一,前面我們介紹了springboot的快速啟動,大家肯定對springboot也有所了解,下面我們來介紹一下springboot怎么集成多數(shù)據(jù)源。
在有的項目開發(fā)中需要在一個項目中訪問多個數(shù)據(jù)源或者兩個項目之間通信(實質(zhì)上是互相訪問對方的數(shù)據(jù)庫),在這里,我們介紹一下在一個項目中如何集成多個數(shù)據(jù)源(即訪問多個不同的數(shù)據(jù)庫),因為在項目中有時會有這種需求,比如在一個大型項目開發(fā)中,一個數(shù)據(jù)庫中保存數(shù)據(jù)的索引,各種使用頻繁的數(shù)據(jù),另一個數(shù)據(jù)庫中保存其他的數(shù)據(jù)。
1.下面我們來討論一個問題,怎么集成多數(shù)據(jù)源,就是怎么讓一個項目訪問多個數(shù)據(jù)庫?
有的人會說使用注解,沒錯,這是一種辦法,因為springboot對的最大好處就是避免了繁瑣的xml配置文件,大量的使用注解來開發(fā),方便簡潔,但是在這里如果集成多數(shù)據(jù)源使用注解的話會很麻煩,有沒有其他的辦法呢?答案是肯定的,我們可以分模板來訪問多個數(shù)據(jù)庫,也就是分包。
2.如何分包來訪問多個數(shù)據(jù)源?
在這里,我們用一個簡單的案例來說明,我們訪問新建一個spingboot項目,訪問test1,test2這兩個數(shù)據(jù)庫,首先,我們先看代碼。
首先,我們需要導入相關(guān)依賴在pom文件中,這里,因為我的項目已經(jīng)提前有了父pom,所以不再考慮依賴的版本問題,怎么建立父pom可參考上一篇文章。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance" xsi:schemalocation="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelversion>4.0.0</modelversion> <parent> <groupid>cn.shinelon.springboot</groupid> <artifactid>microboot</artifactid> <version>0.0.1-snapshot</version> </parent> <artifactid>springboot-multidatasources</artifactid> <packaging>war</packaging> <!-- maven項目packaging改為war類型時,必須要加這個插件 --> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupid>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupid> <artifactid>maven-war-plugin</artifactid> <version>2.3</version> <configuration> <failonmissingwebxml>false</failonmissingwebxml> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid> </dependency> <!-- 測試springboot的依賴 --> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- 測試時加入這兩個依賴,當修改代碼的時候就不用每次修改后重啟服務(wù)器了 --> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework</groupid> <artifactid>springloaded</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-devtools</artifactid> </dependency> <!-- springboot 集成jsp必須要借助這兩個依賴 --> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupid> <artifactid>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactid> </dependency> <!-- springboot集成mybatis --> <dependency> <groupid>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupid> <artifactid>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactid> <version>1.3.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>mysql</groupid> <artifactid>mysql-connector-java</artifactid> </dependency> </dependencies></project> |
在上面配置的pom文件中,有點要說明,因為要訪問數(shù)據(jù)庫,所以我整合了mybatis,還有一個是整合jsp,不過在這個項目中無關(guān),是我之前寫代碼留下來的,可不必關(guān)心。
下面,我們還要在scr/main/sources目錄下新建一個application.properties資源文件,注意,這個文件名必須是application,這個是固定的,springboot默認訪問該文件,不要自己亂改名稱。然后在這個資源文件中配置自定義數(shù)據(jù)源。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
spring.datasource.test1.driverclassname=com.mysql.jdbc.driverspring.datasource.test1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1spring.datasource.test1.username=rootspring.datasource.test1.password=.....spring.datasource.test2.driverclassname=com.mysql.jdbc.driverspring.datasource.test2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test2spring.datasource.test2.username=rootspring.datasource.test2.password=..... |
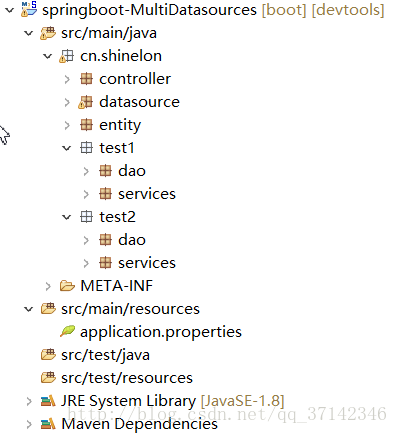
配置好數(shù)據(jù)源后我們就可以開進行分模塊來訪問這兩個數(shù)據(jù)源了。首先在src/mian/java目錄下創(chuàng)建好各個包,然后開始開發(fā),新建一個datasource包來放置需要訪問的兩個數(shù)據(jù)源的代碼,然后在新建兩個模塊包test1和test2,從包名我們就可以看出來這兩個包是用來操作這兩個數(shù)據(jù)庫,在這兩個包下可以分別建立dao層和service層的包,然后建立一個controller控制層。下面是項目的目錄樹圖。
然后我們來寫datasource中的代碼,其實就是像我們以前在xml文件中配置的sqlsessionfactory和數(shù)據(jù)源一個原理。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
import javax.sql.datasource;import org.apache.ibatis.session.sqlsessionfactory;import org.mybatis.spring.sqlsessionfactorybean;import org.mybatis.spring.sqlsessiontemplate;import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.mapperscan;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.qualifier;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.datasourcebuilder;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.configurationproperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.primary;import org.springframework.core.io.support.pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver;import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.datasourcetransactionmanager;@configuration@mapperscan(basepackages="cn.shinelon.test1",sqlsessionfactoryref="test1sqlsessionfactory")public class datasource1 { /** * 配置test1數(shù)據(jù)庫 * @return */ @bean(name="test1datasource") @configurationproperties(prefix="spring.datasource.test1") public datasource testdatasource() { return datasourcebuilder.create().build(); } /** * 創(chuàng)建sqlsessionfactory * @param datasource * @return * @throws exception */ @bean(name="test1sqlsessionfactory") public sqlsessionfactory testsqlsessionfactory(@qualifier("test1datasource")datasource datasource) throws exception { sqlsessionfactorybean bean=new sqlsessionfactorybean(); bean.setdatasource(datasource); //如果還有分頁等其他事務(wù)// bean.setmapperlocations(new pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver().// getresources("classpath:mybatis/test1/*.xml")); return bean.getobject(); } /** * 配置事務(wù)管理 * @param datasource * @return */ @bean(name="test1transactionmanager") public datasourcetransactionmanager testtransactionmanager( @qualifier("test1datasource")datasource datasource) { return new datasourcetransactionmanager(datasource); } @bean(name="test1sqlsessiontemplate") public sqlsessiontemplate testsqlsessiontemplate(@qualifier("test1sqlsessionfactory") sqlsessionfactory sqlsessionfactory) { return new sqlsessiontemplate(sqlsessionfactory); }} |
上面的是訪問的test1數(shù)據(jù)庫的配置,需要注意的是@configurationproperties(prefix=”spring.datasource.test1”)這個配置中的屬性prefix的值必須和資源文件中的前綴是一樣的,否則是訪問不到的,還有@primary ,如果不加這個注解,啟動將會報錯,因為服務(wù)器先要有一個默認不知道默認要先訪問的數(shù)據(jù)源是哪個,必須指明,下面是test2數(shù)據(jù)庫的配置,和上面一樣的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
import javax.sql.datasource;import org.apache.ibatis.session.sqlsessionfactory;import org.mybatis.spring.sqlsessionfactorybean;import org.mybatis.spring.sqlsessiontemplate;import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.mapperscan;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.qualifier;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.datasourcebuilder;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.configurationproperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.primary;import org.springframework.core.io.support.pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver;import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.datasourcetransactionmanager;@configuration@mapperscan(basepackages="cn.shinelon.test2",sqlsessionfactoryref="test2sqlsessionfactory")@primary //指定 默認的訪問的數(shù)據(jù)源public class datasource2 { /** * 配置test2數(shù)據(jù)庫 * @return */ @bean(name="test2datasource") @configurationproperties(prefix="spring.datasource.test2") @primary //指定 默認的訪問的數(shù)據(jù)源 public datasource testdatasource() { return datasourcebuilder.create().build(); } /** * 創(chuàng)建sqlsessionfactory * @param datasource * @return * @throws exception */ @bean(name="test2sqlsessionfactory") @primary //指定 默認的訪問的數(shù)據(jù)源 public sqlsessionfactory testsqlsessionfactory(@qualifier("test2datasource")datasource datasource) throws exception { sqlsessionfactorybean bean=new sqlsessionfactorybean(); bean.setdatasource(datasource); //如果還有分頁等其他事務(wù)// bean.setmapperlocations(new pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver().// getresources("classpath:mybatis/test2/*.xml")); return bean.getobject(); } /** * 配置事務(wù)管理 * @param datasource * @return */ @bean(name="test2transactionmanager") @primary //指定 默認的訪問的數(shù)據(jù)源 public datasourcetransactionmanager testtransactionmanager( @qualifier("test2datasource")datasource datasource) { return new datasourcetransactionmanager(datasource); } @bean(name="test2sqlsessiontemplate") public sqlsessiontemplate testsqlsessiontemplate(@qualifier("test2sqlsessionfactory") sqlsessionfactory sqlsessionfactory) { return new sqlsessiontemplate(sqlsessionfactory); }} |
然后我們在每一個模塊中寫dao層和service代碼來進行操作。
dao層代碼如下
|
1
2
3
4
|
public interface user1dao { @insert("insert into user values(null,#{username},#{age})") public void insert(@param("username")string username,@param("age")int age);} |
在這里,我們向數(shù)據(jù)庫插入一條數(shù)據(jù)。
service層代碼如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@servicepublic class user1service { @autowired public user1dao user1dao; public void insert(string username,int age) { user1dao.insert(username, age); }} |
test2包下dao層和service層的代碼都是同樣的,這里就省略了。
然后我們來開始寫controller層的代碼。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;import org.springframework.boot.springapplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.springbootapplication;import org.springframework.context.annotation.componentscan;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;import cn.shinelon.test1.services.user1service;import cn.shinelon.test2.services.user2service;@springbootapplication@componentscan(basepackages={"cn.shinelon.datasource","cn.shinelon.test1","cn.shinelon.test2"})@restcontrollerpublic class usercontroller { @autowired public user1service user1service; @autowired public user2service user2service; @requestmapping("/add") public string insert(string username,int age) { user1service.insert(username, age); user2service.insert(username, age); return "insert success"; } public static void main(string[] args) { springapplication.run(usercontroller.class, args); }} |
上面代碼中 ,需要注意的是@componentscan(basepackages={“cn.shinelon.datasource”,”cn.shinelon.test1”,”cn.shinelon.test2”})這個注解,必須添加,這樣服務(wù)器才會掃描到這幾個包中的配置。
下面我們補全代碼,還要建立一個實體類
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class user { private int id; private string username; private int age; //省略get,set方法 } |
最后的整個項目圖如下

總結(jié)
以上就是本文關(guān)于springboot集成多數(shù)據(jù)源解析的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家有所幫助。有什么問題可以隨時留言,小編會及時回復(fù)大家的。感謝朋友們對本站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_37142346/article/details/78488452