背景
想必大家在項(xiàng)目中都有遇到把一個(gè)列表的多個(gè)字段累加求和的情況,也就是一個(gè)列表的總計(jì)。有的童鞋問,這個(gè)不是給前端做的嗎?后端不是只需要把列表返回就行了嘛。。。沒錯(cuò),我也是這樣想的,但是在一場和前端的撕逼大戰(zhàn)中敗下陣來之后,這個(gè)東西就落在我身上了。當(dāng)時(shí)由于工期原因,時(shí)間比較緊,也就不考慮效率和易用性了,只是滿足當(dāng)時(shí)的需求,就隨便寫了個(gè)方法統(tǒng)計(jì)求和。目前稍微閑下來了,就把原來的代碼優(yōu)化下。我們先來看一下原來的代碼...
原代碼
工具類
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
|
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.math.BigDecimal;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.List;/** * * @ClassName CalculationUtil * * @Description TODO(計(jì)算工具類) * * @Author 我恰芙蓉王 * * @Date 2020年04月21日 11:37 * * @Version 1.0.0 * **/public class CalculationUtil { //拼接get set方法的常量 public static final String GET = "get"; public static final String SET = "set"; /** * 功能描述: 公用統(tǒng)計(jì)小計(jì)方法 * * @param list 原數(shù)據(jù)列表集合 * @param fields 運(yùn)算的屬性數(shù)組 * @創(chuàng)建人: 我恰芙蓉王 * @創(chuàng)建時(shí)間: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09 * @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回統(tǒng)計(jì)好的對象 **/ public static <T> T totalCalculationForBigDecimal(List<T> list, String... fields) throws Exception { if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) { return null; } Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass(); //返回值 Object object = clazz.newInstance(); list.stream().forEach(v -> Arrays.asList(fields).parallelStream().forEach(t -> { try { String field = StringUtils.capitalize(t); //獲取get方法 Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + field); //獲取set方法 Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + field, BigDecimal.class); Object objectValue = getMethod.invoke(object); setMethod.invoke(object, (objectValue == null ? BigDecimal.ZERO : (BigDecimal) objectValue).add((BigDecimal) getMethod.invoke(v))); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }) ); return (T) object; } /** * 功能描述: 公用統(tǒng)計(jì)小計(jì)方法 * * @param list 原數(shù)據(jù)列表集合 * @param fields 運(yùn)算的屬性數(shù)組 * @創(chuàng)建人: 我恰芙蓉王 * @創(chuàng)建時(shí)間: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09 * @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回統(tǒng)計(jì)好的對象 **/ public static <T> T totalCalculationForDouble(List<T> list, String... fields) throws Exception { if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) { return null; } Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass(); //返回值 Object object = clazz.newInstance(); list.stream().forEach(v -> Arrays.asList(fields).parallelStream().forEach(t -> { try { String field = StringUtils.capitalize(t); //獲取get方法 Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + field); //獲取set方法 Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + field, Double.class); Object objectValue = getMethod.invoke(object); setMethod.invoke(object, add((objectValue == null ? new Double(0) : (Double) objectValue), (Double) getMethod.invoke(v))); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }) ); return (T) object; } /** * 功能描述: 公用統(tǒng)計(jì)小計(jì)方法 * * @param list 原數(shù)據(jù)列表集合 * @param fields 運(yùn)算的屬性數(shù)組 * @創(chuàng)建人: 我恰芙蓉王 * @創(chuàng)建時(shí)間: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09 * @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回統(tǒng)計(jì)好的對象 **/ public static <T> T totalCalculationForFloat(List<T> list, String... fields) throws Exception { if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) { return null; } Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass(); //返回值 Object object = clazz.newInstance(); list.stream().forEach(v -> Arrays.asList(fields).parallelStream().forEach(t -> { try { String field = StringUtils.capitalize(t); //獲取get方法 Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + field); //獲取set方法 Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + field, Float.class); Object objectValue = getMethod.invoke(object); setMethod.invoke(object, add((objectValue == null ? new Float(0) : (Float) objectValue), (Float) getMethod.invoke(v))); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }) ); return (T) object; } /** * 提供精確的加法運(yùn)算。 * * @param v1 被加數(shù) * @param v2 加數(shù) * @return 兩個(gè)參數(shù)的和 */ public static Double add(Double v1, Double v2) { BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1.toString()); BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2.toString()); return b1.add(b2).doubleValue(); } /** * 提供精確的加法運(yùn)算。 * * @param v1 被加數(shù) * @param v2 加數(shù) * @return 兩個(gè)參數(shù)的和 */ public static Float add(Float v1, Float v2) { BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1.toString()); BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2.toString()); return b1.add(b2).floatValue(); }} |
實(shí)體類
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic class Order { //訂單號 private String orderNo; //訂單金額 private Double money; //折扣 private Double discount;}@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic class Phone { //手機(jī)名 private String name; //成本 private BigDecimal cost; //售價(jià) private BigDecimal price;} |
測試
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { List<Order> orderList = new ArrayList<Order>() { { add(new Order("D20111111", 256.45, 11.11)); add(new Order("D20111112", 123.85, 1.11)); add(new Order("D20111113", 546.13, 2.14)); add(new Order("D20111114", 636.44, 0.88)); } }; List<Phone> phoneList = new ArrayList<Phone>() { { add(new Phone("蘋果", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22"))); add(new Phone("三星", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22"))); add(new Phone("華為", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22"))); add(new Phone("小米", new BigDecimal("123.11"), new BigDecimal("222.22"))); } }; Order orderTotal = totalCalculationForDouble(orderList, "money", "discount"); System.out.println("總計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)為 :" + orderTotal); Phone phoneTotal = totalCalculationForBigDecimal(phoneList, "cost", "price"); System.out.println("總計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)為 :" + phoneTotal);} |
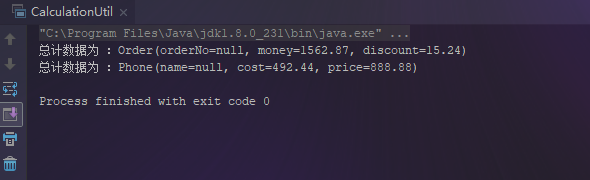
通過以上代碼可以看出,效果是實(shí)現(xiàn)了,但是缺點(diǎn)也是很明顯的:
1.太過冗余,相同代碼太多,多個(gè)方法只有少數(shù)代碼不相同(工具類中黃色標(biāo)注的地方);
2.效率低,列表中每個(gè)元素的每個(gè)屬性都要用到反射賦值;
3.靈活性不夠,要求實(shí)體類中需要參加運(yùn)算的屬性都為同一類型,即必須都為Double,或必須都為BigDecimal;
4.硬編碼,直接在方法調(diào)用時(shí)把實(shí)體類中的字段寫死,既不符合JAVA編碼規(guī)范也容易出錯(cuò),而且當(dāng)該實(shí)體類中的屬性名變更的時(shí)候,IDE無法提示我們相應(yīng)的傳參的變更,極容易踩坑。
因?yàn)轫?xiàng)目中用的JDK版本是1.8,當(dāng)時(shí)在寫的時(shí)候就想通過方法引用規(guī)避掉這種硬編碼的方式,因?yàn)樵贛ybatis-Plus中也有用到方法引用賦值條件參數(shù)的情況,但還是因?yàn)闀r(shí)間緊急,就沒去研究了。
今天就順著這個(gè)方向去找了一下實(shí)現(xiàn)的方法,把代碼優(yōu)化了部分,如下:
優(yōu)化后
首先,我是想通過傳參為方法引用的方式來獲取Getter方法對應(yīng)的屬性名,通過了解,JDK8中已經(jīng)給我們提供了實(shí)現(xiàn)方式,首先聲明一個(gè)自定義函數(shù)式接口(需要實(shí)現(xiàn)Serializable)
|
1
2
3
4
|
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface SerializableFunction<T, R> extends Function<T, R>, Serializable {} |
然后定義一個(gè)反射工具類去解析這個(gè)自定義函數(shù)式接口,在此工具類中有對方法引用解析的具體實(shí)現(xiàn),在此類中規(guī)避掉缺點(diǎn)4
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;import java.lang.invoke.SerializedLambda;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.Method;/** * @ClassName ReflectionUtil * @Description TODO(反射工具類) * @Author 我恰芙蓉王 * @Date 2020年09月08日 15:10 * @Version 2.0.0 **/public class ReflectionUtil { public static final String GET = "get"; public static final String SET = "set"; /** * 功能描述: 通過get方法的方法引用返回對應(yīng)的Field * * @param function * @創(chuàng)建人: 我恰芙蓉王 * @創(chuàng)建時(shí)間: 2020年09月08日 16:20:56 * @return: java.lang.reflect.Field **/ public static <T> Field getField(SerializableFunction<T, ?> function) { try { /** * 1.獲取SerializedLambda */ Method method = function.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("writeReplace"); method.setAccessible(Boolean.TRUE); /** * 2.利用jdk的SerializedLambda,解析方法引用,implMethodName 即為Field對應(yīng)的Getter方法名 */ SerializedLambda serializedLambda = (SerializedLambda) method.invoke(function); //獲取get方法的方法名 String getter = serializedLambda.getImplMethodName(); //獲取屬性名 String fieldName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(getter.replace(GET, "")); /** * 3.獲取的Class是字符串,并且包名是“/”分割,需要替換成“.”,才能獲取到對應(yīng)的Class對象 */ String declaredClass = serializedLambda.getImplClass().replace("/", "."); Class clazz = Class.forName(declaredClass, false, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()); /** * 4.通過Spring中的反射工具類獲取Class中定義的Field */ return ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, fieldName); } catch (ReflectiveOperationException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }} |
接著改寫原來計(jì)算工具類中的代碼,在此類中將原缺點(diǎn)的1,2,3點(diǎn)都規(guī)避了,將原來冗余的多個(gè)方法精簡成一個(gè) totalCalculation ,通過 methodMap 對象將get,set方法緩存(但此緩存還有優(yōu)化的空間,可以將方法中的緩存對象提到tomcat內(nèi)存或redis中),通過動(dòng)態(tài)獲取字段類型來實(shí)現(xiàn)不同類型的累加運(yùn)算
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
|
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.math.BigDecimal;import java.util.*;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;import static io.renren.modules.test1.ReflectionUtil.GET;import static io.renren.modules.test1.ReflectionUtil.SET;/** * * @ClassName CalculationUtil * * @Description TODO(計(jì)算工具類) * * @Author 我恰芙蓉王 * * @Date 2020年04月21日 11:37 * * @Version 1.0.0 * **/public class CalculationUtil { /** * 功能描述: 公用統(tǒng)計(jì)小計(jì)方法 * * @param list 原數(shù)據(jù)列表集合 * @param functions 參與運(yùn)算的方法引用 * @創(chuàng)建人: 我恰芙蓉王 * @創(chuàng)建時(shí)間: 2020年05月12日 17:50:09 * @return: org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T 返回統(tǒng)計(jì)好的對象 **/ public static <T> T totalCalculation(List<T> list, SerializableFunction<T, ?>... functions) throws Exception { if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) { return null; } //獲取集合中類型的class對象 Class clazz = list.get(0).getClass(); //Getter Setter緩存 Map<SerializableFunction, Map<String, Method>> methodMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); //遍歷字段,將Getter Setter放入緩存中 for (SerializableFunction function : functions) { Field field = ReflectionUtil.getField(function); //獲取get方法 Method getMethod = clazz.getMethod(GET + StringUtils.capitalize(field.getName())); //獲取set方法 Method setMethod = clazz.getMethod(SET + StringUtils.capitalize(field.getName()), field.getType()); //將get set方法封裝成一個(gè)map放入緩存中 methodMap.put(function, new HashMap<String, Method>() { { put(GET, getMethod); put(SET, setMethod); } }); } //計(jì)算 T result = list.parallelStream().reduce((x, y) -> { try { Object newObject = x.getClass().newInstance(); Arrays.asList(functions).parallelStream().forEach(f -> { try { Map<String, Method> fieldMap = methodMap.get(f); //獲取緩存的get方法 Method getMethod = fieldMap.get(GET); //獲取緩存的set方法 Method setMethod = fieldMap.get(SET); //調(diào)用x參數(shù)t屬性的get方法 Object xValue = getMethod.invoke(x); //調(diào)用y參數(shù)t屬性的get方法 Object yValue = getMethod.invoke(y); //反射賦值到newObject對象 setMethod.invoke(newObject, add(xValue, yValue, getMethod.getReturnType())); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); return (T) newObject; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; }).get(); return result; } /** * 功能描述: 提供精確的加法運(yùn)算 * * @param v1 加數(shù) * @param v2 被加數(shù) * @param clazz 參數(shù)的class類型 * @創(chuàng)建人: 我恰芙蓉王 * @創(chuàng)建時(shí)間: 2020年09月08日 10:55:56 * @return: java.lang.Object 相加之和 **/ public static Object add(Object v1, Object v2, Class clazz) throws Exception { BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1.toString()); BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2.toString()); Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class); return constructor.newInstance(b1.add(b2).toString()); }} |
測試實(shí)體類
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic class People { //名字 private String name; //年齡 private Integer age; //存款 private BigDecimal money; //身高 private Double height;} |
調(diào)用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { List<People> list = new ArrayList<People>() { { add(new People("張三", 18, BigDecimal.valueOf(10000), 168.45)); add(new People("李四", 20, BigDecimal.valueOf(20000), 155.68)); add(new People("王五", 25, BigDecimal.valueOf(30000), 161.54)); add(new People("趙六", 21, BigDecimal.valueOf(30000), 166.66)); } }; People total = CalculationUtil.totalCalculation(list, People::getAge, People::getMoney, People::getHeight); System.out.println("總計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)為 :" + total);} |

總結(jié)
java8的lambda表達(dá)式確實(shí)極大的簡化了我們的代碼,提高了編碼的效率,流計(jì)算更是使數(shù)據(jù)的運(yùn)算變得高效快捷,也增加了代碼的可(zhuang)讀(bi)性。如今java14都出來了,希望在空余時(shí)間也能多去了解一下新版本的新特性,而不能老是抱著(你發(fā)任你發(fā),我用java8)的心態(tài)去學(xué)習(xí),畢竟技術(shù)的更新迭代是極快的。
到此這篇關(guān)于使用java8的方法引用替換硬編碼的示例代碼的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)java8的方法引用替換硬編碼內(nèi)容請搜索服務(wù)器之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持服務(wù)器之家!
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/-tang/p/13633732.html