主要目的:
解決ArrayList 類不能改變大小的問題,主要實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)組列表動(dòng)態(tài)調(diào)整大小。
1、數(shù)組類型如何選擇?由于我們不清楚數(shù)組中具體存入什么類型的數(shù)據(jù), 我們可以聲明一個(gè)對(duì)象Object [ ] ,這樣,數(shù)組列表就可以存儲(chǔ)任何類型的數(shù)據(jù)了。
2、泛型<> :如果定義的一個(gè)類或接口有一個(gè)或多個(gè)類型變量,則可以使用泛型。
ArrayList<String>本身就是泛型,各種類型的變量都可以組裝成對(duì)應(yīng)的List,而不必針對(duì)每個(gè)類型分別實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)構(gòu)建ArrayList的類。
泛型字母所代表含義:
E表示集合的元素類型,
K 和 V分別表示表的關(guān)鍵字與值的類型 *
T(需要時(shí)還可以用臨近的字母 U 和 S)表示“任意類型”
3、實(shí)現(xiàn)功能:我們主要實(shí)現(xiàn)arraylist的基本的增,刪,改,等功能。
核心思路:主要根據(jù)所需求大小進(jìn)行調(diào)整,需要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建一個(gè)新的數(shù)組,將老數(shù)組值賦予新數(shù)組再進(jìn)行詳細(xì)的變動(dòng)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
|
package com.customArray0905;public class CustomArraryList<E> { Object[] data; int Size; public int getSize() { return Size; } //返回?cái)?shù)組下標(biāo)為index的元素的值 public E get(int index) { if(index<0 || index>=Size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); //否則return null } return (E) data[index]; } //自定義更改下標(biāo)為index的元素值的方法 public void set(int index, E e) { if(index<0 || index>=Size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); //否則return null } data[index] = e; } public void add(E e) { ///創(chuàng)建新對(duì)象 容量擴(kuò)大一個(gè) Object[] newdata = new Object[Size + 1]; //將array中的元素重新存入更新容量后的newArray數(shù)組中去 for (int i = 0; i < Size; i++) { newdata[i] = data[i]; } data = newdata; data[Size++] = e; } //自定義移除下標(biāo)為index的元素的方法 public void remove(int index) { ///創(chuàng)建新對(duì)象 容量減少一個(gè) Object[] newdata = new Object[Size - 1]; int j = 0; //判斷index大小是否合適存在數(shù)組中 if(index<0 || index>=Size) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); //否則return null } //得到老對(duì)象里下標(biāo)之前的所有元素并存入新對(duì)象 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { newdata[j] = data[i]; j++; } //得到老對(duì)象里下標(biāo)之后的所有元素并存入新對(duì)象 for (int i = index + 1; i < Size; i++) { newdata[j] = data[i]; j++; } data = newdata; Size--; } //清除array中所有的元素 public void clear() { for(int i = 0;i<Size;i++) { data[i] = null; } Size = 0; } public static void main(String[] args) { CustomArraryList<String> myList = new CustomArraryList<>(); //Add System.out.println("測(cè)試1,ADD方法"); myList.add("1"); myList.add("2"); myList.add("3"); myList.add("4"); myList.add("5"); for (int i = 0; i < myList.getSize(); i++) { System.out.println(myList.get(i)); } //Remove,Set myList.remove(2); myList.set(3, "7"); System.out.println("測(cè)試2,移除index=2的數(shù)據(jù),并設(shè)置index=3的數(shù)據(jù)值為7,"); for (int i = 0; i < myList.getSize(); i++) { System.out.println(myList.get(i)); } //Clear myList.clear(); myList.add("1"); for (int i = 0; i < myList.getSize(); i++) { System.out.println("測(cè)試3,clear方法,僅剩下新添加數(shù)據(jù) "+myList.get(i)); } //拋出錯(cuò)誤 System.out.println("測(cè)試4,拋出set錯(cuò)誤"); myList.set(2,"2"); }} |
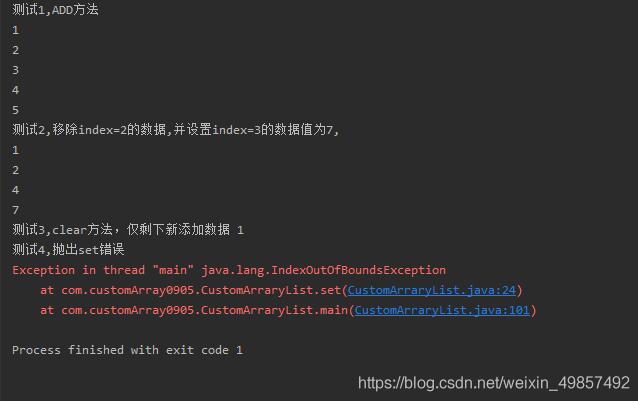
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
補(bǔ)充知識(shí):java Arrays快速打印數(shù)組的數(shù)據(jù)元素列表
1、Arrays.toString
用來快速打印一維數(shù)組的數(shù)據(jù)元素列表
2、Arrays.deepToString 快速打印一個(gè)二維數(shù)組的數(shù)據(jù)元素列表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public static strictfp void main(String[] args) { String[][] arr = {{"aaa","bbb"},{"ccc"}}; for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++){ for(int y=0;y<arr[x].length;y++){ System.out.println(arr[x][y]); } } //Arrays.deepToString 快速打印一個(gè)二維數(shù)組的數(shù)據(jù)元素列表 System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(arr)); } |
以上這篇Java自定義數(shù)組列表的實(shí)現(xiàn)操作就是小編分享給大家的全部?jī)?nèi)容了,希望能給大家一個(gè)參考,也希望大家多多支持服務(wù)器之家。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_49857492/article/details/108513330