本文實例為大家分享了java使用緩沖流復制文件的具體代碼,供大家參考,具體內容如下
[1] 程序設計
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
/*-------------------------------1.緩沖流是一種處理流,用來加快節點流對文件操作的速度2.bufferedinputstream:輸入緩沖流3.bufferedoutputstream:輸出緩沖流4.在正常的java開發中都使用緩沖流來處理文件,因為這樣可以提高文件處理的效率5.這里設計程序:使用緩沖流復制一個較大的視頻文件--------------------------------*/package pack04;import java.io.*;public class copyfile { public static void main(string[] args) { string src = "d:/test/加勒比海盜-黑珍珠號的詛咒.rmvb"; //源文件路徑,該文件大小為3.01gb string dst = "d:/test/加勒比海盜-黑珍珠號的詛咒-java復制.rmvb"; //目標文件路徑 long starttime = system.currenttimemillis(); //獲取復制前的系統時間 copy(src, dst); long endtime = system.currenttimemillis(); //獲取復制后的系統時間 system.out.println("spend time: " + (endtime-starttime) ); //輸出復制需要的時間,毫秒計 } //定義一個用于復制文件的靜態方法,參數src代表源文件路徑,參數dst代表目標文件路徑 public static void copy(string src, string dst) { //提供需要讀入和寫入的文件 file filein = new file(src); file fileout = new file(dst); bufferedinputstream bis = null; bufferedoutputstream bos = null; try { //創建相應的節點流,將文件對象作為形參傳遞給節點流的構造器 fileinputstream fis = new fileinputstream(filein); fileoutputstream fos = new fileoutputstream(fileout); //創建相應的緩沖流,將節點流對象作為形參傳遞給緩沖流的構造器 bis = new bufferedinputstream(fis); bos = new bufferedoutputstream(fos); //具體的文件復制操作 byte[] b = new byte[65536]; //把從輸入文件讀取到的數據存入該數組 int len; //記錄每次讀取數據并存入數組中后的返回值,代表讀取到的字節數,最大值為b.length;當輸入文件被讀取完后返回-1 while( (len=bis.read(b)) != -1 ) { bos.write(b, 0, len); bos.flush(); } } catch(ioexception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } finally { //關閉流,遵循先開后關原則(這里只需要關閉緩沖流即可) try { bos.close(); } catch (ioexception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } try { bis.close(); } catch (ioexception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } } }} |
[2] 測試結果
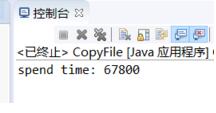
測試結果顯示,復制3.01gb大小的文件所用的時間約為1min。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/EarthPioneer/p/9363289.html