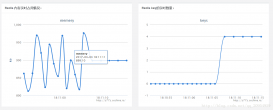
本文介紹了Spring線程池ThreadPoolTaskExecutor配置,分享給大家,具體如下:
1. ThreadPoolTaskExecutor配置
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<!-- spring thread pool executor --> <bean id="taskExecutor" class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor"> <!-- 線程池維護(hù)線程的最少數(shù)量 --> <property name="corePoolSize" value="5" /> <!-- 允許的空閑時(shí)間 --> <property name="keepAliveSeconds" value="200" /> <!-- 線程池維護(hù)線程的最大數(shù)量 --> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="10" /> <!-- 緩存隊(duì)列 --> <property name="queueCapacity" value="20" /> <!-- 對(duì)拒絕task的處理策略 --> <property name="rejectedExecutionHandler"> <bean class="java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$CallerRunsPolicy" /> </property> </bean> |
屬性字段說(shuō)明
corePoolSize:線程池維護(hù)線程的最少數(shù)量
keepAliveSeconds:允許的空閑時(shí)間
maxPoolSize:線程池維護(hù)線程的最大數(shù)量
queueCapacity:緩存隊(duì)列
rejectedExecutionHandler:對(duì)拒絕task的處理策略
2. execute(Runable)方法執(zhí)行過(guò)程
如果此時(shí)線程池中的數(shù)量小于corePoolSize,即使線程池中的線程都處于空閑狀態(tài),也要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建新的線程來(lái)處理被添加的任務(wù)。
如果此時(shí)線程池中的數(shù)量等于 corePoolSize,但是緩沖隊(duì)列 workQueue未滿,那么任務(wù)被放入緩沖隊(duì)列。
如果此時(shí)線程池中的數(shù)量大于corePoolSize,緩沖隊(duì)列workQueue滿,并且線程池中的數(shù)量小于maxPoolSize,建新的線程來(lái)處理被添加的任務(wù)。
如果此時(shí)線程池中的數(shù)量大于corePoolSize,緩沖隊(duì)列workQueue滿,并且線程池中的數(shù)量等于maxPoolSize,那么通過(guò)handler所指定的策略來(lái)處理此任務(wù)。也就是:處理任務(wù)的優(yōu)先級(jí)為:核心線程corePoolSize、任務(wù)隊(duì)列workQueue、最大線程 maximumPoolSize,如果三者都滿了,使用handler處理被拒絕的任務(wù)。
當(dāng)線程池中的線程數(shù)量大于corePoolSize時(shí),如果某線程空閑時(shí)間超過(guò)keepAliveTime,線程將被終止。這樣,線程池可以動(dòng)態(tài)的調(diào)整池中的線程數(shù)。
3. 示例代碼
Junit Test
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)@ContextConfiguration(classes = { MultiThreadConfig.class })public class MultiThreadTest { @Autowired private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor; @Autowired private MultiThreadProcessService multiThreadProcessService; @Test public void test() { int n = 20; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { taskExecutor.execute(new MultiThreadDemo(multiThreadProcessService)); System.out.println("int i is " + i + ", now threadpool active threads totalnum is " + taskExecutor.getActiveCount()); } try { System.in.read(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }} |
MultiThreadDemo
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/** * 多線程并發(fā)處理demo * @author daniel.zhao * */public class MultiThreadDemo implements Runnable { private MultiThreadProcessService multiThreadProcessService; public MultiThreadDemo() { } public MultiThreadDemo(MultiThreadProcessService multiThreadProcessService) { this.multiThreadProcessService = multiThreadProcessService; } @Override public void run() { multiThreadProcessService.processSomething(); }} |
MultiThreadProcessService
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Servicepublic class MultiThreadProcessService { public static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(MultiThreadProcessService.class); /** * 默認(rèn)處理流程耗時(shí)1000ms */ public void processSomething() { logger.debug("MultiThreadProcessService-processSomething" + Thread.currentThread() + "......start"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } logger.debug("MultiThreadProcessService-processSomething" + Thread.currentThread() + "......end"); }} |
MultiThreadConfig
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Configuration@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.xxx.multithread" })@ImportResource(value = { "classpath:config/application-task.xml" })@EnableSchedulingpublic class MultiThreadConfig {} |
以上就是本文的全部?jī)?nèi)容,希望對(duì)大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務(wù)器之家。
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/redcool/p/6426173.html