ListView是Android中經(jīng)常會(huì)使用的東西,綁定數(shù)據(jù)對(duì)于初學(xué)者來(lái)說(shuō),尤其是剛接觸編程的人來(lái)說(shuō),往往會(huì)覺(jué)得很難理解,我上大二的時(shí)候?qū)W的java,但是基本上相當(dāng)于沒(méi)有學(xué),什么都沒(méi)寫(xiě)過(guò),真正接觸編程就是開(kāi)始上手學(xué)android,把這些記錄下來(lái),自己可以回頭看下,也可以讓新手更好的理解。高手繞過(guò)....
Android中Adapter我是這么理解的,是數(shù)據(jù)和視圖之間的橋梁,數(shù)據(jù)在adapter中做處理,然后顯示到視圖上面。
Adapter有很多種,有ArrayAdapter<T>, BaseAdapter, CursorAdapter, HeaderViewListAdapter, ListAdapter, ResourceCursorAdapter, SimpleAdapter, SimpleCursorAdapter, SpinnerAdapter, WrapperListAdapter.
我在項(xiàng)目中用到過(guò)的就ArrayAdapter<T>, (數(shù)組也可以是對(duì)象數(shù)組),BaseAdapter(所有Adapter的基類(lèi)),SimpleAdapter,CursorAdapter(數(shù)據(jù)來(lái)源是cursor),SimpleCursorAdapter,感覺(jué)有必要總結(jié)一下。
最基本的要數(shù)sdk官網(wǎng)上面給的這個(gè)代碼例子了http://developer.android.com/resources/tutorials/views/hello-listview.html。
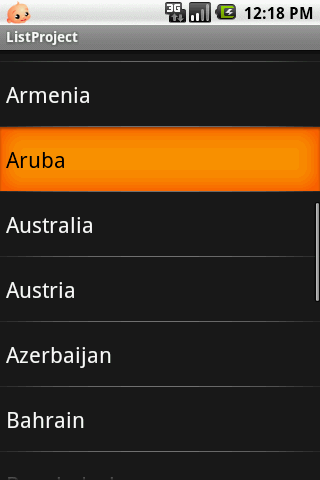
我自己寫(xiě)的一個(gè)例子,先上圖,再貼上代碼:
package com.cz.list.demo;
import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter; import android.widget.ListView;
public class ArrayListDemo extends Activity {
private ListView listView; private String[] adapterData;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.array_list_layout);
/* 找到這個(gè)listView */
listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.array_list);
/* 我們要在listView上面沒(méi)條顯示的數(shù)據(jù),放到一個(gè)數(shù)組中 */ adapterData = new String[] { "Afghanistan", "Albania", "Algeria",
"American Samoa", "Andorra", "Angola", "Anguilla", "Antarctica", "Antigua and Barbuda", "Argentina", "Armenia",
"Aruba", "Australia", "Austria", "Azerbaijan", "Bahrain", "Bangladesh", "Barbados", "Belarus", "Belgium", "Belize",
"Benin", "Bermuda", "Bhutan", "Bolivia", "Bosnia and Herzegovina", "Botswana", "Bouvet Island" };
/* 這個(gè)是數(shù)組string類(lèi)型的數(shù)組 */
// ArrayAdapter<String> arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>( // ArrayListDemo.this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,
// adapterData);
/* 設(shè)置ListView的Adapter */ listView.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(ArrayListDemo.this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, adapterData)); }
}
代碼中寫(xiě)的有注釋?zhuān)矣X(jué)得要解釋的有幾點(diǎn),都是很基礎(chǔ)的,高手就見(jiàn)笑了.
1. 適配器的作用是數(shù)據(jù)和視圖之間的橋梁
2. 這個(gè)小例子是要顯示一個(gè)數(shù)組,我們就用ArrayAdapter,數(shù)組適配器,數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)據(jù)類(lèi)型<>是String類(lèi)型的,數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)據(jù)類(lèi)型還可以是其他的包括對(duì)象類(lèi)型的
3. ArrayAdapter<String> arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(
ArrayListDemo.this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,
adapterData);
這段代碼是創(chuàng)建一個(gè)數(shù)組適配器的代碼,里面有三個(gè)參數(shù),第一個(gè)參數(shù)是上下文,就是當(dāng)前的Activity, 第二個(gè)參數(shù)是android sdk中自己內(nèi)置的一個(gè)布局,它里面只有一個(gè)TextView,這個(gè)參數(shù)是表明我們數(shù)組中每一條數(shù)據(jù)的布局是這個(gè)view,就是將每一條數(shù)據(jù)都顯示在這個(gè)view上面;第三個(gè)參數(shù)就是我們要顯示的數(shù)據(jù)。listView會(huì)根據(jù)這三個(gè)參數(shù),遍歷adapterData里面的每一條數(shù)據(jù),讀出一條,顯示到第二個(gè)參數(shù)對(duì)應(yīng)的布局中,這樣就形成了我們看到的listView. 不知道剛學(xué)的同學(xué)懂了沒(méi)有...
本文出自 “生如夏花” 博客