最近看android framework層代碼,看到了threadlocal這個類,有點兒陌生,就翻了各種相關博客一一拜讀;自己隨后又研究了一遍源碼,發現自己的理解較之前閱讀的博文有不同之處,所以決定自己寫篇文章說說自己的理解,希望可以起到以下作用:
- 可以疏通研究結果,加深自己的理解;
- 可以起到拋磚引玉的作用,幫助感興趣的同學疏通思路;
- 分享學習經歷,同大家一起交流和學習。
一、 threadlocal 是什么
threadlocal 是java類庫的基礎類,在包java.lang下面;
官方的解釋是這樣的:
implements a thread-local storage, that is, a variable for which each thread has its own value. all threads share the same threadlocal object, but each sees a different value when accessing it, and changes made by one thread do not affect the other threads. the implementation supports null values.
大致意思是:
可以實現線程的本地存儲機制,threadlocal變量是一個不同線程可以擁有不同值的變量。所有的線程可以共享同一個threadlocal對象,但是不同線程訪問的時候可以取得不同的值,而且任意一個線程對它的改變不會影響其他線程。類實現是支持null值的(可以在set和get方法傳遞和訪問null值)。
概括來講有三個特性:
- 不同線程訪問時取得不同的值
- 任意線程對它的改變不影響其他線程
- 支持null
下面分別對這些特性進行實例驗證,首先定義一個test類,在此類中我們鑒證上邊所提到的三個特性。類定義如下:
test.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public class test{ //定義threadlocal private static threadlocal name; public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{ name = new threadlocal(); //define thread a thread a = new thread(){ public void run(){ system.out.println("before invoke set,value is:"+name.get()); name.set(“thread a”); system.out.println("after invoke set, value is:"+name.get()); } } ; //define thread b thread b = new thread(){ public void run(){ system.out.println("before invoke set,value is :"+name.get()); name.set(“thread b”); system.out.println("after invoke set,value is :"+name.get()); } } ; // not invoke set, print the value is null system.out.println(name.get()); // invoke set to fill a value name.set(“thread main”); // start thread a a.start(); a.join(); // print the value after changed the value by thread a system.out.println(name.get()); // start thread b b.start(); b.join(); // print the value after changed the value by thread b system.out.println(name.get()) }} |
代碼分析:
從定義中我們可以看到只聲明了一個threadlocal對象,其他三個線程(主線程、thread a和thread b)共享同一個對象;然后,在不同的線程中修改對象的值和在不同的線程中訪問對象的值,并在控制臺輸出查看結果。
看結果:
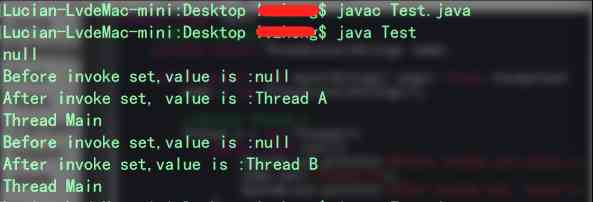
從控制臺輸出結果可以看到里邊有三個null的輸出,這個是因為在輸出前沒有對對象進行賦值,驗證了支持null的特點;再者,還可以發現在每個線程我都對對象的值做了修改,但是在其他線程訪問對象時并不是修改后的值,而是訪問線程本地的值;這樣也驗證了其他兩個特點。
二、 threadlocal的作用
大家都知道它的使用場景大都是多線程編程,至于具體的作用,這個怎么說那?我覺得這個只能用一個泛的說法來定義,因為一個東西的功能屬性定義了以后會限制大家的思路,就好比說菜刀是用來切菜的,好多人就不會用它切西瓜了。
這里,說下我對它的作用的認識,僅供參考,希望能有所幫助。這樣來描述吧,當一個多線程的程序需要對多數線程的部分任務(就是run方法里的部分代碼)進行封裝時,在封裝體里就可以用threadlocal來包裝與線程相關的成員變量,從而保證線程訪問的獨占性,而且所有線程可以共享一個封裝體對象;可以參考下android里的looper。不會用代碼描述問題的程序員不是好程序員;
看代碼:統計線程某段代碼耗時的工具(為說明問題自造)
statisticcosttime.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
// class that statistic the cost timepublic class statisticcosttime{ // record the starttime // private threadlocal starttime = new threadlocal(); private long starttime; // private threadlocal costtime = new threadlocal(); private long costtime; private statisticcosttime(){ } //singleton public static final statisticcosttime shareinstance(){ return instancefactory.instance; } private static class instancefactory{ private static final statisticcosttime instance = new statisticcosttime(); } // start public void start(){ // starttime.set(system. nanotime ()); starttime = system.nanotime(); } // end public void end(){ // costtime.set(system. nanotime () - starttime.get()); costtime = system.nanotime() - starttime; } public long getstarttime(){ return starttime; // return starttime.get(); } public long getcosttime(){ // return costtime.get(); return costtime; } |
好了,工具設計完工了,現在我們用它來統計一下線程耗時試試唄:
main.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
public class main{ public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{ // define the thread a thread a = new thread(){ public void run(){ try{ // start record time statisticcosttime.shareinstance().start(); sleep(200); // print the start time of a system.out.println("a-starttime:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getstarttime()); // end the record statisticcosttime.shareinstance().end(); // print the costtime of a system.out.println("a:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getcosttime()); } catch(exception e){ } } } ; // start a a.start(); // define thread b thread b = new thread(){ public void run(){ try{ // record the start time of b1 statisticcosttime.shareinstance().start(); sleep(100); // print the start time to console system.out.println("b1-starttime:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getstarttime()); // end record start time of b1 statisticcosttime.shareinstance().end(); // print the cost time of b1 system.out.println("b1:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getcosttime()); // start record time of b2 statisticcosttime.shareinstance().start(); sleep(100); // print start time of b2 system.out.println("b2-starttime:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getstarttime()); // end record time of b2 statisticcosttime.shareinstance().end(); // print cost time of b2 system.out.println("b2:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getcosttime()); } catch(exception e){ } } } ; b.start(); }} |
運行代碼后輸出結果是這樣的
注意:輸出結果精確度為納秒級
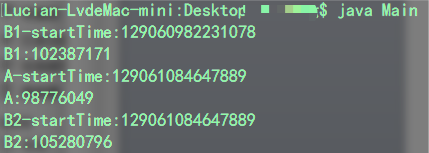
看結果是不是和我們預想的不一樣,發現a的結果應該約等于b1+b2才對呀,怎么變成和b2一樣了那?答案就是我們在定義starttime和costtime變量時,本意是不應共享的,應是線程獨占的才對。而這里變量隨單例共享了,所以當計算a的值時,其實starttime已經被b2修改了,所以就輸出了和b2一樣的結果。
現在我們把statisticcosttime中注釋掉的部分打開,換成threadlocal的聲明方式試下。
看結果:
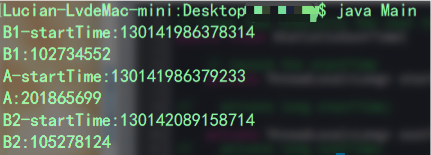
呀!這下達到預期效果了,這時候有同學會說這不是可以線程并發訪問了嗎,是不是只要我用了threadlocal就可以保證線程安全了?答案是no!首先先弄明白為什么會有線程安全問題,無非兩種情況:
1、不該共享的資源,你在線程間共享了;
2、線程間共享的資源,你沒有保證有序訪問;
前者可以用“空間換時間”的方式解決,用threadlocal(也可以直接聲明線程局部變量),后者用“時間換空間”的方式解決,顯然這個就不是threadlocal力所能及的了。
三、 threadlocal 原理
實現原理其實很簡單,每次對threadlocal 對象的讀寫操作其實是對線程的values對象的讀寫操作;這里澄清一下,沒有什么變量副本的創建,因為就沒有用變量分配的內存空間來存t對象的,而是用它所在線程的values來存t對象的;我們在線程中每次調用threadlocal的set方法時,實際上是將object寫入線程對應values對象的過程;調用threadlocal的get方法時,實際上是從線程對應values對象取object的過程。
看源碼:
threadlocal 的成員變量set
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/** * sets the value of this variable for the current thread. if set to * {@code null}, the value will be set to null and the underlying entry will * still be present. * * @param value the new value of the variable for the caller thread. */public void set(t value) { thread currentthread = thread.currentthread(); values values = values(currentthread); if (values == null) { values = initializevalues(currentthread); } values.put(this, value);} |
treadlocal 的成員方法get
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
/** * returns the value of this variable for the current thread. if an entry * doesn't yet exist for this variable on this thread, this method will * create an entry, populating the value with the result of * {@link #initialvalue()}. * * @return the current value of the variable for the calling thread. */@suppresswarnings("unchecked")public t get() { // optimized for the fast path. thread currentthread = thread.currentthread(); values values = values(currentthread); if (values != null) { object[] table = values.table; int index = hash & values.mask; if (this.reference == table[index]) { return (t) table[index + 1]; } } else { values = initializevalues(currentthread); } return (t) values.getaftermiss(this);} |
threadlocal的成員方法initializevalues
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
/** * creates values instance for this thread and variable type. */values initializevalues(thread current) { return current.localvalues = new values();} |
threadlocal 的成員方法values
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
/** * gets values instance for this thread and variable type. */values values(thread current) { return current.localvalues;} |
那這個values又是怎樣讀寫object那?
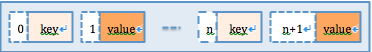
values是作為threadlocal的內部類存在的;這個values里包括了一個重要數組object[],這個數據就是解答問題的關鍵部分,它是用來存儲線程本地各種類型treadlocal變量用的;那么問題來了,具體取某個類型的變量時是怎么保證不取到其他類型的值那?按一般的做法會用一個map根據key-value映射一下的;對的,思路就是這個思路,但是這里并沒有用map來實現,是用一個object[]實現的map機制;但是,若要用map理解的話,也是不可以的,因為機制是相同的;key其實上對應threadlocal的弱引用,value就對應我們傳進去的object。
解釋下是怎么用object[]實現map機制的(參考圖1);它是用數組下標的奇偶來區分key和value的,就是下表是偶數的位置存儲key,奇數存儲value,就是這樣搞得;感興趣的同學如果想知道算法實現的話,可以深入研究一下,這里我不在詳述了。
結合前面第一個實例分析下存儲情況:
當程序執行時存在a,b和main三個線程,分別在線程中調用name.set()時同時針對三個線程實例在堆區分配了三塊相同的內存空間來存儲values對象,以name引用作為key,具體的object作為值存進三個不同的object[](參看下圖):

四、 總結
threadlocal 不能完全解決多線程編程時的并發問題,這種問題還要根據不同的情況選擇不同的解決方案,“空間換時間”還是“時間換空間”。
threadlocal最大的作用就是把線程共享變量轉換成線程本地變量,實現線程之間的隔離。
以上就是本文關于快速了解java中threadlocal的全部內容,希望對大家有所幫助。如有不足之處,歡迎留言指出。感謝朋友們對本站的支持。
原文鏈接:https://www.2cto.com/kf/201608/541771.html