocation,那么它首先更新出租車的位置,然后判斷它是否到達目的地。如果已經到達,它會通知dispatcher:它需要一個新的目的地。因為setlocation和notifyavailable都是同步方法,因此掉用setlocation線程首先獲取taxi的鎖,然后在獲取dispatcher的鎖。同樣,掉用getimage的線程首先獲取dispatcher的鎖,再獲取每一個taxi的鎖,這兩個線程按照不同的順序來獲取鎖,因此可能導致死鎖。
能造成死鎖的代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
|
//會發生死鎖public class cooperatingdeadlock { // 坐標類 class point { private final int x; private final int y; public point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public int getx() { return x; } public int gety() { return y; } } // 出租車類 class taxi { private point location, destination; private final dispatcher dispatcher; public taxi(dispatcher dispatcher) { this.dispatcher = dispatcher; } public synchronized point getlocation() { return location; } public synchronized void setlocation(point location) { this.location = location; if (location.equals(destination)) { dispatcher.notifyavailable(this); } } public synchronized point getdestination() { return destination; } public synchronized void setdestination(point destination) { this.destination = destination; } } class dispatcher { private final set<taxi> taxis; private final set<taxi> availabletaxis; public dispatcher() { taxis = new hashset<>(); availabletaxis = new hashset<>(); } public synchronized void notifyavailable(taxi taxi) { availabletaxis.add(taxi); } public synchronized image getimage() { image image = new image(); for(taxi t:taxis) { image.drawmarker(t.getlocation()); } return image; } } class image{ public void drawmarker(point p) { } }} |
解決方案:使用開放掉用。
如果再調用某個方法時不需要持有鎖,那么這種調用就被稱為開放掉用。這種調用能有效的避免死鎖,并且易于分析線程安全。
修改后的代碼如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
//此方案不會造成死鎖public class cooperatingnodeadlock { // 坐標類 class point { private final int x; private final int y; public point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public int getx() { return x; } public int gety() { return y; } } // 出租車類 class taxi { private point location, destination; private final dispatcher dispatcher; public taxi(dispatcher dispatcher) { this.dispatcher = dispatcher; } public synchronized point getlocation() { return location; } public void setlocation(point location) { boolean reacheddestination; synchronized (this) { this.location = location; reacheddestination = location.equals(destination); } if (reacheddestination) { dispatcher.notifyavailable(this); } } public synchronized point getdestination() { return destination; } public synchronized void setdestination(point destination) { this.destination = destination; } } class dispatcher { private final set<taxi> taxis; private final set<taxi> availabletaxis; public dispatcher() { taxis = new hashset<>(); availabletaxis = new hashset<>(); } public synchronized void notifyavailable(taxi taxi) { availabletaxis.add(taxi); } public image getimage() { set<taxi> copy; synchronized (this) { copy = new hashset<>(taxis); } image image = new image(); for(taxi t:copy) { image.drawmarker(t.getlocation()); } return image; } } class image{ public void drawmarker(point p) { } }} |
總結:活躍性故障是一個非常嚴重的問題,因為當出現活躍性故障時,除了終止應用程序之外沒有其他任何機制可以幫助從這種故障中恢復過來。最常見的活躍性故障就是鎖順序死鎖。在設計時應該避免產生順序死鎖:確保線程在獲取多個鎖時采用一直的順序。最好的解決方案是在程序中始終使用開放掉用。這將大大減小需要同時持有多個鎖的地方,也更容易發現這些地方。
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的java中常見的死鎖以及解決方法詳解整合,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時回復大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對服務器之家網站的支持!
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/qdh186/article/details/86497809