概述
merkletree被廣泛的應用在比特幣技術中,本文旨在通過代碼實現一個簡單的merkletree,并計算出merkle tree的 treeroot。
merkle tree 是一種數據結構,用于驗證在計算機之間和之間存儲,處理和傳輸的任何類型的數據。
目前,merkle樹的主要用途是確保從對等網絡中接收的數據塊未受損和未改變,和檢查其他對等網絡沒有撒謊發送假數據塊。
merkle tree應用舉例
比特幣
gita
mazon's dynamo
gassandra
比特幣中的應用
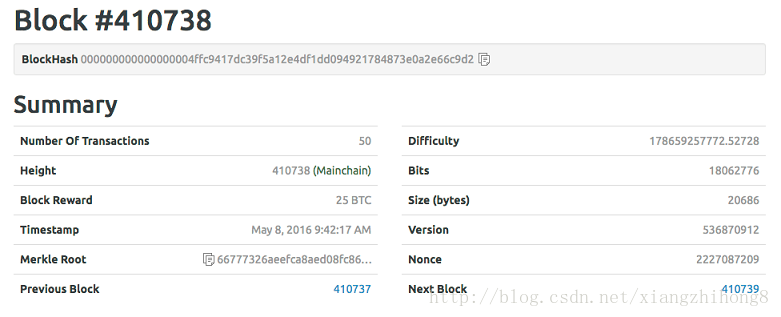
比特幣中每個塊中都包含了所有交易的集合簽名,這個簽名就是用merkle tree實現的,merkle樹用于比特幣以匯總塊中的所有事務,產生整個事務集合的整體數字指紋,提供非常有效的過程來驗證事務是否包括在塊中。
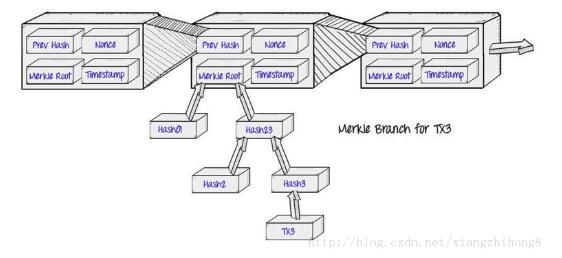
merkle樹一個很重要的用處是檢查塊中是否包含指定的交易,merkle樹是通過遞歸哈希節點對來構造的,直到只有一個哈希。
merkle tree 代碼實現
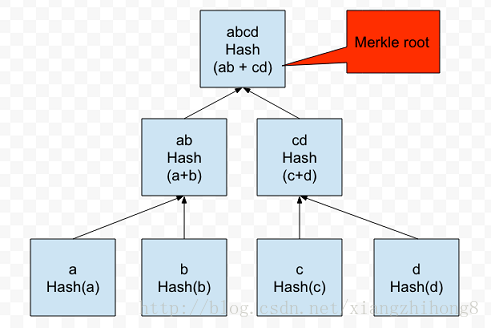
哈希樹的跟節點稱為merkle根,merkle樹可以僅用log2(n)的時間復雜度檢查任何一個數據元素是否包含在樹中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
|
package test;import java.security.messagedigest;import java.util.arraylist;import java.util.list;public class merkletrees { // transaction list list<string> txlist; // merkle root string root; /** * constructor * @param txlist transaction list 交易list */ public merkletrees(list<string> txlist) { this.txlist = txlist; root = ""; } /** * execute merkle_tree and set root. */ public void merkle_tree() { list<string> temptxlist = new arraylist<string>(); for (int i = 0; i < this.txlist.size(); i++) { temptxlist.add(this.txlist.get(i)); } list<string> newtxlist = getnewtxlist(temptxlist); while (newtxlist.size() != 1) { newtxlist = getnewtxlist(newtxlist); } this.root = newtxlist.get(0); } /** * return node hash list. * @param temptxlist * @return */ private list<string> getnewtxlist(list<string> temptxlist) { list<string> newtxlist = new arraylist<string>(); int index = 0; while (index < temptxlist.size()) { // left string left = temptxlist.get(index); index++; // right string right = ""; if (index != temptxlist.size()) { right = temptxlist.get(index); } // sha2 hex value string sha2hexvalue = getsha2hexvalue(left + right); newtxlist.add(sha2hexvalue); index++; } return newtxlist; } /** * return hex string * @param str * @return */ public string getsha2hexvalue(string str) { byte[] cipher_byte; try{ messagedigest md = messagedigest.getinstance("sha-256"); md.update(str.getbytes()); cipher_byte = md.digest(); stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder(2 * cipher_byte.length); for(byte b: cipher_byte) { sb.append(string.format("%02x", b&0xff) ); } return sb.tostring(); } catch (exception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } return ""; } /** * get root * @return */ public string getroot() { return this.root; } } |
數據準備
我們將交易的數據,放入到list中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
list<string> temptxlist = new arraylist<string>();temptxlist.add("a");temptxlist.add("b");temptxlist.add("c");temptxlist.add("d");temptxlist.add("e"); |
實現過程
準備交易數據
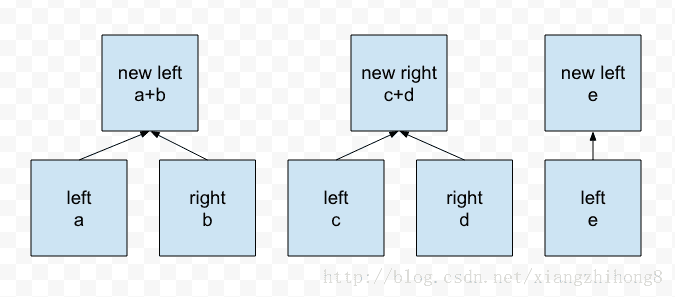
計算出每個數據的hash值,從左到右逐步組成樹的左右節點
執行循環知道最后只剩下一個數據
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
private list<string> getnewtxlist(list<string> temptxlist) { list<string> newtxlist = new arraylist<string>(); int index = 0; while (index < temptxlist.size()) { // left string left = temptxlist.get(index); index++; // right string right = ""; if (index != temptxlist.size()) { right = temptxlist.get(index); } // sha2 hex value string sha2hexvalue = getsha2hexvalue(left + right); newtxlist.add(sha2hexvalue); index++; } |
測試
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package test;import java.util.arraylist;import java.util.list;public class app { public static void main(string [] args) { list<string> temptxlist = new arraylist<string>(); temptxlist.add("a"); temptxlist.add("b"); temptxlist.add("c"); temptxlist.add("d"); temptxlist.add("e"); merkletrees merkletrees = new merkletrees(temptxlist); merkletrees.merkle_tree(); system.out.println("root : " + merkletrees.getroot()); } } |
執行結果

本文從簡單二叉樹的形式實現了簡單的merkletree,計算出treeroot,但是實際上的的merkletree不拘謹與二叉樹還可能是多叉樹。
本文90%來著于翻譯,原文地址
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/xiangzhihong8/article/details/53931213