首先,@value需要參數,這里參數可以是兩種形式:@Value("#{configProperties['t1.msgname']}")或者@Value("${t1.msgname}");
其次,下面我們來看看如何使用這兩形式,在配置上有什么區別:
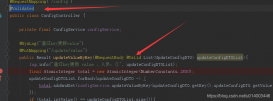
1、 @Value("#{configProperties['t1.msgname']}")這種形式的配置中有“configProperties”,其實它指定的是配置文件的加載對象:配置如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:/config/t1.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean> |
這樣配置就可完成對屬性的具體注入了;
2、 @Value("${t1.msgname}")這種形式不需要指定具體加載對象,這時候需要一個關鍵的對象來完成PreferencesPlaceholderConfigurer,這個對象的配置可以利用上面配置1中的配置,也可以自己直接自定配置文件路徑。
如果使用配置1中的配置,可以寫成如下情況:
|
1
2
3
|
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PreferencesPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="properties" ref="configProperties"/> </bean> |
如果直接指定配置文件的話,可以寫成如下情況:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PreferencesPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location"> <value>config/t1.properties</value> </property> </bean> |
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/qiuhan/article/details/47089329